5 API Operation Definition
5.1 Introduction
This clause defines data structures and operations of the NGSI-LD API. No specific binding is assumed. Clause 6 maps these operations and data types to the HTTP REST binding.
5.2 Data Types
5.2.1 Introduction
Implementations shall support the data types defined by the clauses below. For each member defined by each data type (including nested ones) a term shall be added to the Core @context, as mandated by clause 4.5.
None of the members described admit a null value directly, as when a JSON-LD processor encounters null, the associated entry or value is always removed when expanding the JSON-LD document.
However, in the context of a partial update or merge operation (see clauses 5.5.8 and 5.5.12), an NGSI-LD Null shall be used to indicate the removal of a target member. Thus, for representing deleted elements in notifications and in the temporal evolution, the URI "urn:ngsi-ld:null" is used as a Property value or Relationship object and the JSON object {"@none": "urn:ngsi-ld:null"} for the languageMap of a LanguageProperty, respectively. In all other cases, implementations shall raise an error of type BadRequestData if an NGSI-LD Null value is encountered.
As null cannot be used as a value in JSON-LD, there is still the possibility of using a JSON null literal {"@type": "@json", "@value": null} instead. JSON literals are not to be expanded in JSON-LD and thus the respective element is not removed during JSON-LD expansion.
Non-normative JSON Schema [i.11] definitions of the referred data types are also available at [i.13].
The use of URI in the context of the present document also includes the use of International Resource Identifiers (IRIs) as defined in IETF RFC 3987 [23], which extends the use of characters to Unicode characters [22] beyond the ASCII character set, enabling the support of languages other than English.
5.2.2 Common members
The JSON-LD representation of NGSI-LD Entity, Property, Relationship, Context Source Registration and Subscription can include the common members described by Table 5.2.2‑1.
Those members are read-only, and shall be automatically generated by NGSI-LD implementations. They shall not be provided by Context Producers. In the event that they are provided (in update or create operations) NGSI-LD implementations shall ignore them.
In query or retrieve operations implementations shall only generate common members (Table 5.2.2‑1) when the Context Consumer explicitly asks for their inclusion. Clause 6.3.11 defines the mechanism offered by the HTTP binding for such purpose.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
createdAt
|
string
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Entity creation timestamp. See clause
4.8
|
modifiedAt
|
string
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Entity last modification timestamp. See clause
4.8
|
deletedAt
|
string
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Entity deletion timestamp. See clause
4.8 It is only used in notifications reporting deletions and in the temporal representation of Entities (clause 4.5.6), Properties (clause 4.5.7), Relationships (clause 4.5.8) and LanguageProperties (clause 5.2.32) and VocabProperties (clause 5.2.35) and JsonProperties (clause 5.2.38) |
5.2.3 @context
When encoding NGSI-LD Entities, Context Source Registrations, Subscriptions and Notifications, as pure JSON-LD (MIME type "application/ld+json"), @context @context (as described in clause 4.4) shall be included as a special member of the corresponding JSON-LD Object. Table 5.2.3‑1 gives a precise definition of this special member.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
@context
|
URI, JSON Object, or JSON Array
|
See [2], section 5.1.
|
0..1
|
JSON-LD @context.
|
5.2.4 Entity
This type represents the data needed to define an NGSI-LD Entity as mandated by clause 4.5.1.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.4‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
1
|
Entity ID.
|
type
|
String or String[]
|
1
|
Entity Type(s). Both short hand string(s) (type name) or URI(s) are
allowed
|
|
expiresAt
|
String
|
DateTime (see clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System temporal Property representing the expiration date for the
storage of the Entity. See clause
4.22
|
scope
|
String or String[]
|
See clause
4.18
|
0..1
|
Scope
|
location
|
GeoProperty
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.7
|
0..1
|
Default geospatial Property of an entity. See clause
4.7
|
observationSpace
|
GeoProperty
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.7
|
0..1
|
See clause
4.7
|
operationSpace
|
GeoProperty
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.7
|
0..1
|
See clause
4.7
|
<Property name>
|
Property or Property[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definitions in clauses 5.2.5
|
0..N
|
Property as mandated by clause
4.5.2
|
GeoProperty or GeoProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.7
|
0..N
|
GeoProperty as mandated by clause
4.5.2
|
|
LanguageProperty or LanguageProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.32
|
0..N
|
LanguageProperty as mandated by clause
4.5.18
|
|
JsonProperty or JsonProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.38
|
0..N
|
JsonProperty as mandated by clause
4.5.24
|
|
VocabProperty or VocabProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.35
|
0..N
|
VocabProperty as mandated by clause
4.5.20
|
|
ListProperty or ListProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.36
|
0..N
|
ListProperty as mandated by clause
4.5.21
|
|
<Relationship name>
|
Relationship or Relationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.6
|
0..N
|
Relationship as mandated by clause
4.5.3
|
ListRelationship or ListRelationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.37
|
0..N
|
ListRelationship as mandated by clause
4.5.22
|
|
NOTE 1:
For
each
Property
(or
subclass
of
Property
)
identified
by
the
same
Property
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
NOTE 2:
For
each
Relationship
(or
subclass
of
Relationship
)
identified
by
the
same
Relationship
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
|
||||
5.2.5 Property
This type represents the data needed to define a Property as mandated by clause 4.5.2.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.5‑1 below. The datatype definition defines all the required attributes for the normalized representation. In the concise representation, the Attribute type member can be omitted as type="Property" can be inferred from the presence of the value member. Furthermore, in the concise representation of a Property, the value member cannot be a GeoJSON Object (as defined in clause 4.7) as it would be interpreted as a GeoProperty (see clause 5.2.7).
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "Property"
|
1
|
Node type.
|
value
|
Any JSON value as defined by IETF RFC 8259 [6]
|
See NGSI-LD Value definition in clause
3.1
|
1
|
Property Value.
|
datasetId
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
0..1
|
It allows identifying a set or group of property values
|
expiresAt
|
String
|
DateTime (see clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System temporal Property representing the expiration date for the
storage of the Property. See clause
4.22
|
observedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Timestamp. See clause
4.8
|
unitCode
|
String
|
As mandated by [15]
|
0..1
|
Property Value's unit code
|
valueType
|
String
|
0..1
|
The native JSON-LD @type for the Property Value. A String Value
which shall be type coerced to a URI based on the supplied
@context
|
|
<Property name>
|
Property or Property[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause 5.2.5
|
0..N
|
Properties of the Property
|
GeoProperty or GeoProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.7
|
0..N
|
GeoProperties of the Property
|
|
LanguageProperty or LanguageProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.32
|
0..N
|
LanguageProperties of the Property
|
|
JsonProperty or JsonProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.38
|
0..N
|
JsonProperties of the Property
|
|
VocabProperty or VocabProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.35
|
0..N
|
VocabProperties of the Property
|
|
ListProperty or ListProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.36
|
0..N
|
ListProperties of the Property
|
|
<Relationship name>
|
Relationship or Relationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.6
|
0..N
|
Relationships of the Property
|
ListRelationship or ListRelationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.37
|
0..N
|
ListRelationships of the Property
|
|
NOTE 1:
For
each
Property
(or
subclass
of
Property
)
identified
by
the
same
Property
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
NOTE 2:
For
each
Relationship
(or
subclass
of
Relationship
)
identified
by
the
same
Relationship
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
|
||||
The following output only members (defined by Table 5.2.5-2) of the Property data structure are also defined. They are read-only and shall be generated by NGSI-LD implementations. They shall not be provided by Context Producers. In the event that they are provided (in update or create operations) NGSI-LD implementations shall ignore them.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
createdAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated creation timestamp. See clause
4.8
|
deletedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
It is only used in notifications reporting deletions
|
0..1
|
System generated deletion timestamp. See clause
4.8
|
instanceId
|
String
|
Valid URI. Only used in temporal representation of Properties
|
0..1
|
URI uniquely identifying a Property instance as mandated by clause
4.5.7
|
modifiedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated last modification timestamp. See clause
4.8
|
previousValue
|
Any JSON value as defined by IETF RFC 8259 [6]
|
Only used in Notifications, if the showChanges option is
explicitly requested
|
0..1
|
Previous Property Value
|
5.2.6 Relationship
This type represents the data needed to define a Relationship as mandated by clause 4.5.3.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.6‑1 below. The datatype definition defines all the required attributes for the normalized representation. In the concise representation, the Attribute type member can be omitted as type="Relationship" can be inferred from the presence of the object member.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "Relationship"
|
1
|
Node type
|
object
|
String or String[]
|
Valid URI or an Array of Valid URIs
|
1
|
Relationship's target object
|
datasetId
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
0..1
|
It allows identifying a set or group of target relationship objects
|
expiresAt
|
String
|
DateTime (see clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System temporal Property representing the expiration date for the
storage of the Relationship. See clause
4.22
|
objectType
|
String or String[]
|
0..1
|
Node Type of the Relationship's target object. Both short hand string(s)
(type name) or URI(s) are allowed
|
|
observedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Timestamp. See clause
4.8
|
<Property name>
|
Property or Property[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause 5.2.5
|
0..N
|
Properties of the Relationship
|
GeoProperty or GeoProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.7
|
0..N
|
GeoProperties of the Relationship
|
|
LanguageProperty or LanguageProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.32
|
0..N
|
LanguageProperties of the Relationship
|
|
JsonProperty or JsonProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.38
|
0..N
|
JsonProperties of the Relationship
|
|
VocabProperty or VocabProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.35
|
0..N
|
VocabProperties of the Relationship
|
|
ListProperty or ListProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.36
|
0..N
|
ListProperties of the Relationship
|
|
<Relationship name>
|
Relationship or Relationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.6
|
0..N
|
Relationships of the Relationship
|
ListRelationship or ListRelationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.37
|
0..N
|
ListRelationships of the Relationship
|
|
NOTE 1:
For
each
Property
(or
subclass
of
Property
)
identified
by
the
same
Property
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
NOTE 2:
For
each
Relationship
(or
subclass
of
Relationship
)
identified
by
the
same
Relationship
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
|
||||
The following output only members (defined by Table 5.2.6-2) of the Relationship data structure are also defined. They are read-only and shall be generated by NGSI-LD implementations. They shall not be provided by Context Producers. In the event that they are provided (in update or create operations) NGSI-LD implementations shall ignore them.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
createdAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated creation timestamp. See clause
4.8
|
deletedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
It is only used in notifications reporting deletions
|
0..1
|
System generated deletion timestamp. See clause
4.8
|
entity
|
Entity or Entity[] (see note)
|
See datatype definition in clause 5.2.4.
Only used in Linked Entity Retrieval, if the join=inline option
is explicitly requested
|
0..1
|
An inline Entity obtained by Linked Entity Retrieval, corresponding to
the Relationship's target object. See clause
4.5.23.2
|
instanceId
|
String
|
Valid URI. Only used in temporal representation of Relationships
|
0..1
|
URI uniquely identifying a Relationship instance as mandated by clause
4.5.8
|
modifiedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated last modification timestamp. See clause
4.8
|
previousObject
|
String
|
Valid URI. Only used in Notifications, if the showChanges option
is explicitly requested
|
0..1
|
Previous Relationship's target object
|
NOTE:
one-to-N
Relationships
expand
to
an
array
of
Entity
elements,
since
there
can
be
more
than
one
target
object
URI
specified.
|
||||
5.2.7 GeoProperty
This type represents the data needed to define a GeoProperty.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.7‑1 below. The datatype definition defines all the required attributes for the normalized representation. In the concise representation, the Attribute type member can be omitted as "GeoProperty" can be inferred from the presence of the value member holding a GeoJSON Geometry as mandated by clause 4.7.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "GeoProperty"
|
1
|
Node type
|
value
|
JSON Object
|
As mandated by clause
4.7
|
1
|
Geolocation encoded as GeoJSON [8]
|
datasetId
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
0..1
|
It allows identifying a set or group of property values
|
expiresAt
|
String
|
DateTime (see clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System temporal Property representing the expiration date for the
storage of the GeoProperty. See clause
4.22
|
observedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Timestamp. See clause
4.8
|
valueType
|
String
|
0..1
|
The native JSON-LD @type for the GeoProperty Value. A String
Value which shall be type coerced to a URI based on the supplied
@context
|
|
<Property name>
|
Property or Property[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause 5.2.5 | 0..N | Properties of the GeoProperty |
GeoProperty or GeoProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause 5.2.7 | 0..N | GeoPropertiesof the GeoProperty | |
| LanguageProperty or LanguageProperty[] (see note 1) | See datatype definition in clause 5.2.32 | 0..N | LanguagePropertiesof the GeoProperty | |
| JsonProperty or JsonProperty[] (see note 1) | See datatype definition in clause 5.2.38 | 0..N | JsonPropertiesof the GeoProperty | |
| VocabProperty or VocabProperty[] (see note 1) | See datatype definition in clause 5.2.35 | 0..N | VocabPropertiesof the GeoProperty | |
ListProperty or ListProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause 5.2.36 | 0..N | ListPropertiesof the GeoProperty | |
<Relationship name>
|
Relationship or Relationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause 5.2.6 | 0..N | Relationships of the GeoProperty |
| ListRelationship or ListRelationship[] (see note 2) | See datatype definition in clause 5.2.37 | 0..N | ListRelationshipsof the GeoProperty | |
NOTE 1:
For
each
Property
(or
subclass
of
Property
)
identified
by
the
same
Property
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
NOTE 2:
For
each
Relationship
(or
subclass
of
Relationship
)
identified
by
the
same
Relationship
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
|
||||
The following output only members (defined by Table 5.2.7-2) of the GeoProperty data structure are also defined. They are read-only and shall be generated by NGSI-LD implementations. They shall not be provided by Context Producers. In the event that they are provided (in update or create operations) NGSI-LD implementations shall ignore them.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
createdAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated creation timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
deletedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
It is only used in notifications reporting deletions
|
0..1
|
System generated deletion timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
instanceId
|
String
|
Valid URI. Only used in temporal representation of GeoProperties
|
0..1
|
URI uniquely identifying a GeoProperty instance as mandated by clause
4.5.7.
|
modifiedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated last modification timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
previousValue
|
Any JSON value as defined by IETF RFC 8259 [6]
|
Only used in Notifications, if the
showChanges option is explicitly requested
|
0..1
|
Previous GeoProperty Value.
|
5.2.8 EntityInfo
This type represents what Entities, Entity Types or group of Entity IDs (as a regular expression pattern mandated by IEEE 1003.2™ [11]) can be provided (by Context Sources).
The JSON members shall follow the indications provided in Table 5.2.8‑1. id takes precedence over idPattern.
Notice that Cardinality of type being 1 implies that it is not possible to register what Entities can be provided by a Context Source just by their id or idPattern (i.e. without specifying their type).
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
0..1
|
Entity identifier.
|
idPattern
|
String
|
Regular expression as per IEEE 1003.2™ [11]
|
0..1
|
A regular expression which denotes a pattern that shall be matched by
the provided or subscribed Entities.
|
type
|
String or String[]
|
Fully Qualified Name of an Entity Type or the Entity Type name as a
short-hand string. See clause
4.6.2
|
1
|
Entity Type (or JSON array, in case of Entities with multiple Entity
Types).
|
5.2.9 CSourceRegistration
This type represents the data needed to register a new Context Source.
The supported JSON members shall follow the indications provided in Table 5.2.9‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String
|
Valid URI.
Unique registration identifier. (JSON-LD @id).
|
0..1
|
Generated at creation time, if it is not provided, it will be assigned
during registration process and returned to client.
It cannot be later modified in update operations.
|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "ContextSourceRegistration"
|
1
|
JSON-LD @type
Use reserved type for identifying Context Source Registration.
|
registrationName
|
String
|
Non-empty string
|
0..1
|
A name given to this Context Source
Registration
|
contextSourceAlias
|
String
|
Non-empty string. Pseudonym field as defined in IETF RFC 7230 [27]
|
0..1
|
A previously retrieved unique id for a registered Context Source which is used to identify
loops.
In the multi-tenancy use case (see clause
4.14), this id shall be used to identify a specific
Tenant within a registered Context Source.
|
description
|
String
|
Non-empty string
|
0..1
|
A description of this Context Source
Registration.
|
information
|
RegistrationInfo[]
|
See data type definition in clause
5.2.10. Empty array (0 length) is not allowed
|
1
|
Describes the Entities, Properties and Relationships for which the Context Source may be able to provide
information.
|
datasetId
|
String[]
|
Valid URIs,"@none"
for including the default Attribute instances.
|
0..1
|
Specifies the datasetIds of Attributes that the Context Source can provide, defined as per
clause
4.5.5.
|
tenant
|
String
|
0..1
|
Identifies the Tenant that has to be
specified in all requests to the Context
Source that are related to the information registered in this
Context Source Registration. If not
present, the default Tenant is
assumed. Should only be present in systems supporting multi-tenancy.
|
|
observationInterval
|
TimeInterval
|
See data type definition in clause
5.2.11
|
0..1
|
If present, the Context Source can be
queried for Temporal Entity Representations. (If latest Entity
information is also provided, a separate Context Registration is needed
for this purpose). The observationInterval specifies the time
interval for which the Context Source
can provide Entity information as specified by the observedAt
Temporal Property. A temporal query based on the observedAt
Temporal Property, which is the default, is matched against the
observationInterval for overlap.
|
managementInterval
|
TimeInterval
|
See data type definition in clause
5.2.11
|
0..1
|
If present, the Context Source can be
queried for Temporal Entity Representations. (If latest Entity
information is also provided, a separate Context Registration is needed
for this purpose). The managementInterval specifies the time
interval for which the Context Source
can provide Entity information as specified by the createdAt,
modifiedAt and deletedAt Temporal Properties. A temporal
query based on the createdAt, modifiedAt or
deletedAt Temporal Property is matched against the
managementInterval for overlap.
|
location
|
GeoJSON Geometry as mandated by clause
4.7
|
0..1
|
Location for which the Context
Source may be able to provide information.
|
|
observationSpace
|
GeoJSON Geometry as mandated by clause
4.7
|
0..1
|
Geographic location that includes the observation spaces of all entities
as specified by their respective observationSpace
GeoProperty for which the Context
Source may be able to provide information.
|
|
operationSpace
|
GeoJSON Geometry as mandated by clause
4.7
|
0..1
|
Geographic location that includes the operation spaces of all entities
as specified by their respective operationSpace
GeoProperty for which the Context
Source may be able to provide information.
|
|
expiresAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Provides an expiration date. When passed the Context Source Registration will become
invalid and the Context Source might
no longer be available.
|
endpoint
|
String
|
It shall be a dereferenceable URI
|
1
|
Endpoint expressed as dereferenceable URI through which the Context Source exposes its NGSI-LD
interface.
|
contextSourceInfo
|
KeyValuePair[]
|
0..1
|
Generic {key, value} array to convey optional information to provide
when contacting the registered Context
Source.
|
|
scope
|
String or
String[]
|
Scope(s)
|
0..1
|
Scopes (see clause
4.18) for which the Context
Source has Entities.
|
mode
|
String
|
It shall be one of:
"inclusive", "exclusive", "redirect" or "auxiliary"
The mode is assumed to be "inclusive" if
not explicitly defined
|
0..1
|
The definition of the mode of distributed operation (see clause
4.3.6) supported by the registered Context Source.
|
operations
|
String[]
|
Entries are limited to the named API operations and named operation
groups (see clause
4.20)
|
0..1
|
The definition limited subset of API operations supported by the
registered Context Source.
If undefined, the default set of operations is "federationOps" (see clause
4.20).
|
refreshRate
|
String
|
String representing a duration in ISO 8601 format [17]
|
0..1
|
An indication of the likely period of time to elapse between updates at
this registered endpoint.
Brokers may optionally use this information to help implement caching.
|
management
|
Registration
Management
Info
|
See data type definition in clause
5.2.34
|
0..1
|
Holds additional optional registration management information that can
be used to limit unnecessary distributed operation requests.
|
<CSource Property name>
|
Any JSON value as defined by IETF RFC 8259 [6]
|
0..N
|
Each Context Source Property pertains
to a characteristic of the Context
Source the Context Source
Registration describes.
|
The members (defined by Table 5.2.9-2) of the CSourceRegistration data structure are also defined. They are read-only and shall be automatically generated by NGSI-LD implementations. In the event that they are provided (in update or create operations) NGSI-LD implementations shall ignore them.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
status
|
String
|
Allowed values:
"ok" "failed" |
0..1
|
Read-only., Status of the Registration. It shall be "ok" if the last attempt to perform a
distributed operation succeeded. It shall be "failed" if the last attempt to perform a
distributed operation failed.
|
timesSent
|
Number
|
0 or greater value
|
0..1
|
Number of times that the
registration triggered a distributed operation, including failed
attempts.
|
timesFailed
|
Number
|
0 or greater value
|
0..1
|
Number of times that the
registration triggered a distributed operation request that
failed.
|
lastSuccess
|
String
|
DateTime(clause 4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Timestamp corresponding to the
instant when the last successfully distributed operation was sent.
Created on first successful operation.
|
| lastFailure |
String
|
DateTime(clause 4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Timestamp corresponding to the instant when the last distributed operation resulting in a failure (for instance, in the HTTP binding, an HTTP response code other than 2xx) was returned. |
5.2.10 RegistrationInfo
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.10‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
entities
|
EntityInfo[]
|
See data type definition in clause
5.2.8. Empty array (0 length) is not allowed. Restrictions in clause
4.3.6 apply as well
|
0..1
|
Describes the entities for which the CSource may be able to provide
information.
|
propertyNames
|
String[]
|
Property names as short hand strings or URIs. Empty array is not
allowed. Restrictions in clause
4.3.6 apply as well
|
0..1
|
Describes the Properties that the CSource may be able to provide.
|
relationshipNames
|
String[]
|
Relationship names as short hand strings or URIs. Empty array is not
allowed. Restrictions in clause
4.3.6 apply as well
|
0..1
|
Describes the Relationships that the CSource may be able to provide.
|
At least one element of RegistrationInfo shall be present.
5.2.11 TimeInterval
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.11‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
startAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
1
|
Describes the start of the time interval
|
endAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Describes the end of the time interval. If not present the interval is
open
|
5.2.12 Subscription
This datatype represents a Context Subscription.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.12‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
0..1
|
Subscription identifier (JSON-LD @id). Generated at creation
time, if it is not provided, it will be assigned during subscription
process and returned to client.
It cannot be later modified in update operations.
|
|||
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "Subscription"
|
1
|
JSON-LD @type.
|
|||
subscriptionName
|
String
|
0..1
|
A (short) name given to this Subscription.
|
||||
description
|
String
|
0..1
|
Subscription description.
|
||||
entities
|
EntitySelector[]
|
See data type definition in clause
5.2.33. Empty array (0 length) is not allowed.
Mandatory if timeInterval is present, unless the execution of the
request is limited to local scope (see clause
5.5.13)
|
0..1
|
Entities subscribed.
|
|||
watchedAttributes
|
String[]
|
Attribute name as short hand strings or URIs. Empty array (0 length) is
not allowed.
if timeInterval is present it shall not appear (0 cardinality)
|
0..1
|
Watched Attributes (Properties or Relationships). If not defined it
means any Attribute.
|
|||
localOnly
|
Boolean
|
0..1
|
If localOnly=true then the subscription only pertains to the
Entities stored locally.
|
||||
notificationTrigger
|
String[]
|
Valid notification triggers are "entityCreated", "entityUpdated", "entityDeleted", "attributeCreated", "attributeUpdated", "attributeDeleted"
|
0..1
|
The notification triggers listed indicate what kind of changes shall
trigger a notification. If not present, the default is the combination
"attributeCreated" and "attributeUpdated". "entityUpdated" is equivalent to the
combination "attributeCreated", "attributeUpdated" and "attributeDeleted"
|
|||
timeInterval
|
Number
|
Greater than 0
if watchedAttributes is present it shall not appear (0
cardinality)
|
0..1
|
Indicates that a notification shall be delivered periodically regardless
of attribute changes. Actually, when the time interval (in seconds)
specified in this value field is reached.
|
|||
q
|
String
|
A valid query string as per clause
4.9
|
0..1
|
Query that shall be met by subscribed entities in order to trigger the
notification.
|
|||
expandValues
|
String
|
Comma separated list of attribute names
|
0..1
|
Values of the identified attributes should be expanded against the
supplied @context using JSON-LD type coercion prior to executing
the query.
|
|||
jsonKeys
|
String
|
Comma separate list of attribute names
|
0..1
|
Values of the identified attributes are to be considered uninterpretable
as JSON-LD and should not be expanded against the supplied
@context using JSON-LD type coercion prior to executing the
query.
|
|||
geoQ
|
GeoQuery
|
See data type definition in clause 5.2.13
|
0..1
|
Geoquery that shall be met by subscribed entities in order to trigger
the notification.
|
|||
csf
|
String
|
A valid query string as per clause
4.9
|
0..1
|
Context source filter that shall be met by Context Source Registrations describing
Context Sources to be used for Entity
Subscriptions.
|
|||
isActive
|
Boolean
|
true by default
|
0..1
|
Allows clients to temporarily pause the subscription by making it
inactive. true indicates that the Subscription is under
operation. false indicates that the subscription is paused, and
notifications shall not be delivered.
|
|||
notification
|
NotificationParams
|
See data type definition in clause
5.2.14
|
1
|
Notification details.
|
|||
expiresAt
|
String
|
DateTime (see clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Expiration date for the subscription.
|
|||
throttling
|
Number
|
Greater than 0. Fractional values are allowed. If timeInterval is
present it shall not appear (0 cardinality)
|
0..1
|
Minimal period of time in seconds which shall elapse between two
consecutive notifications.
|
|||
temporalQ
|
TemporalQuery
|
See data type definition in clause
5.2.21
|
0..1
|
Temporal Query to be used only in
Context Registration Subscriptions for matching Context Source Registrations of Context Sources providing temporal
information.
|
|||
scopeQ
|
String
|
See clause
4.19
|
0..1
|
Scope query.
|
|||
lang
|
String
|
A natural language filter in the form of a IETF RFC 5646 [28] language code
|
0..1
|
Language filter to be applied to the query (clause
4.15).
|
|||
datasetId
|
String[]
|
Valid URIs,"@none"
for including the default Attribute instances.
|
0..1
|
Specifies the datasetIds of the Attribute instances to be selected for
each matched Attribute as per clause
4.5.5.
|
|||
jsonldContext
|
String
|
Dereferenceable URI
|
The dereferenceable URI of the JSON-LD @context to be used when
sending a notification resulting from the subscription. If not provided,
the @context used for the subscription shall be used as a
default.
|
||||
ngsildConformance
|
String
|
A semantically versioned string in the form major.minor, which
conforms to a version of the NGSI-LD specification
|
0..1
|
If provided the notification shall undergo a backwards compatibility
operation as defined by clause
4.3.6.8 and be amended to conform to the supplied version of the
NGSI-LD specification.
|
|||
splitEntities
|
Boolean
|
default decided by implementation; it should be configurable. The
parameter does not apply in case localOnly is true.
|
0..1
|
If true it is assumed that single Entities are distributed
between different Context Brokers and/or Context Sources and this has to
be taken into account when applying any kind of filters (q, geoQ,
scopeQ, Attributes etc.). If false it is expected that Context
Broker and/or Context Source always have complete Entities, which allows
applying filters locally.
|
|||
At least one of (a) entities or (b) watchedAttributes shall be present, unless the member localOnly is set to true, in which case the execution of the request is limited to local scope (see clause 5.5.13).
The members (defined by Table 5.2.12-2) of the Subscription data structure are also defined. They are read-only and shall be automatically generated by NGSI-LD implementations. They shall not be provided by Context Subscribers. In the event that they are provided (in update or create operations) NGSI-LD implementations shall ignore them.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
status
|
String
|
Allowed values:
"active" "paused" "expired" |
0..1
|
Read-only. Provided by the system when querying the details of a
subscription
|
5.2.13 GeoQuery
This datatype represents a geoquery used for Subscriptions.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.13‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
geometry
|
String
|
A valid GeoJSON [8]
geometry type excepting GeometryCollection
|
1
|
Type of the reference geometry.
|
coordinates
|
JSON Array or String
|
A JSON Array coherent with the geometry type as per IETF RFC 7946
[8]
|
1
|
Coordinates of the reference geometry. For the sake of JSON-LD
compatibility It can be encoded as a string as described in clause
4.7.1.
|
georel
|
String
|
A valid geo-relationship as defined by clause
4.10
|
1
|
Geo-relationship ("near", "within", etc.).
|
geoproperty
|
String
|
Attribute name as short hand string or URI
|
0..1
|
Specifies the GeoProperty to which the GeoQuery is to be applied. If not
present, the default GeoProperty is location.
|
5.2.14 NotificationParams
5.2.14.1 NotificationParams data type definition
This datatype represents the parameters that allow to convey the details of a notification.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.14.1‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
attributes
|
String[]
|
Attribute name as short hand strings or URIs. Empty array (0 length) is
not allowed
|
0..1
|
A synonym for a combination of the pick andq parameter.
Deprecated
Attribute names to be included in the notification payload body. If
undefined it will mean all Attributes.
|
sysAttrs
|
Boolean
|
false by default
|
0..1
|
If true, the system generated attributes createdAt and
modifiedAt and the system attribute expiresAt are included
in the response payload body, in the case of a deletion also
deletedAt.
|
format
|
String
|
It shall be one of: "normalized", "concise", "simplified" (or its synonym "keyValues")
|
0..1
|
Conveys the representation format of the entities delivered at
notification time. By default, it will be in the normalized format.
|
pick
|
String[]
|
Entity member ("id", "type", "scope"
or a projected Attribute name as a valid attribute projection language
string as per clause
4.21). Empty array (0 length) is not allowed
|
0..1
|
When defined, every Entity within the payload body is reduced down to
only contain the specified Entity members.
|
omit
|
String[]
|
Entity member ("id", "type", "scope"
or a projected Attribute name) as a valid attribute projection
language string as per clause
4.21. Empty array (0 length) is not allowed
|
0..1
|
When defined, the specified Entity members are removed from each Entity
within the payload.
|
showChanges
|
Boolean
|
false by default
|
0..1
|
If true the previous value (previousValue) of
Properties or languageMap (previousLanguageMap) of
Language Properties or object (previousObject) of
Relationships is provided in addition to the current one. This requires
that it exists, i.e. in case of modifications and deletions, but not in
the case of creations.
showChanges cannot be true in case format is "keyValues".
|
join
|
String
|
It shall be one of: "flat", "inline", "@none"
|
0..1
|
String representing the type of Linked
Entity retrieval to apply.
By default, it will be "@none".
|
joinLevel
|
Number
|
Positive Integer
|
0..1
|
Depth of Linked Entity retrieval to
apply. Default is 1. Only applicable if join parameter is "flat", or "inline".
|
endpoint
|
Endpoint
|
See data type definition in clause 5.2.15
|
1
|
Notification endpoint details.
|
5.2.14.2 Output only members
The following output only members (defined by Table 5.2.14.2-1) of the NotificationParams data structure are also defined. They are read-only and shall be automatically generated by NGSI-LD implementations. They shall not be provided by Context Subscribers. In the event that they are provided (in update or create operations) NGSI-LD implementations shall ignore them.
In query or retrieve operations involving Subscriptions, implementations shall generate them as part of their representation.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
timesSent
|
Number
|
Greater than 0
|
0..1
|
Number of times that the notification has been sent. Provided by the
system when querying the details of a subscription
|
timesFailed
|
Number
|
Greater than 0
|
0..1
|
Number of times an unsuccessful response (or timeout) has been received
when delivering the notification. Provided by the system when querying
the details of a subscription
|
lastNotification
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Timestamp corresponding to the instant when the last notification has
been sent. Provided by the system when querying the details of a
subscription
|
lastFailure
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Timestamp corresponding to the instant when the last notification
resulting in failure (for instance, in the HTTP binding, an HTTP
response code different than 200) has been sent. Provided by the system
when querying the details of a subscription
|
lastSuccess
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Timestamp corresponding to the instant when the last successful (200 OK
response) notification has been sent. Provided by the system when
querying the details of a subscription
|
status
|
String
|
Allowed values:
"ok", "failed"
|
0..1
|
Status of the Notification. It shall be "ok" if the last attempt to notify the
subscriber succeeded. It shall be "failed" if the last attempt to notify the
subscriber failed
|
5.2.15 Endpoint
This datatype represents the parameters that are required in order to define an endpoint for notifications. This can include, in addition the endpoint's URI, a generic{key, value} array, named receiverInfo, which contains, in a generalized form, whatever extra information the Context Broker shall convey to the receiver in order for the Context Broker to successfully communicate with receiver (e.g. Authorization material), or for the receiver to correctly interpret the received content (e.g. the Link URL to fetch an @context). Additionally, it can include another generic{key, value} array, named notifierInfo, which contains the configuration that the Context Broker needs to know in order to correctly set up the communication channel towards the receiver (e.g. MQTT-Version, MQTT-QoS, in case of MQTT binding, as defined in clause 7.2).
The supported JSON members shall follow the indications provided in Table 5.2.15‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
uri
|
String
|
Dereferenceable URI
|
1
|
URI which conveys the endpoint which will receive the notification.
|
accept
|
String
|
MIME type. It shall be one of:
"application/json" "application/ld+json" "application/geo+json" |
0..1
|
Intended to convey the MIME type of the notification payload body (JSON,
or JSON-LD, or GeoJSON). If not present, default is "application/json".
|
timeout
|
Number
|
Greater than 0
|
0..1
|
Maximum period of time in
milliseconds which may elapse before a notification is assumed to have
failed. The NGSI-LD system can override this value. This only applies if
the binding protocol always returns a response.
|
cooldown
|
Number
|
Greater than 0
|
0..1
|
Once a failure has
occurred, minimum period of time in milliseconds which shall elapse
before attempting to make a subsequent notification to the same endpoint
after failure. If requests are received before the cooldown period has expired, no notification is sent. |
receiverInfo
|
KeyValuePair[]
|
0..1
|
Generic {key, value} array to convey optional information to the
receiver.
|
|
notifierInfo
|
KeyValuePair[]
|
0..1
|
Generic {key, value} array to set up the communication channel.
|
5.2.16 BatchOperationResult
This datatype represents the result of a batch operation.
The supported JSON members shall follow the indications provided in Table 5.2.16‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
success
|
String[]
|
Array of valid URIs
|
1
|
Array of Entity IDs corresponding to the Entities that were successfully
treated by the concerned operation. Empty Array if no Entity was
successfully treated.
|
errors
|
BatchEntityError[]
|
1
|
One array item per Entity in error. Empty Array if no errors happened.
|
5.2.17 BatchEntityError
This datatype represents an error raised (associated to a particular Entity) during the execution of a batch or distributed operation.
The supported JSON members shall follow the indications provided in Table 5.2.17‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
entityId
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
1
|
Entity ID corresponding to the Entity in error
|
registrationId
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
0..1
|
Registration Id corresponding to a failed distributed operation
(optional)
|
error
|
ProblemDetails (see IETF RFC 7807 [10])
|
1
|
One instance per Entity in error
|
5.2.18 UpdateResult
This datatype represents the result of Attribute update (append or update) operations in the NGSI-LD API regardless of whether local or distributed.
The supported JSON members shall follow the indications provided in Table 5.2.18‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
updated
|
String[]
|
1
|
List of Attributes (represented by their name) that were appended or
updated.
|
|
notUpdated
|
NotUpdatedDetails[]
|
See clause
5.2.19
|
1
|
List which contains the Attributes (represented by their name) that were
not updated, together with the reason for not being updated.
|
5.2.19 NotUpdatedDetails
This datatype represents additional information provided by an implementation when an Attribute update did not happen. See also clause 5.2.18.
The supported JSON members shall follow the indications provided in Table 5.2.19‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
attributeName
|
String
|
1
|
Attribute name
|
|
reason
|
String
|
1
|
Reason for not having changed such Attribute
|
|
registrationId
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
0..1
|
Registration Id corresponding to a failed distributed operation
(optional)
|
5.2.20 EntityTemporal
This datatype represents the Temporal Evolution of an Entity.
This is the same datatype as mandated by clause 5.2.4 with the only deviation that the representation of Properties and Relationships shall be the temporal one (arrays of (Property or Relationship) instances represented by JSON-LD objects) as defined in clauses 4.5.7 and 4.5.8. Alternatively it is possible to specify the EntityTemporal by using the "Simplified temporal representation of an Entity", as defined in clause 4.5.9.
5.2.21 TemporalQuery
This datatype represents a temporal query.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.21‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
timerel
|
String
|
Allowed values: "before", "after" and "between"
|
1
|
Represents the temporal relationship as defined by clause
4.11
|
timeAt
|
String representing the timeAt parameter as defined by clause
4.11
|
It shall be a DateTime
|
1
|
|
endTimeAt
|
String representing the endTimeAt parameter as defined by clause
4.11
|
It shall be a DateTime. Cardinality shall be 1 if timerel
is equal to "between"
|
0..1
|
|
timeproperty
|
String representing a Temporal Property name
|
Allowed values: "observedAt", "createdAt", "modifiedAt" and "deletedAt". If not specified, the default is
"observedAt". (See clause
4.8)
|
0..1
|
5.2.22 KeyValuePair
This datatype represents the optional information that is required when contacting an endpoint for notifications.
The supported members shall follow the indications provided in Table 5.2.22‑1. They are intended to represent a key/value pair.
Example optional information includes additional HTTP Headers such as:
- The HTTP Authentication Header.
- The HTTP Prefer Header (IETF RFC 7240 [26]) used when notifying the GeoJSON Endpoint.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
key
|
String
|
Binding-dependent
|
1
|
The key of the key/value pair
|
value
|
String
|
Binding-dependent
|
1
|
The value of the key/value pair
|
5.2.23 Query
This datatype represents the information that is required in order to convey a query when a "Query Entities" operation or a "Query Temporal Evolution of Entities" operation is to be performed (as per clauses 5.7.2 and 5.7.4, respectively).
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.23‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "Query"
|
1
|
JSON-LD @type
|
|
entities
|
EntitySelector[]
|
See data type definition in clause
5.2.33. Empty array (0 length) is not allowed
|
0..1
|
Entity IDs, id pattern and Entity types that shall be matched by
Entities in order to be retrieved.
|
|
attrs
|
String[]
|
Attribute name as short hand strings or URIs.
Empty array (0 length) is not allowed
|
0..1
|
A synonym for a combination of the pick andq parameters.
Deprecated
List of Attributes that shall be matched by Entities in order to be
retrieved. If not present all Attributes will be retrieved.
|
|
pick
|
String[]
|
Entity member ("id", "type", "scope" or a
projected Attribute name) as a valid attribute projection language
string as per clause
4.21. Empty array (0 length) is not allowed
|
0..1
|
When defined, every Entity within the payload body is reduced down to
only contain the specified Entity members.
|
|
omit
|
String[]
|
Entity member ("id", "type", "scope" or a
projected Attribute name) as a valid attribute projection language
string as per clause
4.21. Empty array (0 length) is not allowed
|
0..1
|
When defined, the specified Entity members are removed from each Entity
within the payload.
|
|
q
|
String
|
A valid query string as per clause
4.9
|
0..1
|
Query that shall be matched by Entities in order to be retrieved.
|
|
expandValues
|
String
|
Comma separated list of attribute names
|
0..1
|
Values of the identified attributes should be expanded against the
supplied @context using JSON-LD type coercion prior to executing
the query.
|
|
jsonKeys
|
String
|
Comma separate list of attribute names
|
0..1
|
Values of the identified attributes are to be considered uninterpretable
as JSON-LD and should not be expanded against the supplied
@context using JSON-LD type coercion prior to executing the
query.
|
|
geoQ
|
GeoQuery
|
See data type definition in clause 5.2.13
|
0..1
|
Geoquery that shall be matched by Entities in order be retrieved.
|
|
csf
|
String
|
A valid query string as per clause
4.9
|
0..1
|
Context source filter that shall be matched by Context Source Registrations describing
Context Sources to be used for
retrieving Entities.
|
|
temporalQ
|
TemporalQuery
|
See data type definition in clause
5.2.21
|
0..1
|
Temporal Query to be present only for "Query Temporal Evolution of Entities" operation
(clause
5.7.4).
|
|
scopeQ
|
String
|
See clause
4.19
|
0..1
|
Scope query.
|
|
lang
|
String
|
A natural language filter in the form of a IETF RFC 5646 [28] language code
|
0..1
|
Language filter to be applied to the query (clause
4.15).
|
|
containedBy
|
String[]
|
Comma separated list of URIs. Empty array (0 length) is not allowed
|
0..1
|
List of entity ids which have previously been encountered whilst
retrieving the Entity Graph.
Only applicable if joinLevel is present.
Only applicable for the "Query Entities" operation (clause
5.7.2).
|
|
datasetId
|
String[]
|
Valid URIs,"@none"
for including the default Attribute instances.
|
0..1
|
Specifies the datasetIds of the Attribute instances to be selected for
each matched Attribute as per clause
4.5.5.
|
|
entityMap
|
Boolean
|
0..1
|
If true, the location of the EntityMap used in the operation is returned in the response. [{[--TAL--]}] [{[--TAL--]}] | ||
entityMapLifetime
|
String
|
String representing a duration in ISO 8601 format [17]
|
0..1
|
Suggested duration for which the requester wants the EntityMap to exist.
The actual expiresAt time of the EntityMap shall be set by the Context
Broker or Context Source, possibly overriding the requested duration.
Only applicable if entityMap is set to true.
|
|
splitEntities
|
Boolean
|
default decided by implementation; it should be configurable. The
parameter does not apply in case the parameter local is
true.
|
0..1
|
If true it is assumed that single Entities are distributed
between different Context Brokers and/or Context Sources and this has to
be taken into account when applying any kind of filters (q, geoQ,
scopeQ, Attributes etc.). If false it is expected that Context
Broker and/or Context Source always have complete Entities, which allows
applying filters locally.
|
|
5.2.24 EntityTypeList
This type represents the data needed to define the entity type list representation as mandated by clause 4.5.10.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.24‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
1
|
URI that is unique within the system scope. Identifier for the entity
type list
|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "EntityTypeList"
|
1
|
JSON-LD @type
|
typeList
|
String[]
|
1
|
List containing the entity type names
|
5.2.25 EntityType
This type represents the data needed to define the elements of the detailed entity type list representation as mandated by clause 4.5.11.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.25‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
1
|
Fully Qualified Name (FQN) of the entity type being described
|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "EntityType"
|
1
|
JSON-LD @type
|
typeName
|
String
|
1
|
Name of the entity type, short name if contained in @context
|
|
attributeNamenames
|
String[]
|
1
|
List containing the names of attributes that instances of the entity
type can have
|
5.2.26 EntityTypeInfo
This type represents the data needed to define the detailed entity type information representation as mandated by clause 4.5.12.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.26‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
1
|
Fully Qualified Name (FQN) of the entity type being described
|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "EntityTypeInfo"
|
1
|
JSON-LD @type
|
typeName
|
String
|
1
|
Name of the entity type, short name if contained in @context
|
|
entityCount
|
Number
|
Unsigned integer
|
1
|
Number of entity instances of this entity type
|
attributeDetails
|
Attribute[]
|
See data type definition in clause
5.2.28. Attribute with only the elements "id", "type",
"attributeName" and "attributeTypes"
|
1
|
List of attributes that entity instances with the specified entity type
can have
|
5.2.27 AttributeList
This type represents the data needed to define the attribute list representation as mandated by clause 4.5.13.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.27‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
1
|
URI that is unique within the system scope. Identifier for the attribute
list
|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "AttributeList"
|
1
|
JSON-LD @type
|
attributeList
|
String[]
|
1
|
List containing the attribute names
|
5.2.28 Attribute
This type represents the data needed to define the attribute information needed as:
- part of the entity type information representation as mandated by clause 4.5.12;
- the detailed attribute list representation as mandated by clause 4.5.14;
- the attribute information representation as mandated by clause 4.5.15.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.28‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
1
|
Full URI of attribute name
|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "Attribute"
|
1
|
JSON-LD @type
|
attributeName
|
String
|
1
|
Name of the attribute, short name if contained in @context
|
|
attributeCount
|
Number
|
Unsigned integer
|
0..1
|
Number of attribute instances with this attribute name
|
attributeTypes
|
String[]
|
0..1
|
List of attribute types (e.g. Property, Relationship,
GeoProperty) for which entity instances exist, which contain an
attribute with this name
|
|
typeNames
|
String[]
|
0..1
|
List of entity type names for which entity instances exist containing
attributes that have the respective name
|
5.2.29 Feature
This data type represents a spatially bounded Entity in GeoJSON format, as mandated by IETF RFC 7946 [8]. The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.29‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
1
|
Entity ID
|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "Feature"
|
1
|
GeoJSON Type
|
geometry
|
GeoJSON Object
|
The value field from the matching GeoProperty (as specified in clause
4.5.16) or null
|
1
|
null if no matching GeoProperty
|
properties
|
FeatureProperties
|
See data type definition
|
1
|
List of attributes as mandated by clause
5.2.31
|
@context
|
URI, JSON Object, or JSON Array
|
See [2], section 5.1.
|
0..1
|
JSON-LD @context. This field is only present if requested in the
payload by the HTTP Prefer Header (IETF RFC 7240 [26])
|
5.2.30 FeatureCollection
This data type represents a list of spatially bounded Entities in GeoJSON format, as mandated by IETF RFC 7946 [8]. The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.30‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "FeatureCollection"
|
1
|
GeoJSON Type
|
features
|
Feature[]
|
See data type definition
|
1..N
|
In the case that no matches are found, features will be an empty
array
|
@context
|
URI, JSON Object, or JSON Array
|
See [2], section 5.1.
|
0..1
|
JSON-LD @context. This field is only present if requested in the
payload by the HTTP Prefer Header (IETF RFC 7240 [26])
|
5.2.31 FeatureProperties
This data type represents the type and the associated attributes (Properties and Relationships) of an Entity in GeoJSON format.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
type
|
String or String[]
|
Entity Type
|
1
|
Entity Type (or JSON array, in case of Entities with multiple Entity
Types). Both short hand string (type name) or URI are allowed.
|
<Property name>
|
Property or Property[], see note 1.
|
See data type definition in clause 5.2.5
|
0..N
|
Property as mandated by clause
4.5.2.
|
GeoProperty or GeoProperty[], see note 1.
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.7
|
0..N
|
GeoProperty as mandated by clause
4.5.2.
|
|
LanguageProperty or LanguageProperty[], see note 1.
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.32
|
0..N
|
LanguageProperty as mandated by clause
4.5.18.
|
|
JsonProperty or JsonProperty[] see note 1.
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.38
|
0..N
|
JsonProperties as mandated by clause
4.5.24.
|
|
VocabProperty or VocabProperty[], see note 1.
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.35
|
0..N
|
VocabProperty as mandated by clause
4.5.20.
|
|
ListProperty or ListProperty[], see note 1.
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.36
|
0..N
|
ListProperty as mandated by clause
4.5.21.
|
|
<Relationship name>
|
Relationship or Relationship[], see note 2.2
|
See data type definition in clause
5.2.6
|
0..N
|
Relationship as mandated by clause
4.5.3.
|
ListRelationship or ListRelationship[], see note 2.
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.37
|
0..N
|
ListRelationship as mandated by clause
4.5.22.
|
|
NOTE 1:
For
each
Property
(or
subclass
of
Property
)
identified
by
the
same
Property
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
NOTE 2:
For
each
Relationship
(or
subclass
of
Relationship
)
identified
by
the
same
Relationship
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
|
||||
5.2.32 LanguageProperty
This type represents the data needed to define a LanguageProperty as mandated by clause 4.5.18. Note that in case of concise representation, the type can be omitted (see clause 4.5.18.3).
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.32‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
type
|
string
|
It shall be equal to "LanguageProperty"
|
1
|
Node type.
|
languageMap
|
JSON object
|
A set of key-value pairs whose keys shall be strings representing IETF
RFC 5646 [28]
language codes and whose values shall be JSON strings or arrays of JSON
strings
|
1
|
String Property Values defined in multiple natural languages.
|
datasetId
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
0..1
|
It allows identifying a set or group of property values.
|
expiresAt
|
String
|
DateTime (see clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System temporal Property representing the expiration date for the
storage of the LanguageProperty. See clause
4.22
|
observedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
valueType
|
String
|
It shall be equal to “langString” (see note 1)
|
0..1
|
The native JSON-LD @type for the languageMap attribute.It
shall align with the RDF datatype [33].
|
<Property name>
|
Property or Property[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clauses 5.2.5
|
0..N
|
Properties of the LanguageProperty.
|
GeoProperty
or GeoProperty[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.7
|
0..N
|
GeoProperties of the LanguageProperty.
|
|
LanguageProperty or LanguageProperty[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.32
|
0..N
|
LanguageProperties of the LanguageProperty.
|
|
JsonProperty or JsonProperty[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.38
|
0..N
|
JsonProperties of the LanguageProperty.
|
|
VocabProperty or VocabProperty[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.35
|
0..N
|
VocabProperties of the LanguageProperty.
|
|
ListProperty
or ListProperty[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.36
|
0..N
|
ListProperties of the LanguageProperty.
|
|
<Relationship name>
|
Relationship
or Relationship[] (see note 3)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.6
|
0..N
|
Relationships of the LanguageProperty.
|
ListRelationship or ListRelationship[] (see note 3)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.37
|
0..N
|
ListRelationships of the LanguageProperty.
|
|
NOTE 1:
1:
The
assigned
@type
for
language
tagged
strings
is
datatype
URI:
http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#langString
[34]
NOTE 2:
For
each
Property
(or
subclass
of
Property
)
identified
by
the
same
Property
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
NOTE 3:
For
each
Relationship
(or
subclass
of
Relationship
)
identified
by
the
same
Relationship
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
|
||||
The following output only members (defined by Table 5.2.32-2) of the LanguageProperty data structure are also defined. They are read-only and shall be generated by NGSI-LD implementations. They shall not be provided by Context Producers. In the event that they are provided (in update or create operations) NGSI-LD implementations shall ignore them.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
createdAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated creation timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
deletedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
It is only used in notifications reporting deletions
|
0..1
|
System generated deletion timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
instanceId
|
String
|
Valid URI. Only used in temporal representation of LanguageProperties
|
0..1
|
URI uniquely identifying a LanguageProperty instance as mandated by clause
4.5.7.
|
modifiedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated last modification timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
previousLanguageMap
|
JSON object
|
A set of key-value pairs whose keys shall be strings representing IETF
RFC 5646 [28]
language codes and whose values shall be JSON strings.
Only used in Notifications, if the showChanges option is
explicitly requested
|
0..1
|
Previous Language Property's languageMap.
|
5.2.33 EntitySelector
This type selects which entity or group of entities are queried or subscribed to by Context Consumers. Entities can be specified by their id, Entity Types or group of Entity IDs (as a regular expression pattern mandated by IEEE 1003.2™ [11]).
The JSON members shall follow the indications provided in Table 5.2.33‑1. id takes precedence over idPattern.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String or String[]
|
Valid URI(s)
|
0..1
|
Entity identifier(s).
|
idPattern
|
String
|
Regular expression as per IEEE 1003.2™ [11]
|
0..1
|
A regular expression which denotes a pattern that shall be matched by
the provided or subscribed Entities.
|
type
|
String
|
A valid type selection string as per clause
4.17. To indicate a request for all Entities (with implied local
scope), "*" is
also allowed as a value.
|
1
|
Selector of Entity Type(s); If type is specified as "*", implying local scope, local scope shall not be explicitly set to be false (clause 5.5.13) for the execution of the corresponding operation. |
5.2.34 RegistrationManagementInfo
This type represents the data to alter the default behaviour of a Context Broker when making a distributed operation request to a registered Context Source. The supported JSON members shall follow the indications provided in Table 5.2.34‑1. Brokers may override these recommendations.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
localOnly
|
Boolean
|
0..1
|
If localOnly=true then distributed operations associated to this
Context Source Registration will act
only on data held directly by the registered Context
Source itself (see clause
4.3.6.4).
|
|
cacheDuration
|
String
|
String representing a duration in ISO 8601 [17] format
|
0..1
|
Minimal period of time which shall elapse between two consecutive context information consumption operations (as defined in clause 5.7) related to the same context data will occur. If the cacheDurationlatency period has not been reached, a cached value for the entity or its attributes shall be returned where available. |
timeout
|
Number
|
Greater than 0
|
0..1
|
Maximum period of time in milliseconds which may elapse before a
forwarded request is assumed to have failed.
|
cooldown
|
Number
|
Greater than 0
|
0..1
|
Minimum period of time in milliseconds which shall elapse before attempting to make a subsequent forwarded request to the same endpoint after failure. If requests are received before the cooldown period has expired, a timeout error response for the registration is automatically returned. |
5.2.35 VocabProperty
This type represents the data needed to define a VocabProperty as mandated by clause 4.5.20. In case of concise representation, the type can be omitted (see clause 4.5.20.3).
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.35‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "VocabProperty"
|
1
|
Node type.
|
vocab
|
String or string[]
|
1
|
String Values which shall be type coerced to URIs based on the supplied
@context.
|
|
datasetId
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
0..1
|
It allows identifying a set or group of property values.
|
expiresAt
|
String
|
DateTime (see clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System temporal Property representing the expiration date for the
storage of the VocabProperty. See clause
4.22
|
observedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
valueType
|
String
|
0..1
|
The native JSON-LD @type for the vocab attribute. A String
Value which shall be type coerced to a URI based on the supplied
@context.
|
|
<Property name>
|
Property
or Property[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definitions in clauses 5.2.5
|
0..N
|
Properties of the VocabProperty.
|
GeoProperty
or GeoProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.7
|
0..N
|
GeoProperties of the VocabProperty.
|
|
LanguageProperty or LanguageProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.32
|
0..N
|
LanguageProperties of the VocabProperty.
|
|
JsonProperty or JsonProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.38
|
0..N
|
JsonProperties of the VocabProperty.
|
|
VocabProperty or VocabProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.35
|
0..N
|
VocabProperties of the VocabProperty.
|
|
ListProperty
or ListProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.36
|
0..N
|
ListProperties of the VocabProperty.
|
|
<Relationship name>
|
Relationship
or Relationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.6
|
0..N
|
Relationships of the VocabProperty.
|
ListRelationship or ListRelationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.37
|
0..N
|
ListRelationships of the VocabProperty.
|
|
NOTE 1:
For
each
Property
(or
subclass
of
Property
)
identified
by
the
same
Property
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
NOTE 2:
For
each
Relationship
(or
subclass
of
Relationship
)
identified
by
the
same
Relationship
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
|
||||
The following output only members (defined by Table 5.2.35-2) of the VocabProperty data structure are also defined. They are read-only and shall be generated by NGSI-LD implementations. They shall not be provided by Context Producers. In the event that they are provided (in update or create operations) NGSI-LD implementations shall ignore them.
name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
createdAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated creation timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
deletedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
It is only used in notifications reporting deletions
|
0..1
|
System generated deletion timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
instanceId
|
String
|
Valid URI. Only used in temporal representation of VocabProperties
|
0..1
|
URI uniquely identifying a VocabProperty instance as mandated by clause
4.5.7.
|
modifiedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated last modification timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
previousVocab
|
String or String[]
|
Only used in Notifications
|
0..1
|
Previous VocabProperty's vocab.
|
5.2.36 ListProperty
This type represents the data needed to define a ListProperty as mandated by clause 4.5.21. Note that in case of concise representation, the type can be omitted (see clause 4.5.21.3).
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.36‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to"ListProperty"
|
1
|
Node type.
|
valueList
|
An array of JSON values as defined by IETF RFC 8259 [6]
|
See NGSI-LD Value definition in clause
3.1
|
1
|
Ordered array of Property Values.
|
datasetId
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
0..1
|
It allows identifying a set or group of property list values
|
expiresAt
|
String
|
DateTime (see clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System temporal Property representing the expiration date for the
storage of the ListProperty. See clause
4.22
|
observedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
datasetId
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
0..1
|
It allows identifying a set or group of property list values.
|
valueType
|
String
|
0..1
|
The native JSON-LD @type for the valueList attribute. A
String Value which shall be type coerced to a URI based on the supplied
@context.
|
|
<Property name>
|
Property
or Property[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clauses 5.2.5
|
0..N
|
Properties of the ListProperty.
|
GeoProperty
or GeoProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.7
|
0..N
|
GeoProperties of the ListProperty.
|
|
LanguageProperty
or LanguageProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.32
|
0..N
|
LanguageProperties of the ListProperty.
|
|
JsonProperty or JsonProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.38
|
0..N
|
JsonProperties of the ListProperty.
|
|
VocabProperty or VocabProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.35
|
0..N
|
VocabProperties of the ListProperty.
|
|
ListProperty
or ListProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.36
|
0..N
|
ListProperties of the ListProperty.
|
|
<Relationship name>
|
Relationship
or Relationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.6
|
0..N
|
Relationships of the ListProperty.
|
ListRelationship or ListRelationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.37
|
0..N
|
ListRelationships of the ListProperty.
|
|
NOTE 1:
For
each
Property
(or
subclass
of
Property
)
identified
by
the
same
Property
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
NOTE 2:
For
each
Relationship
(or
subclass
of
Relationship
)
identified
by
the
same
Relationship
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
|
||||
The following output only members (defined by Table 5.2.36-2) of the ListProperty data structure are also defined. They are read-only and shall be generated by NGSI-LD implementations. They shall not be provided by Context Producers. In the event that they are provided (in update or create operations) NGSI-LD implementations shall ignore them.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
createdAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated creation timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
deletedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
It is only used in notifications reporting deletions
|
0..1
|
System generated deletion timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
instanceId
|
String
|
Valid URI. Only used in temporal representation of ListProperties
|
0..1
|
URI uniquely identifying a ListProperty instance as mandated by clause
4.5.7.
|
modifiedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated last modification timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
previousValueList
|
An array of JSON values as defined by IETF RFC 8259 [6]
|
See NGSI-LD Value definition in clause
3.1
|
1
|
Ordered array of previous Property Values.
|
5.2.37 ListRelationship
This type represents the data needed to define a ListRelationship as mandated by clause 4.5.22. Note that in case of concise representation, the type can be omitted (see clause 4.5.22.3) and the objectList may also be represented as an ordered array of Strings.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.37‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "ListRelationship"
|
1
|
Node type
|
objectList
|
JSON Object[] or
String[]
|
In the normalized form, each array element holds a JSON object containing a single Attribute with a key called "object"and where the value is a valid URI.
In the concise form, each string in the array holds a valid URI
|
1
|
Ordered array of Relationship target objects.
|
datasetId
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
0..1
|
It allows identifying a set or group of relationship list objects.
|
expiresAt
|
String
|
DateTime (see clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System temporal Property representing the expiration date for the
storage of the ListRelationship. See clause
4.22
|
objectType
|
String or String []
|
0..1
|
Node Type of the Relationship's target object.
Both short hand string(s) (type name) or URI(s) are allowed.
|
|
observedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
<Property name>
|
Property or Property[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause 5.2.5
|
0..N
|
Properties of the ListRelationship.
|
GeoProperty
or GeoProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.7
|
0..N
|
GeoProperties of the ListRelationship.
|
|
LanguageProperty or LanguageProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.32
|
0..N
|
LanguageProperties of the ListRelationship.
|
|
JsonProperty or JsonProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.38
|
0..N
|
JsonProperties of the ListProperty.
|
|
VocabProperty or VocabProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.35
|
0..N
|
VocabProperties of the ListRelationship.
|
|
ListProperty
or ListProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.36
|
0..N
|
ListProperties of the ListRelationship.
|
|
<Relationship name>
|
Relationship or Relationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.6
|
0..N
|
Relationships of the ListRelationship.
|
ListRelationship or ListRelationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.37
|
0..N
|
ListRelationships of the ListRelationship.
|
|
NOTE 1:
For
each
Property
(or
subclass
of
Property
)
identified
by
the
same
Property
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
NOTE 2:
For
each
Relationship
(or
subclass
of
Relationship
)
identified
by
the
same
Relationship
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
|
||||
The following output only members (defined by Table 5.2.37-2) of the ListRelationship data structure are also defined. They are read-only and shall be generated by NGSI-LD implementations. They shall not be provided by Context Producers. In the event that they are provided (in update or create operations) NGSI-LD implementations shall ignore them.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
createdAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated creation timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
deletedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
It is only used in notifications reporting deletions
|
0..1
|
System generated deletion timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
entityList
|
Entity[]
|
See datatype definition in clause 5.2.4
Only used in Linked Entity Retrieval,
if the join=inline option is explicitly requested
|
0..1
|
An array of inline Entities obtained by Linked Entity retrieval, corresponding to
the ListRelationship's target objects See clause
4.5.23.2.
|
instanceId
|
String
|
Valid URI. Only used in temporal representation of
ListRelationships
|
0..1
|
URI uniquely identifying a ListRelationship instance as mandated
by clause
4.5.8.
|
modifiedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause 4.6.3) |
0..1
|
System generated last modification timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
previousObjectList
|
JSON Object[] or
String[]
|
In the normalized form, each array element holds a JSON object containing a containing a single Attribute with a key called "object"and where the value is a valid URI.
In the concise form, each string in the array holds a valid URI
|
0..1
|
Ordered array of previous Relationship target objects.
|
5.2.38 JsonProperty
This type represents the data needed to define a JsonProperty as mandated by clause 4.5.24. In case of concise representation, the type can be omitted (see clause 4.5.24.3).
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.38‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "JsonProperty"
|
1
|
Node type.
|
json
|
JSON
|
1
|
Raw unexpandable JSON which shall not be interpreted as JSON-LD using
the supplied @context.
|
|
datasetId
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
0..1
|
It allows identifying a set or group of property values.
|
expiresAt
|
String
|
DateTime (see clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System temporal Property representing the expiration date for the
storage of the JsonProperty. See clause
4.22
|
observedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
Timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
valueType
|
String
|
0..1
|
The native JSON-LD @type for the json attribute. A String
Value which shall be type coerced to a URI based on the supplied
@context.
|
|
<Property name>
|
Property
or Property[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definitions in clauses 5.2.5
|
0..N
|
Properties of the JsonProperty.
|
GeoProperty
or GeoProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.7
|
0..N
|
GeoProperties of the JsonProperty.
|
|
LanguageProperty or LanguageProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.32
|
0..N
|
LanguageProperties of the JsonProperty.
|
|
JsonProperty or JsonProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.38
|
0..N
|
JsonProperties of the JsonProperty.
|
|
VocabProperty or VocabProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.35
|
0..N
|
VocabProperties of the JSONPropertry.
|
|
ListProperty
or ListProperty[] (see note 1)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.36
|
0..N
|
ListProperties of the JsonProperty.
|
|
<Relationship name>
|
Relationship
or Relationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.6
|
0..N
|
Relationships of the JsonProperty.
|
ListRelationship or ListRelationship[] (see note 2)
|
See datatype definition in clause
5.2.37
|
0..N
|
ListRelationships of the JsonProperty.
|
|
NOTE 1:
For
each
Property
(or
subclass
of
Property
)
identified
by
the
same
Property
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
NOTE 2:
For
each
Relationship
(or
subclass
of
Relationship
)
identified
by
the
same
Relationship
name,
there
can
be
one
or
more
instances
separated
by
datasetId.
|
||||
The following output only members (defined by Table 5.2.38-2) of the JsonProperty data structure are also defined. They are read-only and shall be generated by NGSI-LD implementations. They shall not be provided by Context Producers. In the event that they are provided (in update or create operations) NGSI-LD implementations shall ignore them.
name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
createdAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated creation timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
deletedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
It is only used in notifications reporting deletions
|
0..1
|
System generated deletion timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
instanceId
|
String
|
Valid URI. Only used in temporal representation of JsonProperties
|
0..1
|
|
modifiedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
0..1
|
System generated last modification timestamp. See clause
4.8.
|
previousJson
|
JSON
|
Only used in Notifications
|
0..1
|
Previous JsonProperty's json.
|
5.2.39 EntityMap
This type represents the data needed to define an EntityMap as mandated by clause 4.5.25.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.39‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
1
|
EntityMap ID.
|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "EntityMap"
|
1
|
Node type.
|
expiresAt
|
String
|
DateTime (see clause
4.6.3)
|
1
|
Expiration date for the EntityMap.
|
The following output only members (defined by Table 5.2.39-2) of the EntityMap data structure are also defined. They are read-only and shall be generated by NGSI-LD implementations. They shall not be provided by ContextConsumers. In the event that they are provided in update operations NGSI-LD implementations shall ignore them.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
entityMap
|
JSON
|
A set of key-value pairs whose keys shall be strings representing Entity
ids and whose values shall be an array holding every CSourceRegistration
id which is relevant to the ongoing Context Information Consumption
request (see clause
4.21).
The key "@none" shall be used to refer to
an Entity that is held locally
|
1
|
System generated mapping of Entities to CSourceRegistrations.
|
linkedMaps
|
JSON
|
A set of key-value pairs whose keys shall be strings representing
CSourceRegistration ids which are relevant to the ongoing Context
Information request and whose values shall represent the associated
EntityMap id used by the ContextSource.
|
1
|
System generated mapping of Context CSourceRegistrations to a URI
indicating which EntityMaps was used by the Context Source.
|
5.2.40 Context Source Identity
This type represents the data uniquely identifying a Context Source, and if the Context Source supports multi-tenancy (see clause 4.14) uniquely identifying a Tenant within that Context Source.
The supported JSON members shall follow the requirements provided in Table 5.2.40‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restriction
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
1
|
Context Source ID.
|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "ContextSourceIdentity"
|
1
|
Node type.
|
contextSourceExtras
|
JSON
|
0..1
|
Instance specific information relevant to the configuration of the Context Source itself in raw unexpandable
JSON which shall not be interpreted as JSON-LD using the supplied
@context.
|
|
contextSourceUptime
|
String
|
String representing a duration in ISO 8601 [17] format
|
1
|
Total Duration that the Context
Source has been available.
|
contextSourceTimeAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
1
|
Current time observed at the Context
Source. Timestamp See clause
4.8.
|
contextSourceAlias
|
String
|
Non-empty string. Pseudonym field as defined in IETF RFC 7230 [27]
|
1
|
A unique id for a Context Source
which can be used to identify loops.
In the multi-tenancy use case (see clause
4.14), this id shall be identify a specific Tenant within a registered Context Source.
|
5.3 Notification data types
5.3.1 Notification
This datatype represents the parameters that allow building a notification to be sent to a subscriber. How to build this notification is detailed in clause 5.8.6.
The supported JSON members shall follow the indications provided in Table 5.3.1‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
1
|
Notification identifier (JSON-LD @id). It shall be automatically
generated by the implementation.
|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "Notification"
|
1
|
JSON-LD @type.
|
subscriptionId
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
1
|
Identifier of the subscription that originated the notification.
|
notifiedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (clause
4.6.3)
|
1
|
Timestamp corresponding to the instant when the notification was
generated by the system.
|
data
|
NGSI-LD Entity[] or FeatureCollection
|
1
|
The content of the notification as NGSI-LD Entities.
See clause 5.2.4.
If the notification has been triggered from a Subscription that has the
notification.
endpoint.accept field set to application/geo+json then data is returned as a
FeatureCollection. In this case, if the
notification.endpoint.receiverInfo contains the key "Prefer" and it is set to the value "body=json", then the FeatureCollection
will not contain an @context field.
If endpoint.accept is not set or holds another value then
Entity[] is returned.
|
5.3.2 CSourceNotification
This datatype represents the parameters that allow building a Context Source Notification to be sent to a subscriber. How to build this notification is detailed in clause 5.11.7.
The supported JSON members shall follow the indications provided in Table 5.3.2‑1.
Name
|
Data Type
|
Restrictions
|
Cardinality
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
id
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
1
|
CSource notification identifier (JSON-LD @id).
|
type
|
String
|
It shall be equal to "ContextSourceNotification"
|
1
|
JSON-LD @type.
|
subscriptionId
|
String
|
Valid URI
|
1
|
Identifier of the subscription that originated the notification.
|
notifiedAt
|
String
|
DateTime (see clause
4.6.3)
|
1
|
Timestamp corresponding to the instant when the notification was
generated by the system.
|
data
|
CSource
Registration[]
|
1
|
The content of the notification as NGSI-LD CSourceRegistrations. See clause
5.2.9.
|
|
triggerReason
|
String
|
TriggerReasonEnumeration (see clause
5.3.3)
|
1
|
Indicates whether the CSources in the CSourceRegistration(s) in data are
newly matching (initial notification or creation), have been updated
(but still match) or do not match any longer.
|
5.3.3 TriggerReasonEnumeration
The enumeration can take one of the following values:
- "newlyMatching" - describes the case that the notified Context Source Registration(s) newly match(es) the identified subscription. This value is used in the first notification and whenever a new Context Source Registration matching the Subscription has been registered, or an existing Context Source Registration that did not match before has been updated in such a way that it matches now.
- "updated" - describes the case that the notified Context Source Registration that was part of a previous notification has been updated, but still matches the Subscription.
- "noLongerMatching" - describes the case that the notified Context Source Registration that was part of a previous notification no longer matches the Subscription, i.e. as a result of an update or because it was deleted.
5.4 NGSI-LD Fragments
When updating NGSI-LD elements (Entities, Attributes, Context Source Registrations or Subscriptions) it is necessary to have a means of describing a set of modifications to their content.
An NGSI-LD Fragment is a JSON Merge Patch document [16] and [i.10] which describes changes to be made to a target JSON-LD document using a syntax that closely mimics the document being modified.
An NGSI-LD Fragment is a JSON-LD Object which shall include the following members:
- id (optional for certain bindings where it can be determined from the operation signature). It shall be equal to the id of the target (mutated) NGSI-LD element. Attribute Fragments do not contain explicit ids.
- type (optional for certain bindings where it can be determined from the operation signature). It shall contain the Type name(s) of the target NGSI-LD element.
- A member (following the same data representation and nesting structure) for each new member to be added to the target NGSI-LD element.
- A member (following the same data representation and nesting structure) for each new member to be modified in the target NGSI-LD element, which value shall correspond to the new member value to be given.
{"id": "urn:ngsi-ld:Subscription:MySubscription","type": "Subscription","endpoint": {"uri": "http://example.org/newNotificationEndPoint"}}
- A member (following the same data representation and nesting structure) with value equal to an NGSI-LD Null shall cause for the member to be removed from the target NGSI-LD element.
{"id": "urn:ngsi-ld:TemperatureSensor:001","type": "TemperatureSensor","batteryLevel": {"type": "Property","value": 7,"observedAt": "2022-03-14T12:51:02.000Z","providedBy": "urn:ngsi-ld:null"},"uncharged" : {"type": "Property","value": "urn:ngsi-ld:null"}}
5.5 Common Behaviours
5.5.1 Introduction
This clause defines common behaviours for the API operations.
When comparing URIs, implementations shall follow the recommendations of IETF RFC 3986 [5], section 6.
5.5.2 Error types
Table 5.5.2‑1 details a list of error types defined by NGSI-LD. The particular conditions under which error type shall be raised are defined when describing each operation supported by the API.
Error Type
|
Description
|
|---|---|
https://uri.etsi.org/ngsi-ld/errors/InvalidRequest
|
The request associated to the operation is syntactically invalid or
includes wrong content
|
https://uri.etsi.org/ngsi-ld/errors/BadRequestData
|
The request includes input data which does not meet the requirements of
the operation
|
https://uri.etsi.org/ngsi-ld/errors/AlreadyExists
|
The referred element already exists
|
https://uri.etsi.org/ngsi-ld/errors/OperationNotSupported
|
The operation is not supported
|
https://uri.etsi.org/ngsi-ld/errors/ResourceNotFound
|
The referred resource has not been found
|
https://uri.etsi.org/ngsi-ld/errors/InternalError
|
There has been an error during the operation execution
|
https://uri.etsi.org/ngsi-ld/errors/TooComplexQuery
|
The query associated to the operation is too complex and cannot be
resolved
|
https://uri.etsi.org/ngsi-ld/errors/TooManyResults
|
The query associated to the operation is producing so many results that
can exhaust client or server resources. It should be made more
restrictive
|
https://uri.etsi.org/ngsi-ld/errors/LdContextNotAvailable
|
A remote JSON-LD @context referenced in a request cannot be retrieved by
the NGSI-LD Broker and expansion or compaction cannot be performed
|
https://uri.etsi.org/ngsi-ld/errors/NoMultiTenantSupport
|
The NGSI-LD API implementation does not support multiple tenants
|
https://uri.etsi.org/ngsi-ld/errors/NonexistentTenant
|
The addressed tenant does not exist
|
5.5.3 Error response payload body
When reporting errors back to clients, NGSI-LD implementations shall generate a JSON object in accordance with IETF RFC 7807 [10], section 3.1, including, at least the following terms:
- type: Error type as per clause 5.5.2.
- title: Error title which shall be a short string summarizing the error.
- detail: A detailed message that should convey enough information about the error.
Even though IETF RFC 7807 [10] defines a specific MIME type for error payloads, NGSI-LD implementations shall use the standard JSON MIME type ("application/json") when reporting errors, so that old clients or existing tools are not broken.
{"type": "https://uri.etsi.org/ngsi-ld/errors/ResourceNotFound","title": "Resource not found.","detail": "urn:ngsi-ld:Device:widget001 was not found","status": 404,"instance": "urn:ngsi-ld:Device:widget001"}
5.5.4 General NGSI-LD validation
All the operations that take a JSON-LD document as input shall process such JSON-LD document as follows:
- If the request payload body is not a valid JSON document then an error of type InvalidRequest shall be raised.
- If the data included by the JSON-LD document is not syntactically correct, according to the @context or the API data type definitions, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- A Context Producer may supply an additional hint regarding the overall validity of the payload body and the version of the NGSI-LD specification that the API datatype definitions conform to. When receiving such an annotated context production request, a Context Broker that it is only partially capable of interpreting the datatypes held within the payload body may use this information to amend the data held within the payload through applying fallbacks (see clause 4.3.6.8) prior to validation.
- Any attempt to use "urn:ngsi-ld:null" as a first level member value ("<key>": "urn:ngsi-ld:null"), with the exception of NGSI-LD Fragments (see clause 5.4) used in partial update and merge operations (as mandated by clause 5.5.8 and clause 5.5.12) or to represent deleted Properties in concise representation as part of notifications, shall result in an error of type BadRequestData.
- Any attempt to use "urn:ngsi-ld:null" as the right-hand side of value in a Property, as the right-hand side of object in a Relationship or to use {"@none": "urn:ngsi-ld:null"} as the right-hand side of languageMap, with the exception of NGSI-LD Fragments (see clause 5.4) used in update and merge operations (as mandated by clause 5.5.8 and clause 5.5.12) and the representation of deleted Properties, Relationships or Language Properties in notifications and the temporal evolution, shall result in an error of type BadRequestData.
- Any attempt to use "urn:ngsi-ld:null" as the value of a key value pair within a JSON object, which is the right-hand side of the value of a Property, with the exception of NGSI-LD Fragments used in merge operations (see clause 5.5.12), shall result in an error of type BadRequestData.
5.5.5 Default @context assignment
If the input provided by an API client does not include any @context, then the implementation shall at minimum assign the Core @context to such an input. In addition, the Context Broker implementation may allow configuring a default user @context (with default terms), to be used when no user @context is provided. The Core @context shall always take precedence.
5.5.6 Operation execution and generic error handling
When executing an operation if an unexpected error happens and the operation cannot be completed, implementations shall raise an error of type InternalError. This includes, as well, situations such as database timeouts, etc.
If the NGSI-LD endpoint is not capable of executing the requested operation, an error of type OperationNotSupported shall be raised. This may happen in a distributed architecture where a Context Broker might not be able to store Entities (only to forward queries to Context Sources), and as a result, certain operations such as "Create Entity" might not be supported.
When a query operation is so complex that cannot be resolved by an NGSI-LD system, implementations shall raise an error of type TooComplexQuery.
When a query operation is producing so many results that can potentially exhaust client or server resources, or it can be just impractical to be managed, implementations shall raise an error of type TooManyResults. The threshold conditions used as criteria to raise such error is up to each implementation.
When a remote JSON-LD @context referenced by an incoming request is not available, implementations shall raise an error of type LdContextNotAvailable. If the remote JSON-LD @context is invalid, implementations shall raise an error of type BadRequestData.
5.5.7 Term to URI expansion or compaction
NGSI-LD API operations allow clients to use short-hand strings as non-qualified names, particularly for Property, Relationship or Type names and VocabProperty values. For instance, an API client can refer to the term "Vehicle" as a non-qualified type name. When executing API update-related operations, NGSI-LD systems shall expand terms to URIs, in order to obtain and store Fully Qualified Names. Likewise, when executing query-related operations, NGSI-LD systems shall compact URIs (Fully Qualified Names) to short terms in order to provide short-hand strings to context consumers.
The term to URI expansion or compaction shall be performed using a @context as described by the JSON-LD specification [2] (section 5.1), and in clause 4.4. In the absence of a user @context, the term expansion or compaction shall be performed according to clause 5.5.5.
For the avoidance of doubt, the @context used to perform compaction or expansion of terms shall be the one provided by each API call (or the default @context in its absence), and not any other @context which might have been supplied previously. For instance, when performing "Query Entity" operations (clause 5.7.2), the @context used to perform URI expansion and compaction shall be the one provided by the request.
In case of HTTP binding via GET (clause 6.4.3.2) of the "Query Entity" operation, this means using the JSON-LD Link Header as described by the JSON-LD specification [2], section 6.2. In case of HTTP binding via POST (clause 6.23.3.1), of the "Query Entity" operation, this means giving the @context either via Link Header or within the payload body, depending on the Content-Type Header being "application/json" or "application/ld+json", respectively.
It is important to warn users that updating a @context could lead to behaviour that might be perceived as inconsistent. If, for instance, a fully qualified name that qualified a given short-hand name is changed, from that moment onwards, the short-hand name is referencing a different Attribute. This will effectively change the results of queries that use the given short name, possibly not giving back anymore the expected set of results.
Moreover, this user @context shall not:
- Contain JSON-LD Scoped Contexts (see [2], section 4.1.8).
- Be embedded into NGSI-LD Attributes, i.e. there cannot be parts of the user @context other than at the top level of the NGSI-LD document.
Parts of user @context that are not following the two points above should result in an error of type BadRequestData, because JSON-LD Scoped Contexts and nested embedded @context could be used to modify terms defined in the Core @context or to reshape NGSI-LD Elements during the expansion of terms.
As the Core @context is protected and cannot be overridden, when performing term to URI expansion or compaction, implementations shall always consider the Core @context as having absolute precedence, regardless of the position of the Core @context in the @context array of elements. Nonetheless, NGSI-LD data providers may use appropriate term prefixing to ensure that a proper term to URI expansion or compaction is performed.
At compaction time, in the event that no matching term is found in the current @context, implementations shall render Fully Qualified Names.
5.5.8 Partial Update Patch Behaviour
The Partial Update Patch procedure modifies an existing NGSI-LD element by overwriting the data at the Attribute level, replacing it with the data provided in the NGSI-LD Fragment.
When updating NGSI-LD elements (Entities, Context Source Registrations or Context Subscriptions) using NGSI-LD Fragments, implementations shall determine the exact set of changes being requested by comparing the content of the provided Fragment (patch) against the current content (a JSON-LD object) of the target element.
With respect to update operations, implementations shall perform an algorithm equivalent to the one described below (adapted from IETF RFC 7396 [16]), in order to observe the name to URI expansion rules and the JSON-LD null processing):
- For each member of the Fragment perform the term to URI expansion.
- If the provided Fragment (a JSON Merge Patch document) contains members that do not appear within the target (their URIs do not match), those members are added to the target.
- For each member of the Fragment contained by the target, the target member value is replaced by the value given in the Fragment. In the case of a member representing a reified Property or Relationship including a datasetId, such member is only replaced if the datasetId is the same, otherwise the member of the Fragment is added as a new instance to the target. If no datasetId is present, the default Attribute instance is targeted and replaced if present and otherwise added. In case of a member type (of an entity) in Entity Fragments, all included Entity Types are added, if they are not already contained in the type member of the target.
- For each member of the Fragment, whose value is an NGSI-LD Null, contained by the target, the target member is deleted. In the case of deleting a specific Attribute instance with a datasetId, the handling shall be in accordance with the description found in clause 5.6.5. A datasetId cannot be deleted by setting it to the value "urn:ngsi-ld:null".
{"temperature": {"type": "Property","value": 25,"unitCode": "CEL""observedAt": "2022-03-14T01:59:26.535Z"}}
{"type": "Property","value": 100,"observedAt": "2022-03-14T13:00:00.000Z"}
5.5.9 Pagination Behaviour
When resolving NGSI-LD Query operations, NGSI-LD Systems shall exhibit the behaviour described by the present clause:
- Let Md be equal to the default maximum number of NGSI-LD Elements to be retrieved by the API during each query pagination iteration, as defined by the NGSI-LD implementation.
- Let Mc be equal to the maximum number of NGSI-LD Elements to be retrieved as requested by the NGSI-LD Client. If Mc is undefined then it shall be equal to Md.
- Let L be the maximum number of NGSI-LD Elements to be retrieved by the API during each query pagination iteration. L shall be equal to Mc.
- During query execution and for each pagination iteration, the query resolution mechanisms of the NGSI-LD System shall ensure that only up to a maximum of L NGSI-LD Elements are retrieved and returned to the NGSI-LD client, i.e. the maximum page size per iteration shall not overpass L. Nonetheless, implementations shall take care of not overpassing a maximum size of response payload body, which, in practice, implies that, under certain circumstances, the number of Elements retrieved per page can be lower than L.
- After the retrieval of each page (containing at most L NGSI-LD Elements) implementations shall check whether there are pending NGSI-LD Elements to be retrieved in the context of the current query. If that is the case, implementations shall flag NGSI-LD Clients of the existence of such NGSI-LD Elements. Ultimately, the flagging mechanisms used shall depend on each API binding but shall be present as mandated by the present clause.
- When flagging the existence of additional NGSI-LD Elements (pages) pending to be retrieved, generally, implementations shall provide NGSI-LD Clients pointers to get access to both the following page of NGSI-LD Elements and the previous one, according to the current pagination iteration.
- The pointer to the previous page of NGSI-LD Elements shall be included for all pagination iterations excepting the first one, as, obviously, there will be no previous NGSI-LD Elements.
- When the last page of NGSI-LD Elements is reached, only the pointer to the previous page shall be provided to NGSI-LD Clients, so that they can detect that no more NGSI-LD Elements are available.
- The pointers to NGSI-LD Elements shall contain all the parameters needed to allow NGSI-LD Clients to retrieve the next and previous page, without further interactions with the API.
While iterating over a set of pages, there might be changes in the target result set, due to additions or removals of NGSI-LD Elements occurring in between. Implementations may detect those situations and may warn NGSI-LD Clients appropriately. During pagination, the same @context shall be used. An attempt to use a different @context should result in an BadRequestData error.
The general pagination behaviour described in only requires pointers to the following and previous pages, which can be implemented in a completely opaque way. Pagination may also be implemented in a transparent way, giving the Context Consumer more control over the process. In this case, the parameters limit and offset should be used, allowing the Context Consumer to adapt the size of the page using limit and jump to a desired set of elements in the results using offset.
In the case of queries based on Entity maps, the set of Entities considered for the result is fixed with the initial query creating the Entity map. However, the Entity information itself can be dynamic, so filters shall be rechecked before returning results. In the case of split Entities, the Entities in the Entity map can only be considered as candidate Entities, since, at the time of Entity map creation, the Entities have not been aggregated and thus the filters could not be applied. This can only be done when preparing a page for pagination. Thus, Entities not or no longer fitting the query shall be removed from the Entity map during pagination. Pages shall always be filled to the maximum, as long as Entities are available. When using the previous link, the set of Entities on the previous page may not be the same as before, due to dynamic changes resulting in Entities no longer fulfilling the filter criteria of the query. As a result, the first page when going backward, and the last page, when going forward, may have less than the maximum number of Entities.
5.5.10 Multi-Tenant Behaviour
If a Tenant is specified for an NGSI-LD operation, the operation shall only be applied to information related to the specified Tenant. If no Tenant is specified, the operation shall apply to the implicitly existing default Tenant. If a Tenant is explicitly specified, but the system implementing the NGSI-LD API does not support multi-tenancy, an error of type NoMultiTenantSupport should be raised.
In case an operation applies to a Tenant, this information shall also be provided in the response to the operation. This also applies to notifications sent as a result of subscriptions (clauses 5.8 and 5.11).
A Tenant is represented in form of a String. How the Tenant is specified for an API operation is protocol binding specific. How Tenants are created, is implementation-specific.
One implementation option is to support the implicit creation of Tenants. This means that a Tenant is implicitly created when an NGSI-LD operation for creating information targets a new Tenant; this is the case for:
- Create Entity (clause 5.6.1).
- Batch Entity Creation (clause 5.6.7).
- Create or Update Temporal Evolution of an Entity (clause 5.6.11).
- Create Subscription (clause 5.8.1).
- Register Context Source (clause 5.9.2).
- Create Context Source Registration (clause 5.11.2).
All other NGSI-LD operations, e.g. for retrieving, updating, appending or deleting information that target a non-existing Tenant should raise an error of type NonexistentTenant.
If the system implementing the NGSI-LD API does not support multiple Tenants, the attempt to register a Context Source with Tenant information in the Context Source Registration should also result in an error of type NoMultiTenantSupport.
5.5.11 More than one instance of the same Entity in an Entity array
5.5.11.0 Foreword
The following operations operate on an array of entities (as input payload):
- Batch Entity Creation (clause 5.6.7)
- Batch Entity Creation or Update (Upsert) (clause 5.6.8)
- Batch Entity Update (clause 5.6.9)
- Batch Entity Delete (clause 5.6.10)
- Batch Entity Merge (clause 5.6.20)
It is allowed for such an input Entity array to contain more than one instance of the same entity (those instances have identical ids).
In order for such a request to be correctly handled, those instances that have the same id are processed by the Broker in the order they have in the array: the higher the index in the array, the later it will be processed. If the order is altered, the outcome may be altered.
All Entities and Attributes in the batch will get the same modifiedAt timestamp, so it makes sense to distinguish them via the observedAt temporal property.
Implementations shall treat the entity instances as if they had all arrived in separate requests.
The following clauses specify the behaviour in each case.
5.5.11.1 Batch Entity Creation case
The first occurrence of an entity in the input array (the oldest one) is used for the creation of the entity. Any subsequent instance of the same entity is reported as an error (entity already exists) in the response.
5.5.11.2 Batch Entity Creation or Update (Upsert) case
This operation has two modes of operation, with an optional flag to select between the two. The default behaviour is to replace any already existing entities, while the optional behaviour is to update already existing entities. Non existing entities are created in both modes.
If the entity does not yet exist, the first occurrence of an entity is used to create the entity, and subsequent instances of that same entity are used to either replace (default behaviour) or to update (optional behaviour) the entity. These replace or update operations shall be done in chronological order.
Only the entity resulting from merging all of the entity instances, in the correct order, is maintained in the current state (as defined in clause 4.3.1). For Temporal Evolution of Entities (as defined in clause 4.3.1), all entity instances shall be taken into account, in the correct order.
5.5.11.3 Batch Entity Update case
This operation has two modes of operation, with an optional flag to select between the two. The default behaviour is to replace any already existing attributes of the entities, while the optional behaviour is to preserve already existing attributes of the entities.
Brokers shall send separate notifications for each individual update, taking throttling into account.
5.5.11.4 Batch Entity Delete case
The Batch Entity Delete operation has as input an array of Entity IDs, for the entities to be deleted. If an Entity ID is replicated in the array, the first occurrence will delete the entity, while subsequent occurrences of the same Entity ID will provoke an error in the response (entity does not exist).
5.5.11.5 Batch Entity Merge case
The Batch Entity Merge operation has as input an array of Entity IDs, for the entities to be merged. If an Entity ID is replicated in the array, these merge operations shall be done in chronological order. Only the entity resulting from merging all of the entity instances, in the correct order, is maintained in the current state (as defined in clause 4.3.1). For Temporal Evolution of Entities (as defined in clause 4.3.1), all entity instances shall be taken into account, in the correct order.
5.5.12 Merge Patch Behaviour
The merge patch procedure modifies an existing NGSI-LD element by applying the set of changes found in an NGSI-LD Fragment data to the target resource. Unlike the partial update patch behaviour (described in clause 5.5.8), which replaces the complete element on the first level, e.g. a whole Attribute, the procedure described in this clause merges the provided information with the existing information up to an arbitrary depth, e.g. including going into JSON objects representing a Property value.
When merging NGSI-LD Entities using NGSI-LD Fragments, implementations shall determine the exact set of changes being requested by comparing the content of the provided Fragment (patch) against the current content (a JSON-LD object) of the target element.
With respect to merge operations, implementations shall perform an algorithm equivalent to the one described below (adapted from IETF RFC 7396 [16], in order to observe the name to URI expansion rules and JSON-LD null processing):
- For each member of the Fragment perform the term to URI expansion.
- If the provided Fragment (a JSON Merge Patch document) contains members that do not appear within the target (their URIs do not match), those members are added to the target.
- For each member of the Fragment contained by the target, the target member value is merged with the value given in the Fragment. NGSI-LD Nulls within the Fragment are given special meaning to indicate the removal of existing values within the target member value. In the case of a member representing a reified Property or Relationship including a datasetId, such member is only updated if the datasetId is the same, otherwise the member of the Fragment is added as a new instance to the target. If no datasetId is present, the default Attribute instance is targeted and merged if present and otherwise added. In case of a member type (of an Entity) in Entity Fragments, all included Entity Types are added, if they are not already contained in the type member of the target.
- For each member of the Fragment, whose value is an NGSI-LD Null, contained by the target, the target member is removed. In the case of deleting a specific Attribute instance with a datasetId, the handling shall be according to the description in clause 5.6.5. A datasetId cannot be deleted by setting it to the value "urn:ngsi-ld:null".
5.5.13 Limiting operations to local scope
The API provides a binding-specific mechanism to limit the execution of operations to a local scope, i.e. to only execute it based on information available in the Context Source or Context Broker directly targeted by the request. This enables limiting cascading distributed operations (clause 4.3.6.4) and, in some cases, also enables broader local operations, e.g. pertaining to all entities, which would be too expensive in the distributed case.
The localOnly member in the Subscription (clause 5.5.12) requests that the subscription only matches Entities stored locally.
The localOnly member in the RegistrationManagementInfo (clause 5.2.34) of a Context Source Registration request that, when contacting the registered Context Source, a local scope shall be specified. Thus, the registered Context Source only provides its local information, not information from further Context Sources in its own Context Registry.
If the request limits the execution of the operation to the local scope, Context Source Registrations from the Context Registry are not required and thus do not need to be requested.
5.5.14 Distributed Transactional Behaviour
The following operations may occur as part of a distributed transactional request:
- Retrieve Entity (clause 5.7.1)
- Query Entities (clause 5.7.2)
- Retrieve Temporal Evolution of an Entity (clause 5.7.3)
- Query Temporal Evolution of Entities (clause 5.7.4)
In the case that a client wishes to indicate to a Context Broker that a request is part of a unitary sequence of requests, the Context Broker shall create and cache an EntityMap for future use and should return the location of said EntityMap in a specific field. The caching strategy and expiry time shall take into account a suggested expiry time, if present, and depend on implementation specific configurations. Context Sources should indicate that they do not support EntityMaps, through declining to return the location of an EntityMap when requested to do so.
If a subsequent request references an existent EntityMap, it shall be used for the purposes of Entity registration matching, and queries shall be filtered to only consider the Entities listed. Subsequent requests referencing an EntityMap shall use the same parameters as in the original request that created the EntityMap, except for the specification of Entity identifiers or parameters related to pagination, or, in the case of temporal requests, the temporal query. If an EntityMap has expired, or cannot be accessed, no inference can be made as to which entities are held within the Context Sources and a new one shall be created. An EntityMap fixes the Entities to be considered for subsequent requests based on it. The creating Context Source shall remove Entities from the EntityMap that do not match the filters of the query at the time of processing. Other components shall only be allowed to update the expiry timestamp of the EntityMap, which can optionally be extended if the Context Sources implementation allows for it.
5.6 Context Information Provision
5.6.1 Create Entity
5.6.1.1 Description
This operation allows creating a new NGSI-LD Entity.
5.6.1.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can create an Entity within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.1.2‑1.
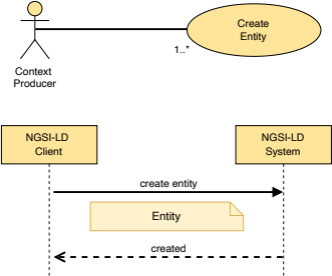
5.6.1.3 Input data
A JSON-LD document representing an NGSI-LD Entity as mandated by clause 5.2.4.
5.6.1.4 Behaviour
Implementations shall exhibit the following behaviour:
- Execute the behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation.
- If an exclusive Context Source Registration already exists for this id (URI), Attributes from matching input data are forwarded for remote processing:
- For matching Registrations where the Create Entity operation is supported, the operation is forwarded to the registration endpoint. If the endpoint then raises an error, this shall result in an error in case the complete create failed or in a partial success if some parts of the create succeeded.
- For matching Registrations where the Create Entity operation is not supported, this shall result in an error of type Conflict if the complete Create Entity operation failed or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.The matching Attributes are then removed from the Fragment and not processed further.
- If any redirect Context Source Registrations exist that match against the input data, that input data is forwarded for remote processing by one or more matching endpoints:
- For matching Registrations where the Create Entity operation is supported, matching input data is forwarded. If any such endpoint then raises an error, this shall result in an error in case the complete create has failed or in a partial success if some parts of the create has succeeded.
- For matching redirect Registrations where the Create Entity operation is not supported, this shall result in an error of type Conflict if the complete Create Entity operation failed or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.
- For any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the remaining input data, that input data is also forwarded for remote processing by matching endpoints in case the Create Entity operation is supported.
- If the Entity already exists locally this shall result in an error of type AlreadyExists, if the complete Create Entity operation has failed or in a partial success if some parts of it has succeeded.
- Any remaining input data shall be used to create the Entity locally.
5.6.1.5 Output data
None.
5.6.2 Update Attributes
5.6.2.1 Description
This operation allows modifying an existing NGSI-LD Entity by updating already existing Attributes (Properties or Relationships) and by appending non-existing ones.
5.6.2.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can update Attributes within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.2.2‑1.
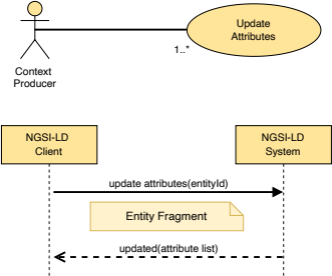
5.6.2.3 Input data
- A URI representing the id of the Entity to be updated (target Entity).
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17 (optional).
- A JSON-LD document representing an NGSI-LD Entity Fragment.
5.6.2.4 Behaviour
- If the Entity ID is not present or it is not a valid URI then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target Entity, because there is no existing Entity whose id (URI), and where specified type, is equivalent to the target entity held locally, and no matching registrations apply (see ), an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- Execute the behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation. NGSI-LD Nulls should be supported by this operation. If NGSI-LD Nulls are found in the payload, but are not supported, an error of type OperationNotSupported shall be raised.
- If an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration matches against the input data, Attributes from matching input data are forwarded for remote processing. For each matching registration:
- If the Update Attributes operation is supported by the registration (see clause 4.3.6), matching input data is forwarded to the Registration endpoint.
- If the Update Attributes operation is not supported by the registration, this shall result in an error of type Conflict if the complete update failed or in a partial success if some parts of the update succeeded.
- The matching Attributes are then removed from the Fragment and not processed further.
- If there are remaining Attributes, for any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the remaining input data, that input data is also forwarded for remote processing to matching endpoints in case the Update Attributes operation is supported by the matched registration.
- Then, implementations shall perform a partial update patch operation over the remains of the target Entity as mandated by clause 5.5.8, using the following procedure.
- For each Attribute (Property or Relationship) included by the Entity Fragment at root level:
- If the target Entity does not include a matching Attribute (considering term expansion rules as mandated by clause 5.5.7) then such Attribute shall be appended to the target Entity.
- If the target Entity already includes a matching Attribute (considering term expansion rules as mandated by clause 5.5.7):
- If a datasetId is present in the Attribute included by the Entity Fragment:
- If no datasetId is present in the Attribute included by the Entity Fragment, the default Attribute instance is targeted:
- If type is included in the Fragment and it includes Entity Type names that are not yet in the target Entity, add them to the list of Entity Type names of the target Entity.
- If scope is included in the Fragment and the target entity includes scope, replace the scope by the one included in the Fragment, otherwise ignore it.
5.6.2.5 Output data
- A status code indicating whether all the new Attributes were updated or only some of them.
- List of Attributes (Properties or Relationships) actually updated.
5.6.3 Append Attributes
5.6.3.1 Description
This operation allows modifying an NGSI-LD Entity by adding new attributes (Properties or Relationships).
5.6.3.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can append new Attributes to an existing Entity within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.3.2‑1.
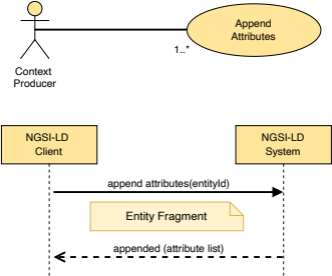
5.6.3.3 Input data
- A URI representing the id of the E to be modified (target Entity).
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17 (optional).
- A JSON-LD document representing an NGSI-LD Entity Fragment.
- An optional flag indicating whether overwriting existing Attributes within the append operation should be permitted or denied. By default, Attribute overwrites are permitted.
5.6.3.4 Behaviour
The following behaviour shall be exhibited by compliant implementations:
- If the Entity ID is not present or it is not a valid URI then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about this Entity, because there is no existing Entity which id (URI), and where specified type, is equivalent held locally to the one passed as a parameter, and no matching registrations apply (see ), an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- The behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation.
- If an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration matches against the input data, the Attributes from matching input data are forwarded for remote processing. For each matching registration:
- If the Append Attributes operation is supported by the registration (see clause 4.3.6), matching input data is forwarded to the Registration endpoint.
- If the Append Attributes operation is not supported by the registration, this shall result in an error of type Conflict if the complete append failed or in a partial success if some parts of the append succeeded.
- The matching Attributes are then removed from the Fragment and not processed further.
- For any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the remaining input data, that input data is also forwarded for remote processing to matching endpoints in case the Append Attributes operation is supported.
- Then, implementations shall perform an Append Attributes operation over the remains of the target Entity as using the following procedure:
- For each Attribute (Property or Relationship) included by the Entity Fragment at root level:
- If a datasetId is present in the Attribute included by the Entity Fragment:
- If overwrite is allowed, then the existing Attribute with the specified datasetId in the target Entity shall be replaced by the new one supplied.- If overwrite is not allowed, the existing Attribute with the specified datasetId in the target Entity shall be left untouched.
- If no datasetId is present in the Attribute included by the Entity Fragment:
- If overwrite is allowed, then the existing default Attribute in the target Entity shall be replaced by the new one supplied.- If overwrite is not allowed the existing default Attribute in the target Entity shall be left untouched.
- If type is included in the Fragment and it includes Entity Type names that are not yet in the target Entity, add them to the list of Entity Type names of the target Entity.
- If scope is included in the Fragment and overwrite is allowed, the scope of the target Entity will become the one included in the Fragment. Otherwise, the Scopes in the Fragment that are not part of the value of scope of the target Entity will be appended to the value of the scope of the target Entity. If there is more than one Scope, the value of scope is represented as a JSON array containing all Scopes.
5.6.3.5 Output data
- A status code indicating whether all the new Attributes were appended or only some of them.
- List of Attributes (Properties and/or Relationships) actually appended.
5.6.4 Partial Attribute update
5.6.4.1 Description
This operation allows performing a partial update on an NGSI-LD Entity's Attribute (Property or Relationship). A partial update only changes the elements provided in an Entity Fragment, leaving the rest as they are. This operation supports the deletion of sub-Attributes but not the deletion of the whole Attribute itself.
5.6.4.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can carry out a partial Attribute update of an Entity within an NGSI-LD System as shown in Figure 5.6.4.2‑1.
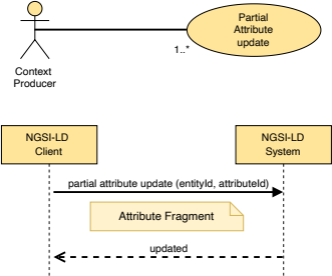
5.6.4.3 Input data
- Entity ID (URI) of the concerned Entity, the target Entity.
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17 (optional).
- Target Attribute (Property or Relationship) to be modified, identified by a name.
- A JSON-LD document representing an NGSI-LD Attribute Fragment.
5.6.4.4 Behaviour
- If the target Entity ID is not a valid URI or it is not present, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the target Attribute name is not valid or it is not present, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the target Attribute is scope, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- The behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation. NGSI-LD Nulls should be supported by this operation. If NGSI-LD Nulls are found in the payload, but are not supported, an error of type OperationNotSupported shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target Entity, because there is no existing Entity whose id (URI), and where specified type, is equivalent held locally, and no matching registrations apply (see ), then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- If an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration matches against the input data, the Attributes from matching input data are forwarded for remote processing. For each matching registration:
- If the Partial Attribute update operation is supported by the registration (see clause 4.3.6), matching input data is forwarded to the Registration endpoint.
- If the Partial Attribute update operation is not supported by the registration, this shall result in an error of type Conflict in case the complete partial Attribute update failed, or in a partial success if some parts of the partial Attribute update succeeded.No further processing is required.
- For any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the input data, that input data is also forwarded for remote processing to matching endpoints in case the Partial Attribute update operation is supported.
- Apply term expansion as mandated by clause 5.5.7, so that the fully qualified name (URI) associated to the target Attribute is properly obtained.
- If the target Entity does not contain the target Attribute:
- as a default instance in case no datasetId is present;
- as an instance with the specified datasetId if present;
- Perform a partial update patch operation on the target Attribute following the algorithm mandated by clause 5.5.8. If present in the provided NGSI-LD Entity Fragment, the type of the Attribute has to be the same as the type of the targeted Attribute fragment, i.e. it is not allowed to change the type of an Attribute.
5.6.4.5 Output data
None.
5.6.5 Delete Attribute
5.6.5.1 Description
This operation allows deleting an NGSI-LD Attribute (Property or Relationship). The Attribute itself and all its children shall be deleted.
5.6.5.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can delete a specific Attribute within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.5.2‑1.
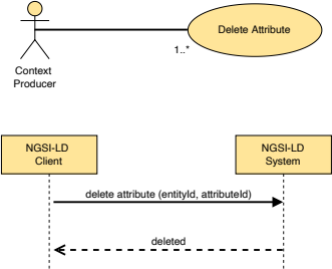
5.6.5.3 Input data
- Entity ID (URI) of the concerned Entity, the target Entity.
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17 (optional).
- Target Attribute (Property or Relationship) to be deleted, identified by a name.
- An optional parameter identifying the datasetId of the target Attribute instance to be deleted. Otherwise the default Attribute instance is targeted.
- An optional flag deleteAll indicating whether also all target Attribute instances with a datasetId are to be deleted.
- An optional JSON-LD @context.
5.6.5.4 Behaviour
- If the target Entity ID is not a valid URI or it is not present, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the target Attribute name is not a valid name or it is not present, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration matches against the input data, the input data (see ), the input data is forwarded. For each matching registration:
- If the Delete Attribute operation is supported by the registration (see clause 4.3.6), matching input data is forwarded to the Registration endpoint.
- If the Delete Attribute update operation is not supported by the matched registration, this shall result in an error of type Conflict in case the complete delete Attribute failed, or in a partial success if some parts of the delete Attribute succeeded.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target Entity, because there is no existing Entity whose id (URI), and where specified type, is equivalent held locally, and no matching registrations apply, then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- For any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the input data, that input data is also forwarded for remote processing to matching endpoints in case the Delete Attribute operation is supported by the matched registration.
- Apply term expansion as mandated by clause 5.5.7 so that the fully qualified name (URI) associated to the target Attribute is properly obtained.
- If the target Entity does not contain the target Attribute then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- If the target Attribute is scope, remove the scope Attribute from the target Entity.
- If the deleteAll flag is set, remove all target Attribute instances from the target Entity.
- Otherwise:
- if a datasetId parameter is provided, remove only the target Attribute instance from the given dataset whose datasetId matches the parameter;
- if no datasetId parameter is provided, remove the default target Attribute instance from the target Entity.
5.6.5.5 Output data
None.
5.6.6.1 Description
This operation allows deleting an NGSI-LD Entity.
5.6.6.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can completely delete an Entity within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.6.2‑1.
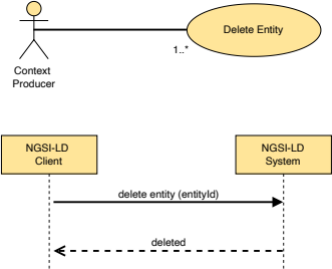
5.6.6.3 Input data
- Entity ID (URI) of the Entity to be deleted, the target Entity.
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17 (optional).
5.6.6.4 Behaviour
- If the target Entity ID is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target Entity, because there is no existing Entity whose id (URI), and where specified type, is equivalent held locally, and no matching registrations apply (see ), then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- If an exclusive or Context Source Registration matches against the id, the request is forwarded for remote processing. For each matching registration:
- If the Delete Entity operation is supported by the registration (see clause 4.3.6), matching input data is forwarded to the Registration endpoint.
- If the Delete Entity update operation is not supported by the matched registration, this shall result in an error of type Conflict in case the complete delete Entity failed, or in a partial success if some parts of the delete Entity succeeded.
- If any redirect Context Source Registrations exist that match against the input data, that input data is forwarded for remote processing by one or more matching endpoints:
- For matching Registrations where the Delete Entity operation is supported (see clause 4.3.6), matching input data is forwarded. If any such endpoint then raises an error, the implementation shall return with the error(s) raised.
- For matching redirect Registrations where the Delete Entity operation is not supported, this shall result in an error of type Conflict in case the complete delete Entity failed, or in a partial success if some parts of the delete Entity succeeded.
- For any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the remaining input data, that input data is also forwarded in the case the Delete Entity operation is supported for remote processing by matching endpoints.
- The input data shall be used to remove the entity locally if it exists.
5.6.6.5 Output data
None.
5.6.7 Batch Entity Creation
5.6.7.1 Description
This operation allows creating a batch of NGSI-LD Entities.
5.6.7.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can create a batch of NGSI-LD Entities within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.7.2‑1.
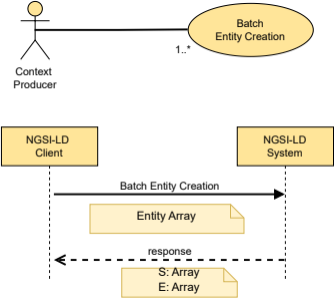
5.6.7.3 Input data
- A JSON-LD Array containing one or more JSON-LD documents each one representing an NGSI-LD Entity as mandated by clause 5.2.4. See clause 5.5.11.1 for information on behaviour when there is more than one instance of the same entity in the input Array.
5.6.7.4 Behaviour
Implementations shall exhibit the following behaviour:
- If the input Array is empty or contains a null value in any of its items an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- Execute the behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation.
- Let S be an array which shall contain a list of Entity IDs, one for each NGSI-LD Entity successfully created. S shall be initialized to the empty array.
- Let E be an array which shall contain a list of BatchEntityError as defined by clause 5.2.17, one for each NGSI-LD Entity which resulted in error. E shall be initialized to the empty array.
- For each Context Source Registration CSR in the Context Registry:
- Let IN be a copy of the original input array.
- Remove from IN all Entities not matched by CSR and remove non-matching Attributes from the remaining Entities.
- Remove all Attributes from the remaining Entities in IN for which there is a matching exclusive Context Source Registration, which is not CSR itself.
- Remove all Attributes from the remaining Entities in IN for which there is a matching redirect Context Source Registration, unless CSR is a redirect Context Source Registration itself.
- If IN is empty, continue with the next Context Source Registration if there is any.
- If the Batch Entity Creation operation is supported by CSR:
- Forward the Batch Entity Creation request with IN as input Array.
- Merge the returned list of Entities successfully created with S.
- Merge the returned list of Entities in Error with E.
- Otherwise, if the Create Entity operation (clause 5.6.1) is supported by CSR:
- For each Entity EN in the input array:
- Otherwise:
- In case CSR is an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration, add an Error of type Conflict for each Entity in IN to E.
- For each of the NGSI-LD Entities included in the input Array execute the behaviour defined by clause 5.6.1, but limited to a local operation, as follows:
- If the Entity was successfully created, then add the corresponding Entity ID to the S array.
- If the Entity creation failed, then a new BatchEntityError shall be added to E containing the failed Entity ID and the related ProblemDetails.
5.6.7.5 Output data
- The list of Entities successfully created (S Array), if all Entities were created correctly; or
- the list of Entities successfully created (S Array) and the list of Entities in error (E Array), if only some or none of the Entities were created.
5.6.8 Batch Entity Creation or Update (Upsert)
5.6.8.1 Description
This operation allows creating a batch of NGSI-LD Entities, updating each of them if they already existed. In some database jargon this kind of operation is known as "upsert".
5.6.8.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can create or update a batch of Entities within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.8.2‑1.
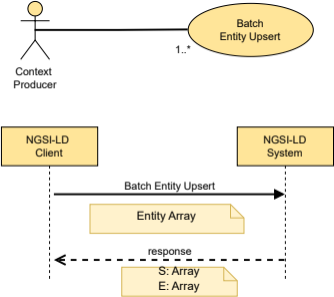
5.6.8.3 Input data
- A JSON-LD Array containing one or more JSON-LD documents each one representing an Entity as mandated by clause 5.2.4. See clause 5.5.11.2 for information on behaviour when there is more than one instance of the same entity in the input Array.
- An optional flag indicating the update mode (only applies in case the Entity already exists):
- Replace. All the existing Entity content shall be replaced (default mode).
- Update. Existing Entity content shall be updated.
5.6.8.4 Behaviour
Implementations shall exhibit the following behaviour:
- If the input Array is empty or contains a null value in any of its items, an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- Execute the behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation.
- Let S be an array which shall contain a list of Entity IDs, one for each NGSI-LD Entity which was successfully processed. S shall be initialized to the empty array.
- Let E be an array which shall contain a list of BatchEntityError as defined by clause 5.2.17, one for each NGSI-LD Entity which resulted in error. E shall be initialized to the empty array.
- For each Context Source Registration CSR in the Context Registry:
- Let IN be a copy of the original input array.
- Remove from IN all Entities not matched by CSR and remove non-matching Attributes from the remaining Entities.
- Remove all Attributes from the remaining Entities in IN for which there is a matching exclusive Context Source Registration, which is not CSR itself.
- Remove all Attributes from the remaining Entities in IN for which there is a matching redirect Context Source Registration, unless CSR is a redirect Context Source Registration itself.
- If IN is empty, continue with the next Context Source Registration if there is any.
- If the Batch Entity Creation or Update (Upsert) operation is supported by CSR:
- Forward the Batch Entity Creation or Update (Upsert) request with IN as input Array.
- Merge the returned list of Entities successfully created with S.
- Merge the returned list of Entities in Error with E.
- Otherwise, if the Create Entity operation (clause 5.6.1) is supported by CSR:
- For each Entity EN in the input array:
- If the Replace Entity operation (clause 5.6.18) is supported by CSR and the value of the update mode flag is Replace or the flag is not set, forward a Replace Entity request for Entity EN.- Otherwise, if the Update Attributes operation (clause 5.6.2) is supported by CSR and the value of the update mode flag is Update, forward an Update Attributes request for Entity EN.- Otherwise add an OperationNotSupported Error for Entity EN related to CSR to E.
- Merge any successful result(s) for Entity EN created or updated with S.
- Merge any error result(s) for Entity EN created or updated with E.
- Otherwise, if the Replace Entity operation (clause 5.6.18) is supported by CSR and the value of the update mode flag is Replace or the flag is not set:
- Forward a Replace Entity request for Entity EN.
- Merge any successful result(s) for Entity EN updated with S.
- Merge any error result(s) for Entity EN updated with E.
- Otherwise, if the Update Attributes operation (clause 5.6.2) is supported by CSR and the value of the update mode flag is Update:
- Forward an Update Attributes request for Entity EN.
- Merge any successful result(s) for Entity EN updated with S.
- Merge any error result(s) for Entity EN updated with E.
- Otherwise:
- In case CSR is an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration, add an Error of type Conflict for each Entity in IN to E.
- For each of the NGSI-LD Entities included in the input Array implementations shall:
- Create the Entity locally if it does not exist (i.e. no Entity with the same Entity ID is present) executing the behaviour defined by clause 5.6.1, but limited to a local operation.
- If there were an existing Entity with the same Entity ID, it shall be completely replaced by the new Entity content provided, if the requested update mode is 'replace'.
- If there were an existing Entity with the same Entity ID, the behaviour defined by clause 5.6.3 shall be executed, but limited to a local operation, if the requested update mode is "update".
- If successful, the local creation or update shall be added to S. If while processing an Entity there is any kind of error or abnormal situation, a BatchEntityError shall be added to E containing the failed Entity ID and the related ProblemDetails.
5.6.8.5 Output data
- none (if all Entities already existed and are successfully updated); or
- the list of Entities successfully created (S Array), if all Entities not existing prior to this request have been successfully created and the others have been successfully updated; or
- the list of Entities successfully created or updated (S Array), and the list of Entities in error (E Array), if only some or none of the Entities have been successfully created or updated.
5.6.9 Batch Entity Update
5.6.9.1 Description
This operation allows updating a batch of NGSI-LD Entities.
5.6.9.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can update a batch of Entities within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.9.2‑1.
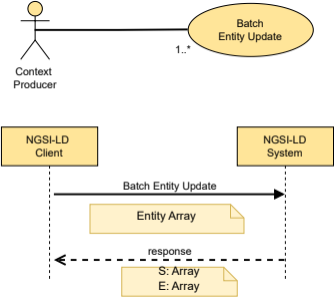
5.6.9.3 Input data
- A JSON-LD Array containing one or more JSON-LD documents each one representing an Entity as mandated by clause 5.2.4. See clause 5.5.11.3 for information on behaviour when there is more than one instance of the same entity in the input Array.
- An optional flag indicating whether Attributes shall be overwritten or not. By default, Attributes will be overwritten.
5.6.9.4 Behaviour
Implementations shall exhibit the following behaviour:
- If the input Array is empty or contains a null value in any of its items, an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- Execute the behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation.
- Let S be an array which shall contain a list of Entity IDs, one for each NGSI-LD Entity which was successfully processed. S shall be initialized as the empty array.
- Let E be an array which shall contain a list of BatchEntityError as defined by clause 5.2.17, one for each NGSI-LD Entity which resulted in error. E shall be initialized as the empty array.
- For each Context Source Registration CSR in the Context Registry:
- Let IN be a copy of the original input array.
- Remove from IN all Entities not matched by CSR and remove non-matching Attributes from the remaining Entities.
- Remove all Attributes from the remaining Entities in IN for which there is a matching exclusive Context Source Registration, which is not CSR itself.
- Remove all Attributes from the remaining Entities in IN for which there is a matching redirect Context Source Registration, unless CSR is a redirect Context Source Registration itself.
- Remove all Entities without Attributes from IN.
- If IN is empty, continue with the next Context Source Registration if there is any.
- If the Batch Entity Update operation is supported by CSR:
- Forward the Batch Entity Update request with IN as input Array.
- Merge the returned list of Entities successfully created with S.
- Merge the returned list of Entities in Error with E.
- Otherwise, if the Update Attributes operation (clause 5.6.2) is supported by CSR and Attribute overwrite is permitted:
- For each Entity EN in the input array:
- Otherwise, if the Append Attributes operation (clause 5.6.3) is supported by CSR and Attribute overwrite is not permitted:
- For each Entity EN in the input array:
- Merge any successful result(s) for Entity EN updated with S.- Merge any error result(s) for Entity EN updated with E.
- Otherwise:
- In case CSR is an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration, add an Error of type Conflict for each Entity in IN to E.
- For each of the NGSI-LD Entities included in the input Array execute the behaviour defined by clause 5.6.3, but limited to a local operation, as follows:
- If the Entity was successfully updated (Attributes appended), then add the corresponding Entity ID to the S array.
- If the Entity update failed, then a new BatchEntityError shall be added to E containing the failed Entity ID and the ProblemDetails associated.
5.6.9.5 Output data
- none (if all Entities are successfully updated); or
- the list of Entities successfully updated (S Array), and the list of Entities in error (E Array), if only some or none of the Entities have been successfully updated.
5.6.10 Batch Entity Delete
5.6.10.1 Description
This operation allows deleting a batch of NGSI-LD Entities.
5.6.10.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can delete a batch of Entities within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.10.2‑1.
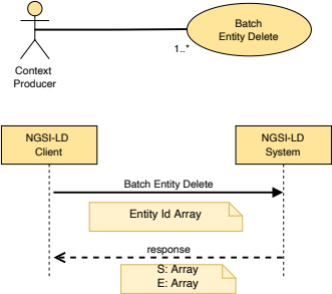
5.6.10.3 Input data
- A JSON-LD Array containing a list of Entity IDs (URIs) that are requested to be deleted. See clause 5.5.11.4 for information on behaviour when there is more than one instance of the same Entity ID in the input Array.
5.6.10.4 Behaviour
Implementations shall exhibit the following behaviour:
- If the input Array is empty or contains a null value in any of its items, an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- Let S be an array which shall contain a list of Entity IDs, one for each NGSI-LD Entity which was successfully processed. S shall be initialized to the empty array.
- Let E be an array which shall contain a list of BatchEntityError as defined by clause 5.2.17, one for each NGSI-LD Entity which resulted in error. E shall be initialized to the empty array.
- For each Context Source Registration CSR in the Context Registry:
- Let IN be a copy of the original input array.
- Remove from IN all Entities not matched by CSR and remove non-matching Attributes from the remaining Entities.
- Remove all Attributes from the remaining Entities in IN for which there is a matching exclusive Context Source Registration, which is not CSR itself.
- Remove all Attributes from the remaining Entities in IN for which there is a matching redirect Context Source Registration, unless CSR is a redirect Context Source Registration itself.
- Remove all Entities without Attributes from IN.
- If IN is empty, continue with the next Context Source Registration if there is any.
- If the Batch Entity Delete operation is supported by CSR:
- Forward the Batch Entity Delete request with IN as input Array.
- Merge the returned list of Entities successfully created with S.
- Merge the returned list of Entities in Error with E.
- Otherwise, if the Delete Entity operation ) is supported by CSR:
- For each Entity EN in the input array:
- Otherwise:
- In case CSR is an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration, add an Error of type Conflict for each Entity in IN to E.
- For each of the NGSI-LD Entity IDs included in the input Array execute the behaviour defined by , but limited to a local operation, as follows:
5.6.10.5 Output data
- none (if all Entities that already existed are successfully deleted); or
- the list of Entities successfully deleted (S Array), and the list of Entities in error (E Array), if some or all of the Entities have not been successfully deleted.
5.6.11 Create or Update (Upsert) Temporal Evolution of an Entity
5.6.11.1 Description
This operation allows creating or updating (by adding new Attribute instances) the Temporal Evolution of an Entity.
5.6.11.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can create the Temporal Evolution of an Entity within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.11.2‑1.
Similarly, if the Entity already exists then an Update scenario will be in place.
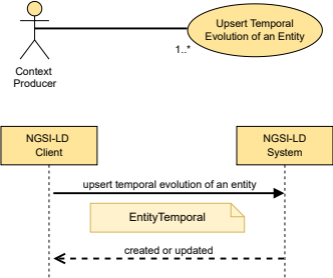
5.6.11.3 Input data
A JSON-LD document representing the Temporal Evolution of an Entity as mandated by clause 5.2.20.
5.6.11.4 Behaviour
Implementations shall exhibit the following behaviour:
- Execute the behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation.
- If an exclusive Context Source Registration already exists for this id (URI), Attributes from matching input data are forwarded for remote processing:
- For matching Registrations where the "Create or Update (Upsert) Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation is supported, the operation is forwarded to the registration endpoint. If the endpoint then raises an error, this shall result in an error in case the complete "Create or Update (Upsert) Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation failed or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.
- For matching Registrations where the "Create Entity" operation is not supported, this shall result in an error of type Conflict in case the complete "Create or Update (Upsert) Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation failed or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.The matching Attributes are then removed from the Fragment and not processed further.
- If any redirect Context Source Registrations exist that match against the input data, that input data is forwarded for remote processing by one or more matching endpoints:
- For matching Registrations where the "Create or Update (Upsert) Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation is supported, matching input data is forwarded. If any such endpoint then raises an error, this shall result in an error in case the complete "Create or Update (Upsert) Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation failed or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.
- For matching redirect Registrations where the "Create or Update (Upsert) Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation is not supported, this shall result in an error of type Conflict in case the complete "Create or Update (Upsert) Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation failed or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.
- For any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the remaining input data, that input data is also forwarded for remote processing by matching endpoints.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint already knows about this Temporal Evolution of an Entity, because there is an existing Temporal Evolution of an Entity whose id (URI) is the same, then all the Attribute instances included by the Temporal Evolution shall be added to the existing Entity as mandated by clause 5.6.12. If type is included in the EntityTemporal Fragment and it includes Entity Type names that are not yet in the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity, add them to the list of Entity Type names of the target Temporal Evolution of anEntity.
- Otherwise, implementations shall create the provided Temporal Evolution of an Entity.
5.6.11.5 Output data
None.
5.6.12 Add Attributes to Temporal Evolution of an Entity
5.6.12.1 Description
This operation allows modifying the Temporal Evolution of an Entity by adding new Attribute instances.
5.6.12.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can add new Attributes or Attribute instances to an existing Temporal Evolution of an Entity within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.12.2‑1.
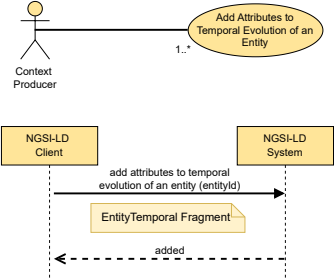
5.6.12.3 Input data
- Entity ID (URI) of the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity to be modified with additional Attributes.
- A JSON-LD document representing an NGSI-LD Fragment of EntityTemporal, including only the new Attribute instance(s), and contained by an Array.
5.6.12.4 Behaviour
The following behaviour shall be exhibited by compliant implementations:
- If the Entity ID is not present or it is not a valid URI then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity, because there is no existing Temporal Evolution of an Entity whose id (URI) is equivalent to the one passed as a parameter held locally and no matching registrations apply, an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- The behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation.
- If an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration matches against the input data, the Attributes from matching input data are forwarded for remote processing. For each matching registration:
- If the "Add Attributes to Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation is supported by the matched registration, matching input data is forwarded to the Registration endpoint.
- If the "Add Attributes to Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation is not supported by the matched registration, this shall result in an error of type Conflict if the complete "Add Attributes to Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation failed or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.
- For any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the remaining input data, that input data is also forwarded for remote processing to matching endpoints.
- If the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity exists locally and matches against the remaining input data, implementations shall do the following:
- For each Attribute (Property or Relationship) instance included by the EntityTemporal Fragment at root level:
- The Attribute (considering term expansion rules as mandated by clause 5.5.7) instance(s) shall be added to the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity.
- If type is included in the EntityTemporal Fragment and it includes Entity Type names that are not yet in the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity, add them to the list of Entity Type names of the target Temporal Evolution of theEntity.
5.6.12.5 Output data
None.
5.6.13 Delete Attribute from Temporal Evolution of an Entity
5.6.13.1 Description
This operation allows deleting an Attribute (Property or Relationship) of the Temporal Evolution of an Entity. The Attribute itself and all its child NGSI-LD elements shall be deleted.
5.6.13.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can delete a specific Attribute of the Temporal Evolution of an Entity within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.13.2‑1.
5.6.13.3 Input data
- Entity ID (URI) of the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity to be modified by removing the target Attribute.
- Target Attribute (Property or Relationship) to be deleted, identified by a name.
- An optional parameter identifying the dataset (datasetId) of the target Attribute instance to be deleted.
- An optional parameter, a flag, (deleteAll) indicating whether all target Attribute instances are to be deleted, regardless of datasetId.
- An optional JSON-LD @context.
5.6.13.4 Behaviour
- If the target Entity ID is not a valid URI or it is not present, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the target Attribute name is not a valid name, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target Entity, because there is no existing Temporal Evolution of an Entity whose id (URI) is equivalent held locally and no matching registrations apply, then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- If an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration matches against the input data, the input data is forwarded. For each matching registration:
- If the "Delete Attribute from Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation is supported by the matched registration, matching input data is forwarded to the Registration endpoint.
- If the "Delete Attribute from Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation is not supported by the matched registration, this shall result in an error of type Conflict in case the complete "Delete Attribute from Temporal Evolution of an Entity" failed, or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.
- For any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the input data, that input data is also forwarded for remote processing to matching endpoints.
- If the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity exists locally, implementations shall do the following:
- Apply term expansion as mandated by clause 5.5.7 so that the fully qualified name (URI) associated to the target Attribute is properly obtained.
- If the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity does not contain the target Attribute then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- If the deleteAll flag is set, remove all target Attribute instances from the target Entity.
- Otherwise:
- if a datasetId parameter is provided, remove only any target Attribute instance from the given dataset;
- if no datasetId parameter is provided, remove only the default target Attribute instance datasetId from the target Entity.
5.6.13.5 Output data
None.
5.6.14 Modify Attribute instance in Temporal Evolution of an Entity
5.6.14.1 Description
This operation allows modifying a specific Attribute (Property or Relationship) instance, identified by its instanceId, of the Temporal Evolution of an Entity.
This operation enables the correction of wrong information that could have been previously added to the Temporal Evolution of an Entity.
5.6.14.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can modify a specific Attribute instance, identified by a given instanceId, of the Temporal Evolution of an Entity within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.14.2‑1.
5.6.14.3 Input data
- Entity ID (URI) of the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity to be modified by changing an instance of the target Attribute.
- Target Attribute (Property or Relationship) to be modified, identified by a name.
- Attribute instance to be modified, identified by its instanceId.
- A JSON-LD document representing an NGSI-LD Fragment of EntityTemporal, including only the new Attribute instance, contained by an Array of exactly one item.
- An optional JSON-LD @context.
5.6.14.4 Behaviour
- If the target Entity ID is not a valid URI or it is not present, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the target Attribute name is not a valid name or it is not present, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the target instanceId is not a valid URI or it is not present, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target Entity, because there is no existing Entity whose id (URI) is equivalent held locally and no matching registrations apply, then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- If an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration matches against the input data, the input data is forwarded. For each matching registration:
- If the "Modify Attribute instance in Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation is supported by the matched registration, matching input data is forwarded to the Registration endpoint.
- If the "Modify Attribute instance in Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation is not supported by the matched registration, this shall result in an error of type Conflict in case the complete Modify Attribute instance in Temporal Evolution of an Entity operation failed, or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.
- For any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the input data, that input data is also forwarded for remote processing to matching endpoints.
- If the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity exists locally, implementations shall do the following:
- Apply term expansion as mandated by clause 5.5.7 so that the fully qualified name (URI) associated to the target Attribute is properly obtained.
- If the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity does not contain the target Attribute then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- If for the target Attribute no instance with the specified instanceId exists, an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- Replace the target Attribute instance identified by the instanceId with the Attribute instance in the EntityTemporal Fragment. The createdAt property of the concerned instance shall remain unchanged, but the modifiedAt property shall be set to the timestamp corresponding to this modification.
5.6.14.5 Output data
None.
5.6.15 Delete Attribute instance from Temporal Evolution of an Entity
5.6.15.1 Description
This operation allows deleting one Attribute instance (Property or Relationship), identified by its instanceId, of the Temporal Evolution of an Entity. The Attribute itself and all its child elements shall be deleted. This operation enables the removal of individual Attribute instances that could have been previously added to the Temporal Evolution of an Entity.
5.6.15.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can delete an Attribute instance, identified by a given instanceId, of the Temporal Evolution of an Entity within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.15.2‑1.
of an Entity use case
5.6.15.3 Input data
- Entity ID (URI) of the target Temporal Evolutionof an Entity to be modified by deleting an instance of the target Attribute.
- Target Attribute (Property or Relationship) to be deleted, identified by a name.
- Attribute instance to be deleted, identified by its instanceId.
- An optional JSON-LD @context.
5.6.15.4 Behaviour
- If the target Entity ID is not a valid URI or it is not present, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the target Attribute name is not a valid name or it is not present, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the target instanceId is not a valid URI or it is not present, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target Entity, because there is no existing Entity whose id (URI) is equivalent held locally and no matching registrations apply, then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- If an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration matches against the input data, the input data is forwarded. For each matching registration:
- If the "Delete Attribute instance from Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation is supported by the matched registration, matching input data is forwarded to the Registration endpoint.
- If the "Delete Attribute instance from Temporal Evolution of an Entity" operation is not supported by the matched registration, this shall result in an error of type Conflict in case the complete "Delete Attribute instance from Temporal Evolution of an Entity" failed, or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.
- For any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the input data, that input data is also forwarded for remote processing to matching endpoints.
- If the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity exists locally, implementations shall do the following:
- Apply term expansion as mandated by clause 5.5.7 so that the fully qualified name (URI) associated to the target Attribute is properly obtained.
- If the target Temporal Evolution of the Entity does not contain the target Attribute then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- If for the target Attribute no instance with the specified instanceId exists, an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- Remove the instance, with the specified instanceId, of the target Attribute from the target Entity.
5.6.15.5 Output data
None.
5.6.16 Delete Temporal Evolution of an Entity
5.6.16.1 Description
This operation allows deleting the Temporal Evolution of an Entity.
5.6.16.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can completely delete the Temporal Evolution of an Entity within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.16.2‑1.
5.6.16.3 Input data
- Entity ID (URI) of the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity to be deleted.
5.6.16.4 Behaviour
- If the target Entity ID is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target Entity because there is no existing Entity whose id (URI) is equivalent held locally and no matching registrations apply, then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- If an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration matches against the input data, the input data is forwarded. For each matching registration:
- If the "Delete Temporal Evolution of Entity" operation is supported by the matched registration, matching input data is forwarded to the Registration endpoint.
- If the "Delete Temporal Evolution of Entity" operation is not supported by the matched registration, this shall result in an error of type Conflict in case the complete "Delete Temporal Evolution of Entity" failed, or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.
- For any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the input data, that input data is also forwarded for remote processing to matching endpoints.
- If the target Temporal Evolution of an Entity exists locally, the entire Temporal Evolution of the Entity shall be removed.
5.6.16.5 Output data
None.
5.6.17 Merge Entity
5.6.17.1 Description
This operation allows modification of an existing NGSI-LD Entity aligning to the JSON Merge Patch processing rules defined in IETF RFC 7396 [16] by adding new Attributes (Properties or Relationships) or modifying or deleting existing Attributes associated with an existing Entity.
5.6.17.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can perform a merge on an Entity within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.17.2‑1.
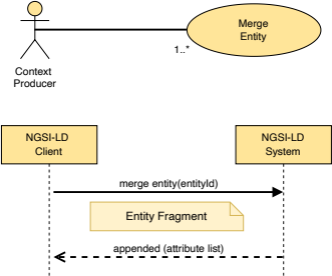
5.6.17.3 Input data
- A URI representing the id of the Entity to be merged (target Entity).
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17 (optional).
- A JSON-LD document representing an NGSI-LD Entity Fragment.
- An optional flag indicating whether the JSON-LD document contains a simplified representation of the entity.
- An optional parameter indicating a common observedAt timestamp to use across merged Attributes.
- An optional parameter representing a common IETF RFC 5646 [28] language tag to use across merged LanguageMap Attributes.
5.6.17.4 Behaviour
The following behaviour shall be exhibited by compliant implementations:
- If the Entity ID is not present or it is not a valid URI then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target Entity, because there is no existing Entity whose id (URI), and where specified type, is equivalent held locally, and no matching registrations apply (see ), then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- If an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration matches against the input data, Attributes from matching input data are forwarded. For each matching registration:
- If the Merge Entity operation is supported by the matched registration (see clause 4.3.6), matching input data is forwarded to the Registration endpoint.
- If the Merge Entity operation is not supported by the matched registration, this shall result in an error of type Conflict in case the complete Merge Entity operation failed, or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.
- For any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the remaining input data, that input data is also forwarded in the case the Merge Entity operation is supported for remote processing to matching endpoints.
- The behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation. NGSI-LD Nulls should be supported by this operation. If NGSI-LD Nulls are found in the payload, but are not supported, an error of type OperationNotSupported shall be raised.
- If the target Entity does not include a matching Attribute (considering term expansion rules as mandated by clause 5.5.7), then such Attribute shall be appended to the target Entity.
- If the target Entity already includes a matching Attribute (considering term expansion rules as mandated by clause 5.5.7):
- If the Attribute (Property or Relationship) to be merged is represented in a simplified representation, the type of any pre-existing Attribute in the target entity shall be preserved.
- If a common language tag is defined and a LanguageProperty Attribute to be merged is represented as a string, the pre-existing languageMap JSON object shall be preserved. The string value shall only replace the value associated to the language tag key found within the languageMap.
- If a common observedAt timestamp is defined and an existing Attribute to be merged previously contained an observedAt sub-Attribute, the observedAt sub-Attribute is also updated using the common timestamp, unless the Entity Fragment itself contains an explicit updated value for the observedAt sub-Attribute.
- If a datasetId is present in the Attribute included by the Entity Fragment:
- If no datasetId is present in the Attribute included by the Entity Fragment, the default Attribute instance is targeted:
- If type is included in the Fragment and it includes Entity Type names that are not yet in the target Entity, add them to the list of Entity Type names of the target Entity.
- If scope is included in the Fragment and overwrite is allowed, the scope of the target Entity will become the one included in the Fragment. Otherwise, the Scopes in the Fragment that are not part of the value of scope of the target Entity will be appended to the value of the scope of the target Entity. If there is more than one Scope, the value of scope is represented as a JSON array containing all Scopes.
5.6.17.5 Output data
- A status code indicating whether all the Attributes were merged successfully.
- List of Attributes (Properties and/or Relationships) actually merged.
5.6.18 Replace Entity
5.6.18.1 Description
This operation allows the modification of an existing NGSI-LD Entity by replacing all of the Attributes (Properties or Relationships).
5.6.18.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can replace an entire Entity within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.18.2‑1.
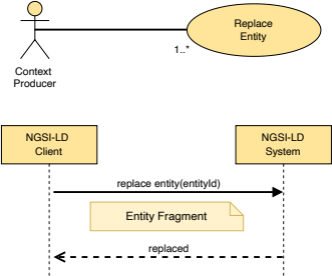
5.6.18.3 Input data
- A URI representing the id of the Entity to be replaced (target Entity).
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17 (optional).
- A JSON-LD document representing an NGSI-LD Entity.
5.6.18.4 Behaviour
- If the target Entity ID is not a valid URI or it is not present, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target Entity, because there is no existing Entity whose id (URI), and where specified type, is equivalent held locally, and no matching registrations apply (see ), then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- The behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation. NGSI-LD Nulls are not supported by this operation.
- If an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration matches against the input data, Attributes from matching input data are forwarded. For each matching registration:
- If the Replace Entity operation is supported by the registration (see clause 4.3.6), matching input data is forwarded to the Registration endpoint.
- If the Replace Entity operation is not supported by the registration, this shall result in an error of type Conflict in case the complete Replace Entity operation failed, or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.
- The matching Attributes are then removed from the Fragment and not processed further.
- For any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the remaining input data, that input data is also forwarded in the case the Replace Entity operation is supported for remote processing to matching endpoints.
- If the target Entity exists locally, completely replace the existing Entity with the same Entity ID with the new Entity content provided. The system generated createdAt Temporal Property of the Entity as defined in clause 4.8 remain unchanged.
5.6.18.5 Output data
None.
5.6.19 Replace Attribute
5.6.19.1 Description
This operation allows the replacement of a single Attribute (Property or Relationship) within an NGSI-LD Entity.
5.6.19.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can carry out a replacement of an Attribute within an Entity within an NGSI-LD System as shown in Figure 5.6.19.2‑1.
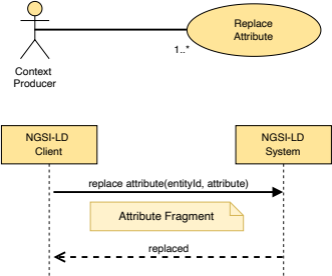
5.6.19.3 Input data
- Entity ID (URI) of the concerned Entity, the target Entity.
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17 (optional).
- Target Attribute (Property or Relationship) to be replaced, identified by a name.
- A JSON-LD document representing an NGSI-LD Attribute Fragment.
5.6.19.4 Behaviour
- If the target Entity ID is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the target Attribute name is not valid, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the target Attribute is scope, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target Entity, because there is no existing Entity whose id (URI), and where specified type, is equivalent held locally, and no matching registrations apply (see ), then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- The behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation.
- If an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration matches against the input data, the input data is forwarded. For each matching registration:
- If the Replace Attribute operation is supported by the registration (see clause 4.3.6), matching input data is forwarded to the Registration endpoint.
- If the Replace Attribute operation is not supported by the registration, this shall result in an error of type Conflict in case the complete Replace Attribute operation failed, or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.
- For any inclusive Context Source Registrations that exist and match against the remaining input data, that input data is also forwarded in the case the Replace Attribute operation is supported for remote processing to matching endpoints.
- Apply term expansion as mandated by clause 5.5.7, so that the fully qualified name (URI) associated to the target Attribute is properly obtained.
- If the target Entity does not contain the target Attribute:
- as a default instance in case no datasetId is present;
- as an instance with the specified datasetId if present;
- then this shall result in an error of type ResourceNotFound in case the complete Replace Attribute operation failed, or in a partial success if some parts of it succeeded.
- Completely replace the existing Attribute with the new Attribute content provided. The system generated createdAt Temporal Property as defined in clause 4.8 remains unchanged.
5.6.19.5 Output data
None.
5.6.20 Batch Entity Merge
5.6.20.1 Description
This operation allows modification of a batch of NGSI-LD Entities according to the JSON Merge Patch processing rules defined in IETF RFC 7396 [16] by adding new attributes (Properties or Relationships) or modifying or deleting existing attributes associated with an existing Entity.
5.6.20.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can merge a batch of Entities within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.20.2‑1.
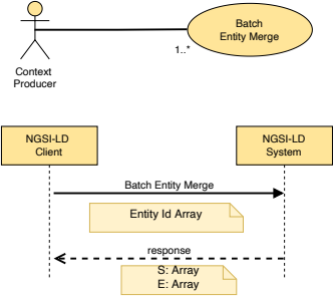
5.6.20.3 Input data
A JSON-LD Array containing one or more JSON-LD documents each one representing an Entity as mandated by clause 5.2.4. See clause 5.5.11.5 for information on behaviour when there is more than one instance of the same entity in the input Array.
5.6.20.4 Behaviour
Implementations shall exhibit the following behaviour:
- Execute the behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation.
- Let S be an array which shall contain a list of Entity IDs, one for each NGSI-LD Entity which was successfully processed. S shall be initialized as the empty array.
- Let E be an array which shall contain a list of BatchEntityError as defined by clause 5.2.17, one for each NGSI-LD Entity which resulted in error. E shall be initialized as the empty array.
- For each Context Source Registration CSR in the Context Registry:
- Let IN be a copy of the original input array.
- Remove from IN all Entities not matched by CSR and remove non-matching Attributes from the remaining Entities.
- Remove all Attributes from the remaining Entities in IN for which there is a matching exclusive Context Source Registration, which is not CSR itself.
- Remove all Attributes from the remaining Entities in IN for which there is a matching redirect Context Source Registration, unless CSR is a redirect Context Source Registration itself.
- Remove all Entities without Attributes from IN.
- If IN is empty, continue with the next Context Source Registration if there is any.
- If the Batch Entity Merge operation is supported by CSR:
- Forward the Batch Entity Merge request with IN as input Array.
- Merge the returned list of Entities successfully created with S.
- Merge the returned list of Entities in Error with E.
- Otherwise, if the Merge Entity operation (clause 5.6.17) is supported by CSR:
- For each Entity EN in the input array:
- Otherwise:
- In case CSR is an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration, add an Error of type Conflict for each Entity in IN to E.
- For each of the NGSI-LD Entities included in the input Array execute the behaviour defined by clause 5.6.17, but limited to a local operation, as follows:
- If the Entity was successfully merged (Attributes updated, appended or deleted), then add the corresponding Entity ID to the S array.
- If the Entity merge failed, then a new BatchEntityError shall be added to E containing the failed Entity ID and the ProblemDetails associated.
5.6.20.5 Output data
- none (if all Entities already existed and are successfully merged); or
- the list of Entities successfully merged (S Array), and the list of Entities in error (E Array), if only some or none of the Entities have been successfully merged.
5.6.21 Purge Entities
5.6.21.1 Description
This operation allows the deletion of entities within an NGSI-LD system based upon a query.
5.6.21.2 Use case diagram
A Context Producer can delete a set of entities which matches a specific query from an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.6.21.2‑1.

5.6.21.3 Input data
- A reference to a JSON-LD @context (optional).
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17 (optional).
Both type names (short hand string) and fully qualified type names (URI) are allowed in the selector. - A list (one or more) of Entity identifiers (optional).
- A restrictive list of Attribute names to be deleted as attributes (optional).
- An exclusionary list Attribute names to be kept as attributes (optional).
- An id pattern as a regular expression (optional).
- An NGSI-LD query (to filter out Entities by Attribute values) as per clause 4.9 (optional).
- An NGSI-LD geoquery (to filter out Entities by spatial relationships) as mandated by clause 4.10 (optional).
- A NGSI-LD Scope query (to filter out Entities based on their Scope) as mandated by clause 4.19 (optional).
- An NGSI-LD query (called context source filter, to filter out Context Sources by the values of properties that describe them) as per clause 4.9 (optional).
In the general case, it is not possible to purge a set of entities by only specifying desired Entity identifiers, without further specifying restrictions on the entities' types or attributes, either explicitly, via selector of Entity types or of Attribute names, or implicitly, within an NGSI-LD Query or GeoQuery. If the execution of the operation is limited to the local scope (see clause 5.5.13), no further restrictions have to be provided.
5.6.21.4 Behaviour
- At least one of the following input data shall be provided:
a) selector of Entity Types;b) list of Attribute names, including at least one non-system Attribute;c) NGSI-LD Query, including at least one non-system Attribute;d) NGSI-LD GeoQuery;e) local scope (see clause 5.5.13).
- If projection attributes are present and indicate the use of Linked Entity retrieval, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the filter conditions specified by the query includes Linked Entity attributes then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- Term to URI expansion of type and Attribute names shall be performed, as mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- Otherwise, implementations shall run a Query Entities operation (clause 5.6.2) to retrieve a list of ids of Entities for deletion, that meet all of the following conditions (given the respective parameter is provided):
[{[--B2plus--]}] id is equal to any of the id(s) passed as a parameter; [{[--B2plus--]}]
- the Entity Type names match the selector of Entity Types (expanded) that is passed as a parameter;
- Attribute matches any of the expanded attribute(s) in the list that is passed as a parameter;
- id matches the id pattern passed as a parameter;
- the filter conditions specified by the query are met (as mandated by clause 4.9);
- the geospatial restrictions imposed by the geoquery are met (as mandated by clause 4.10); if there are multiple instances of the GeoProperty on which the geoquery is based, it is sufficient if any of these instances meets the geospatial restrictions;
- if the Scope query is present, it shall match a present Entity Scope (as mandated by clause 4.19, for an example see annex C, clause C.5.15).And thereafter:
- when no restrictive list of Entity member names is present, the implementation shall delete all Entities that can be found locally using retrieved list of Entity ids;
- when a restrictive list of Entity member names is present, the implementation shall delete the given set of Attributes with those member names from all Entities that can be found locally using retrieved list of Entity ids;
- when an exclusionary list of Entity member names is present, the implementation shall delete all but the given set of Attributes with those member names from all Entities that can be found locally using retrieved list of Entity ids.
- Unless local scope is specified (see clause 5.5.13), for Context Source Registrations that match the query and support the “purgeEntity” operation (see operations and operation groups in clause 4.20), implementations shall do the following:
- If an inclusive, exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration matches against the filter conditions specified, the request is forwarded for remote processing. For each matching registration:
- If the Purge Entity operation is supported by the registration (see clause 4.3.6), matching input data is forwarded to the Registration endpoint.
- If the Purge Entity operation is not supported by the matched registration, this shall result in an error of type Conflict in case the complete purge Entities failed, or in a partial success if some parts of purge Entities succeeded.
5.6.21.5 Output data
None.
5.7 Context Information Consumption
5.7.1 Retrieve Entity
5.7.1.1 Description
This operation allows retrieving an NGSI-LD Entity.
5.7.1.2 Use case diagram
A Context Consumer can retrieve a specific Entity from an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.7.1.2‑1.
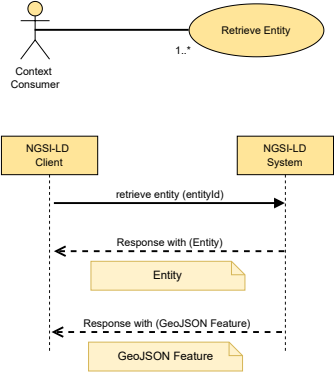
5.7.1.3 Input data
- Entity ID (URI) of the Entity to be retrieved (target Entity).
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17 (optional).
- List of Attribute (Properties or Relationships) names to be retrieved (projection attributes) (optional).
- A restrictive list of Entity member names ("id", "type", "scope" or an Attribute name) to be retrieved (projection attributes as defined by clause 4.21) (optional).
- An exclusionary list of Entity member names ("id", "type", "scope" or an Attribute name) to be removed (projection attributes as defined by clause 4.21) (optional).
- A language filter as defined by clause 4.15 (optional).
- An optional JSON-LD context.
- In the case of a GeoJSON representation:
- The name of the GeoProperty attribute to use as the geometry for the GeoJSON representation as mandated by clause 4.5.16 (optional).
- A datasetId specifying which instance of the value is to be selected if the GeoProperty value has multiple instances as defined by clause 4.5.5 (optional).
- An optional flag indicating whether to include additional Linked Entities corresponding to the Relationships retrieved and how to format those Linked Entities. See clause 4.5.23 (optional).
- A limit to the depth of Linked Entities to search whilst traversing an Entity graph. See clause 4.5.23 (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Linked Entity identifiers previously encountered whilst traversing an Entity graph. See clause 4.5.23 (optional).
- A flag indicating whether to return the location of the EntityMap used within the operation (optional).
- A suggested lifetime for the EntityMap, if EntityMap is to be created (optional).
- The location of a resource holding an EntityMap of matching Entity registrations (optional).
- A datasetId parameter that specifies which Attribute instances are to be selected as defined by clause 4.5.5 (optional).
5.7.1.4 Behaviour
- If the Entity ID is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If geometryProperty parameter is present and the Accept Header is not set to "application/geo+json", then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If projection attributes are present and indicate the use of Linked Entity retrieval and the use of Linked Entity retrieval is not specified, or the projected attribute depth exceeds the Linked Entity retrieval depth, an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target Entity, because there is no existing Entity held locally whose id (URI), and where specified type, is equivalent, and no matching registrations apply, then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- The implementation shall retrieve any Attribute data held locally which is associated with the Entity defined by the Entity ID.
- If the ContextBroker implementation supports the use of EntityMaps then:
- If the location of a resource holding an EntityMap of matching Entity registrations is present it shall be retrieved:
- If the resource cannot be found, or the data has expired, a new EntityMap shall be created.
- If the data has not expired, only the retrieved Entity Map shall be used to determine which Context Source Registrations match the Entity ID.
- If a flag to return an EntityMap was present in the request, and no EntityMap currently exists, then a new EntityMap shall be created.
- For Context Source Registrations that match the Entity ID and support the retrieveEntity operation (see operations and operation groups in clause 4.20), implementations shall do the following:
- If an EntityMap is in use for this operation, and an EntityMap entry linked to a Context Source Registration is found, the location of the linked EntityMap shall be passed as part of any forwarded request.
- For any exclusive, redirect and inclusive Context Source Registrations, the request is forwarded for remote retrieval by matching endpoints, and remote Attribute data for the Entity is received. If an expiresAt DateTime is present on the Entity and the date lies in the past, the Attribute data shall be discarded, otherwise the Attribute data is then merged together according to the algorithm defined in clause 4.5.5.
- For any auxiliary Context Source Registrations the remote Attribute data received is added to the payload only when an Attribute is not present in any of the Attribute data received elsewhere.
- If an EntityMap is in use for this operation, the EntityMap's linked maps are updated to hold the location of every EntityMap used by the Context Source Registrations.
- Term to URI expansion of Attribute names shall be observed as mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- For each Attribute found in the target Entity, when the datasetId parameter is provided in the request:
- Filter the Attribute instances based on the datasetId parameter, i.e. keep only the Attribute instances whose datasetId is specified. The default Attribute instance is matched, if "@none" is specified.
- If there is no Attribute instance whose datasetId matches the value of the parameter, the Attribute shall not be returned with the Entity.
- If the optional Attribute list is present and the NGSI-LD endpoint does know about a matching Entity for the Entity ID, but this Entity does not have any of the Attributes in the Attribute list, then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- If the Accept Header is set to "application/json" or "application/ld+json", return a JSON-LD object representing the Entity as mandated by clause 5.2.4 and containing only the Attributes requested (if present).
- If the Prefer Header [26] is set to "ngsi-ld=<version>" then the ContextBroker shall endeavour to amend the JSON-LD object to conform to the specified version of the NGSI-LD specification as mandated in clause 4.3.6.8, and return a Preference-Applied Header set to "ngsi-ld=<conformant-version>" in the response.
- If the Accept Header is set to "application/geo+json", a GeoJSON Feature object representing the entity as mandated by clause 5.2.29 and containing only the Attributes requested (if present):
- If the Prefer Header is omitted or set to "body=ld+json" then the Feature object will also contain an @context field.
- If the Prefer Header is set to "body=json" the @context is set as a Link Header and removed from the Feature object.
5.7.1.5 Output data
A JSON-LD object representing the target Entity as mandated by clause 5.2.4 or a GeoJSON Feature as mandated by clause 5.2.29.
If a restrictive list of Entity member names is present, every Entity within the payload body is reduced down to only contain the defined Entity members.
If an exclusionary list of Entity member names is present, the defined Entity members listed are removed from each Entity within the payload.
If any of the returned Attributes corresponds to a VocabProperty, the returned value shall be compacted according to the supplied @context.
If a language filter is specified and any of the returned Attributes corresponds to a LanguageProperty, the LanguageProperty in question shall be converted into a Property. The value of this Property shall correspond to the value of the string or strings from the matching key-value pair of the languageMap where the key matches the language filter. A non-reified subproperty lang shall be included in the response indicating the chosen language.
If no match can be made for a LanguageProperty then a single language shall be chosen, up to the implementation.
If inline Linked Entity retrieval (see clause 4.5.23.2) is specified, and any of the returned Attributes corresponds to an annotated Relationship, then unless a URI has been previously encountered, an entity sub-Property shall be included in the response holding the Linked Entity data for each URI corresponding to that Relationship's target object URI. If any of the returned Attributes corresponds to an annotated ListRelationship, then an entityList subproperty shall be included in the response holding the ordered array of Linked Entities corresponding to that ListRelationship's target objectList URIs unless a URI has been previously encountered.
If flattened Linked Entity retrieval (see clause 4.5.23.3) is specified, the response shall be an array of JSON-LD objects representing the target entity itself and the targets of its Relationships. If any of the returned Attributes corresponds to an annotated Relationship, unless a target URI has been previously encountered, the data corresponding to each URI of the Relationship's target object URIs is appended to the array. If any of the returned Attributes corresponds to an annotated ListRelationship, then an ordered array of additional Linked Entities is appended to the array which hold the data corresponding to each of the URIs found within ListRelationship's target objectList unless a URI has been previously encountered.
If the location of a previously generated EntityMap was passed into the request, or a flag to return an EntityMap was present in the request, the location of the EntityMap used in the operation shall be returned in a specific field in the response.
5.7.2 Query Entities
5.7.2.1 Description
This operation allows querying an NGSI-LD system.
5.7.2.2 Use case diagram
A Context Consumer can retrieve a set of entities which matches a specific query from an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.7.2.2‑1.
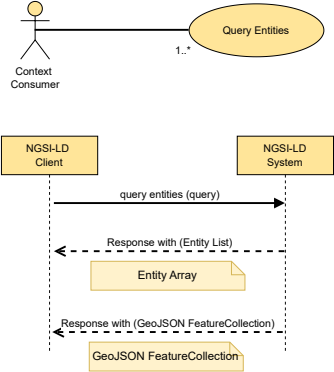
5.7.2.3 Input data
- A reference to a JSON-LD @context (optional).
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17 (optional).
Both type names (short hand string) and fully qualified type names (URI) are allowed in the selector. - A list (one or more) of Entity identifiers (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Attribute names of which at least one shall exist in order for an Entity to be selected, and also used as query projection attributes (optional).
- A restrictive list of Entity member names ("id", "type", "scope" or an Attribute name) to be retrieved (projection attributes as defined by clause 4.21) (optional).
- An exclusionary list member names ("id", "type", "scope" or an Attribute name) to be removed (projection attributes as defined by clause 4.21) (optional).
- An id pattern as a regular expression (optional).
- An NGSI-LD query (to filter out Entities by Attribute values) as per clause 4.9 (optional).
- An NGSI-LD geoquery (to filter out Entities by spatial relationships) as mandated by clause 4.10 (optional).
- In the case of GeoJSON representation:
- The name of the GeoProperty attribute to use as the geometry for the GeoJSON representation as mandated by clause 4.5.16 (optional).
- A datasetId specifying which instance of the value is to be selected if the GeoProperty value has multiple instances as defined by clause 4.5.5 (optional).
- A NGSI-LD Scope query (to filter out Entities based on their Scope) as mandated by clause 4.19 (optional).
- An NGSI-LD query (called context source filter, to filter out Context Sources by the values of properties that describe them) as per clause 4.9 (optional).
- A limit to the number of Entities to be retrieved. See clause 5.5.9.
- A specified language filter as per clause 4.15 (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Attribute names whose values shall be expanded to URIs prior to executing a query (optional).
- An optional flag indicating whether to include additional Linked Entities corresponding to the Relationships retrieved and how to format those Linked Entities. See clause 4.5.23 (optional).
- A limit to the depth of Linked Entities to search whilst traversing an Entity Graph. See clause 4.5.23 (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Linked Entity identifiers previously encountered whilst traversing an Entity Graph. See clause 4.5.23 (optional).
- A flag indicating whether to return the location of the EntityMap used within the operation (optional).
- A suggested lifetime for the EntityMap, if EntityMap is to be created (optional).
- The location of a resource holding an EntityMap of matching Entity registrations (optional).
- A datasetId parameter that specifies which Attribute instances are to be selected as defined by clause 4.5.5 (optional).
- A flag indicating whether split Entities are to be expected, i.e. Entities whose information is distributed across different Context Sources (optional).
In the general case, it is not possible to retrieve a set of entities by only specifying desired Entity identifiers, without further specifying restrictions on the entities' types or attributes, either explicitly, via selector of Entity types or of Attribute names, or implicitly, within an NGSI-LD Query or GeoQuery. If the execution of the operation is limited to the local scope (see clause 5.5.13), no further restrictions have to be provided.
5.7.2.4 Behaviour
- At least one of the following input data shall be provided:
- If projection attributes are present and indicate the use of Linked Entity retrieval, and the use of Linked Entity retrieval is not specified, or the projected attribute depth exceeds the Linked Entity retrieval depth, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the filter conditions specified by the query includes Linked Entity attributes, and the use of Linked Entity retrieval is not specified, or the Linked Entity attribute query depth exceeds the Linked Entity retrieval depth, an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised (too deep query).
- If geometryProperty parameter is present and the Accept Header is not set to "application/geo+json", then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- Otherwise,
- Term to URI expansion of type and Attribute names shall be performed, as mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- If a list of Attribute names whose values shall be expanded to URIs has been supplied, JSON-LD type coercion shall be performed as mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- If split entities flag is explicitly set to true or, if not explicitly set, the default setting of the deployment allows split entities, and local scope is not specified, implementations shall run a query that shall return an Entity Array containing all the Entities found locally, that meet all of the following conditions (given the respective parameter is provided):
- id is equal to any of the id(s) passed as a parameter;
- the Entity Type names match the selector of Entity Types (expanded) that is passed as a parameter;
- id matches the id pattern passed as a parameter.
- otherwise, implementations shall run a query that shall return an Entity Array containing all the Entities found locally, that meet all of the following conditions (given the respective parameter is provided):
- id is equal to any of the id(s) passed as a parameter;
- the Entity Type names match the selector of Entity Types (expanded) that is passed as a parameter;
- Attribute matches any of the expanded attribute(s) in the list that is passed as a parameter;
- id matches the id pattern passed as a parameter;
- the filter conditions specified by the query are met (as mandated by clause 4.9);
- the geospatial restrictions imposed by the geoquery are met (as mandated by clause 4.10); if there are multiple instances of the GeoProperty on which the geoquery is based, it is sufficient if any of these instances meets the geospatial restrictions;
- if the Scope query is present, it shall match a present Entity Scope (as mandated by clause 4.19, for an example see annex C, clause C.5.15);
- if the Attribute list is present, in order for an Entity to match, it shall contain at least one of the Attributes in the projection Attribute list.
- If the ContextBroker implementation supports the use of EntityMaps then:
- If the location of a resource holding an EntityMap of matching Entity registrations is present it shall be retrieved:
- If the resource cannot be found, or the data has expired, a new EntityMap shall be created.
- If the data has not expired, only the retrieved EntityMap shall be used to determine which Context Source Registrations match the Entity ID.
- If a flag to return an EntityMap was present in the request, and no EntityMap currently exists, then a new EntityMap shall be created.
- Unless local scope is specified (see clause 5.5.13), for Context Source Registrations that match the query and support the "queryEntity" operation (see operations and operation groups in clause 4.20), implementations shall do the following:
- If an EntityMap is in use for this operation, and an EntityMap entry linked to a Context Source Registration is found, the location of the EntityMap shall be passed as part of the forwarded request.
- If split entities flag is explicitly set to true or, if not explicitly set, the default setting of the deployment allows split entities, the filters (filter conditions specified by the query, geospatial restrictions imposed by the geoquery, Scope query, Attributes) shall be removed before forwarding the request. These filters then have to be applied after the Entity information from different Context Sources and local information, if there is any, has been aggregated.
- For any exclusive, redirect and inclusive Context Source Registrations, the request is forwarded for remote querying by matching endpoints. The result of each remote query is an Entity Array. Within each Entity Array, any Entities where an expiresAt DateTime is present and the date lies in the past shall be discarded. The Entity Arrays are then merged together with the locally queried result according to the algorithm defined in clause 4.5.5.
- For any auxiliary Context Source Registrations, the request is forwarded for remote querying by matching endpoints. Data from the Entity Array received is added to the payload only when an Attribute is not already present in the merged Entity Arrays are received elsewhere.
- If split Entities flag is explicitly set to true or, if not explicitly set, the default setting of the deployment allows split Entities, and local scope is not specified, the following filters shall be applied on the aggregated Entities:
- the filter conditions specified by the query are met (as mandated by clause 4.9);
- the geospatial restrictions imposed by the geoquery are met (as mandated by clause 4.10); if there are multiple instances of the GeoProperty on which the geoquery is based, it is sufficient if any of these instances meets the geospatial restrictions;
- if the Scope query is present, it shall match a present Entity Scope (as mandated by clause 4.19, for an example see annex C, clause C.5.15);
- if the Attribute list is present, in order for an Entity to match, it shall contain at least one of the Attributes in the projection Attribute list.
- Pagination logic shall be in place as mandated by clause 5.5.9.
If in the process of obtaining the query result it is necessary to issue a Context Source discovery operation, the same Context Source filter input parameter (if present) shall be propagated.
- For each Attribute found in the target Entity, when datasetId parameter is provided in the request:
- Filter the Attribute instances based on the datasetId parameter, i.e. keep only the Attribute instances whose datasetId is specified. The default Attribute instance is matched, if "@none" is specified.
- If there is no Attribute instance whose datasetId matches the value of the parameter, the Attribute shall not be returned with the Entity.
- If the Accept Header is set to "application/json" or "application/ld+json", a JSON-LD array is returned, representing the Entities as mandated by clause 5.2.4 and containing only the Attributes requested (if present).
- If the Prefer Header [26] is set to "ngsi-ld=<version>" then the ContextBroker shall endeavour to amend the elements of the JSON-LD array to conform to the specified version of the NGSI-LD specification as mandated in clause 4.3.6.8, and return a Preference-Applied Header set to "ngsi-ld=<conformant-version>" in the response.
- If the Accept Header is set to "application/geo+json", the response shall be a GeoJSON FeatureCollection as mandated by clause 5.2.30, with each Feature within the FeatureCollection containing only the Attributes requested (if present):
- If the Prefer Header is omitted or set to "body=ld+json" then the FeatureCollection will also contain an @context field.
- If the Prefer Header is set to "body=json" the @context is sent as a Link Header and removed from the FeatureCollection object.
5.7.2.5 Output data
A JSON-LD array representing the matching entities as defined by clause 5.2.4 or in the case of GeoJSON requests a FeatureCollection as mandated by clause 5.2.30. For each matching Entity, only the Attributes specified by the Attribute list parameter shall be included. If such parameter is not present, then all Attributes shall be included.
If a restrictive list of Entity member names is present, every Entity within the payload body is reduced down to only contain the defined Entity members.
If an exclusionary list of Entity member names is present, the defined Entity members listed are removed from each Entity within the payload.
If any of the returned Attributes corresponds to a VocabProperty, the returned value shall be compacted according to the supplied @context.
If a language filter is specified and any of the returned Attributes corresponds to a LanguageProperty, the LanguageProperty in question shall be converted into a Property. The value of this Property shall correspond to the value of the string or strings from matching key-value pair of the languageMap where the key matches the language filter. A non-reified subproperty lang shall be included in the response indicating the chosen language.
If no match can be made for a LanguageProperty, then the default identified by the JSON-LD "@none" shall be chosen if present, otherwise the choice of a single language is up to the implementation.
If inline Linked Entity retrieval (see clause 4.5.23.2) is specified, and any of the returned Attributes corresponds to an annotated Relationship, then unless a URI has been previously encountered, an entity subproperty shall also be included in the response holding the data for each URI corresponding to that Relationship's target object URIs. If any of the returned Attributes corresponds to an annotated ListRelationship, then an entityList subproperty shall also be included in the response holding the ordered data corresponding to that ListRelationship's target objectList URIs, unless a URI has been previously encountered.
If flattened Linked Entity retrieval (see clause 4.5.23.3) is specified, the response shall be an array of JSON-LD objects representing the matching entities and the targets of their Relationships. If any of the returned Attributes corresponds to an annotated Relationship, unless a URI has been previously encountered, then data for each URI corresponding to the Relationship's target object URIs is appended to the array. If any of the returned Attributes corresponds to an annotated ListRelationship, then an array of additional Linked Entities is appended to the array which hold the data corresponding to each of the URIs found within ListRelationship's target objectList unless a URI has been previously encountered.
If the location of a previously generated EntityMap was passed into the request, or a flag to return an EntityMap was present in the request, the location of the EntityMap used in the operation shall be returned in a specific field in the response.
5.7.3 Retrieve Temporal Evolution of an Entity
5.7.3.1 Description
This operation allows retrieving the Temporal Evolution of an Entity.
5.7.3.2 Use case diagram
A Context Consumer can retrieve the Temporal Evolution of an Entity (in the form of a temporal representation) from an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.7.3.2‑1.
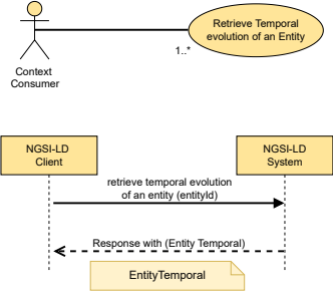
5.7.3.3 Input data
- Entity ID (URI) of the target Temporal Evolutionof an Entity to be retrieved.
- List of Attribute (Properties or Relationships) names to be retrieved (projection attributes) (optional).
- A restrictive list of Entity member names ("id", "type", "scope" or an Attribute name) to be retrieved (projection attributes as defined by clause 4.21) (optional).
- An exclusionary list of Entity member names ("id", "type", "scope" or an Attribute name) to be removed (projection attributes as defined by clause 4.21) (optional).
- An NGSI-LD temporal query as mandated by clause 4.11 (optional).
- A parameter (lastN) conveying that only the last N instances (per Attribute) within the concerned temporal interval shall be retrieved (optional).
- An optional JSON-LD context.
- A flag indicating whether to return the location of the EntityMap used within the operation (optional).
A suggested lifetime for the EntityMap, if EntityMap is to be created (optional).
- The location of a resource holding an EntityMap of matching Entity registrations (optional).
- A datasetId parameter that specifies which Attribute instances are to be selected as defined by clause 4.5.5 (optional).
5.7.3.4 Behaviour
- If the Entity ID is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If projection attributes are present and indicate the use of Linked Entity retrieval, an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target Entity, because there is no existing Entity whose id (URI) is equivalent held locally, and no matching registrations apply, then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- Term to URI expansion of Attribute names shall be observed as mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- The lastN parameter refers to a number, n, of Attribute instances which shall correspond to the last n timestamps (in descending ordering) of the temporal property (by default observedAt) within the concerned temporal interval.
- Let S be the Temporal Evolution of the Entity as mandated by clause 5.2.20 with the specified Entity ID as it is available locally. S is empty in case no Temporal Evolution of the Entity is available locally.
- From S, select only those Attribute instances (corresponding to the Attributes specified by the query or all if none are specified) match the temporal restrictions imposed by the temporal query (as mandated by clause 4.11); i.e. if the time series, for all the concerned Attributes of an Entity, does not include data corresponding to the temporal query interval, then such Entity shall be removed from S, thus it shall not appear in the final result set. Let S1 be this new subset.
- If the ContextBroker implementation supports the use of EntityMaps then:
- If the location of a resource holding an EntityMap of matching Entity registrations is present it shall be retrieved:
- If the resource cannot be found, or the data has expired, a new EntityMap shall be created.
- If the data has not expired, only the retrieved Entity Map shall be used to determine which Context Source Registrations match the Entity ID.
- If a flag to return an EntityMap was present in the request, and no EntityMap currently exists, then a new EntityMap shall be created.
- For Context Source Registrations that match the Entity ID and support the "retrieveTemporal" operation (see operations and operation groups in clause 4.20), implementations shall do the following:
- If an EntityMap is in use for this operation, and an EntityMap entry linked to a Context Source Registration is found, the location of the linked EntityMap shall be passed as part of any forwarded request.
- For any exclusive, redirect and inclusive Context Source, the request is forwarded for remote retrieval by matching endpoints. and remote Attribute data for the Entity is received. The result is then merged together with S1 according to the algorithm defined in clause 4.5.5.
- For any auxiliary Context Source Registrations the remote Attribute data received is added to S1 only when the Attribute instance, whose value of the timeproperty, which is used for the temporal query (observedAt as default), is not present in any of the Attribute instances received from elsewhere.
- If an EntityMap is in use for this operation, the EntityMap's linked maps are updated to hold the location of every EntityMap used by the Context Source Registrations.
- For the set of Attribute Instances that are in S1, when datasetId parameter is provided in the request:
- Filter the Attribute instances based on the datasetId parameter, i.e. keep only the Attribute instances whose datasetId is specified. The default Attribute instance is matched, if "@none" is specified.
- If there is no Attribute instance whose datasetId matches the value of the parameter, remove the complete Attribute from S1.
- From the set of Attribute Instances that are in S1, include in their temporal representation only the Attribute instances (up to lastN) corresponding to the query's projection Attributes, or aggregated values of Attribute instances (if aggregated temporal representation is requested).
In the general case, it is not possible to retrieve a set of entities by only specifying desired Entity identifiers, without further specifying restrictions on the entities' types or attributes, either explicitly, via selector of Entity types or of Attribute names, or implicitly, within an NGSI-LD Query or GeoQuery. If the execution of the operation is limited to the local scope (see clause 5.5.13), no further restrictions have to be provided.
5.7.3.5 Output data
A JSON-LD object representing the Temporal Evolution of the target Entity as mandated by clause 5.2.20.
If a restrictive list of Entity member names is present, every Entity within the payload body is reduced down to only contain the defined Entity members.
If an exclusionary list of Entity member names is present, the defined Entity members listed are removed from each Entity within the payload.
5.7.4 Query Temporal Evolution of Entities
5.7.4.1 Description
This operation allows querying the Temporal Evolution of Entities present in an NGSI-LD system. It is similar to the operation defined by clause 5.7.2 (Query Entities) with the addition of a temporal query.
5.7.4.2 Use case diagram
A Context Consumer can retrieve the Temporal Evolution of a set of Entities which matches a specific query from an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.7.4.2‑1.
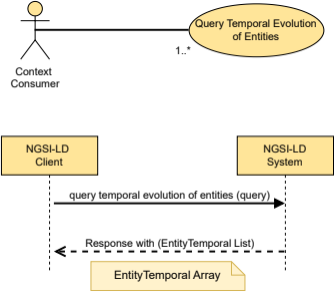
5.7.4.3 Input data
- An NGSI-LD temporal query as mandated by clause 4.11.
- A reference to a JSON-LD @context (optional).
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17 (optional).
Both type name (short hand string) and fully qualified type name (URI) are allowed. - A restrictive list of Entity member names ("id", "type", "scope" or an Attribute name) to be retrieved (projection attributes as defined by clause 4.21) (optional).
- An exclusionary list of Entity member names ("id", "type", "scope" or an Attribute name) to be removed (projection attributes as defined by clause 4.21) (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Entity identifiers (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Attribute names of which at least one shall exist in order for an Entity to be selected, and also used as query projection attributes (optional).
- An id pattern as a regular expression (optional).
- An NGSI-LD query (to filter out Entities by Attribute values) as per clause 4.9 (optional).
- An NGSI-LD geoquery (to filter out Entities by spatial relationships) as mandated by clause 4.10 (optional).
- A NGSI-LD Scope query (to filter out Entities based on their Scope) as mandated by clause 4.19 (optional).
- An NGSI-LD query (called context source filter, to filter out Context Sources by the values of properties that describe them) as per clause 4.9 (optional).
- A limit to the number of Entities to be retrieved. See clause 5.5.9.
- A parameter (lastN) conveying that only the last N instances (per Attribute) within the concerned temporal interval shall be retrieved (optional).
- A specified language filter as per clause 4.15 (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Attribute names whose values shall be expanded to URIs prior to executing a query (optional).
- A flag indicating whether to return the location of the EntityMap used within the operation (optional).
A suggested lifetime for the EntityMap, if EntityMap is to be created (optional).
- The location of a resource holding an EntityMap of matching Entity registrations (optional).
- A datasetId parameter that specifies which Attribute instances are to be selected as defined by clause 4.5.5 (optional).
A flag indicating whether split Entities are to be expected, i.e. Entities whose information is distributed across different Context Sources (optional).
In the general case, it is not possible to retrieve a set of entities by only specifying desired Entity identifiers, without further specifying restrictions on the entities' types or attributes, either explicitly, via selector of Entity types or of Attribute names, or implicitly, within an NGSI-LD query or geoquery. If the execution of the operation is limited to the local scope (see clause 5.5.13), no further restrictions have to be provided.
5.7.4.4 Behaviour
- If a temporal query is not provided then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- At least one of the following input data shall be provided:
- If projection attributes or filter conditions indicate the use of Linked Entity retrieval, an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- Term to URI expansion of type and Attribute names shall be observed mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- If a list of Attribute names whose values shall be expanded to URIs has been supplied, JSON-LD type coercion shall be performed as mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- The lastN parameter refers to a number, n, of Attribute instances which shall correspond to the last n timestamps (in descending ordering) of the temporal property (by default observedAt) within the concerned temporal interval.
- Otherwise,
- Let S be the set of selected Entities i.e. the query result set.
- If split entities flag is explicitly set to true or, if not explicitly set, the default setting of the deployment allows split entities, and local scope is not specified, implementations shall run a query that shall return an Entity Array containing all the Entities found locally, that meet all of the following conditions (given the respective parameter is provided):
If id(s) is provided, keep in S only those Entities whose id is equivalent to any of the id(s) passed as a parameter.
If an id pattern is provided, keep in S only those Entities whose id matches the id pattern.
If a selector of Entity Types is provided, keep in S only those Entities whose Entity Type names match the selector of Entity Types.
From S, select only those Entities any of whose Attribute instances (corresponding to the Attributes specified by the query or all if none are specified) match the temporal restrictions imposed by the temporal query (as mandated by clause 4.11); i.e. if the time series, for all the concerned Attributes of an Entity, does not include data corresponding to the temporal query interval, then such Entity shall be removed from S, thus it shall not appear in the final result set. Let S4 be this new subset.
- Implementations shall run a query that shall return the Temporal Evolution of the matching Entities (all Entities stored locally, in case only a local scope is specified); the logical steps to select the final result set of Entities, and the Attribute instances included as part of their temporal representation, are enumerated as follows:
If id(s) is provided, keep in S only those Entities whose id is equivalent to any of the id(s) passed as a parameter.
If an id pattern is provided, keep in S only those Entities whose id matches the id pattern.
If a selector of Entity Types is provided, keep in S only those Entities whose Entity Type names match the selector of Entity Types.
From S, select only those Entities any of whose Attribute instances (corresponding to the Attributes specified by the query or all if none are specified) match the temporal restrictions imposed by the temporal query (as mandated by clause 4.11); i.e. if the time series, for all the concerned Attributes of an Entity, does not include data corresponding to the temporal query interval, then such Entity shall be removed from S, thus it shall not appear in the final result set. Let S1 be this new subset.
If a values filter query is provided, from S1, select those Entities whose Attribute instances (during the interval defined by the temporal query) meet the matching conditions specified by the query (as mandated by clause 4.9); i.e. the values filter query shall be checked against all the Attribute instances resulting from the initial filtering performed by the temporal query. Let S2 be this new subset.
If no values filter query is provided, then S2 is equal to S1.
If geoquery is present, from S2, select those Entities whose GeoProperty instances meet the geospatial restrictions imposed by the geoquery (as mandated by clause 4.10); those geospatial restrictions shall be checked against the GeoProperty instances that are within the interval defined by the temporal query. Let S3 be this new subset.
If no geoquery is provided, then S3 is equal to S2.
If the Scope query is present, from S3, select those Entities whose Entity Scope instances match the Scope query (as mandated by clause 4.19, for an example see annex C, clause C.5.16). Let S4 be the new subset.
If no Scope query is provided, then S4 is equal to S3.
- If the ContextBroker implementation supports the use of EntityMaps then:
- If the location of a resource holding an EntityMap of matching Entity registrations is present it shall be retrieved:
If the resource cannot be found, or the data has expired, a new EntityMap shall be created.
If the data has not expired, only the retrieved EntityMap shall be used to determine which Context Source Registrations match the Entity ID.
- If a flag to return an EntityMap was present in the request, and no EntityMap currently exists, then a new EntityMap shall be created.
- Unless local scope is specified (see clause 5.5.13), for Context Source Registrations that match the query and support the "queryTemporal" operation (see operations and operation groups in clause 4.20), implementations shall do the following:
- If an EntityMap is in use for this operation, and an EntityMap entry linked to a Context Source Registration is found, the location of the EntityMap shall be passed as part of the forwarded request.
If split entities flag is explicitly set to true or, if not explicitly set, the default setting of the deployment allows split entities, the filters (filter conditions specified by the query, geospatial restrictions imposed by the geoquery, Scope query, Attributes) shall be removed before forwarding the request. These filters then have to be applied after the Entity information from different Context Sources and local information, if there is any, has been aggregated.
- For any exclusive, redirect and inclusive Context Source Registrations that match against the query, the request is forwarded for remote querying by matching endpoints. The result of each remote query is an Entity Array. The returned result is then merged into S4 according to the algorithm defined in clause 4.5.5.
- For any auxiliary Context Source Registrations that match against the query, the request is forwarded for remote querying by matching endpoints. Data from the Entity Array received is merged only into S4 when an Attribute instance, whose value of the timeproperty used for the temporal query, is not already present in S4.
- If split entities flag is explicitly set to true or, if not explicitly set, the default setting of the deployment allows split entities, and local scope is not specified, the following filters have to be applied on the aggregated Entities:
If a values filter query is provided, from S4, select those Entities whose Attribute instances (during the interval defined by the temporal query) meet the matching conditions specified by the query (as mandated by clause 4.9); i.e. the values filter query shall be checked against all the Attribute instances resulting from the initial filtering performed by the temporal query. Let S5 be this new subset.
If no values filter query is provided, then S5 is equal to S4.
If geoquery is present, from S5, select those Entities whose GeoProperty instances meet the geospatial restrictions imposed by the geoquery (as mandated by clause 4.10); those geospatial restrictions shall be checked against the GeoProperty instances that are within the interval defined by the temporal query. Let S6 be this new subset.
If no geoquery is provided, then S6 is equal to S5.
If the Scope query is present, from S6, select those Entities whose Entity Scope instances match the Scope query (as mandated by clause 4.19, for an example see annex C, clause C.5.16). Let S7 be the new subset.
If no Scope query is provided, then S7 is equal to S6.
- Otherwise S7 is equal to S4
- If a datasetId parameter is provided, from S7, for all Entities, filter the Attribute instances based on the datasetIds specified in the parameter, i.e. keep only the Attribute instances whosedatasetId is specified. The default Attribute instance is matched, if "@none" is specified. Remove all Attributes without remaining Attribute instances. Let S8 be this new subset.
- If no datasetId is provided then S8 equals to S7.
- From the set of Entities that are in S8, include in their temporal representation only the Attribute instances (up to lastN) corresponding to the query's projection Attributes, or aggregated values of Attribute instances (if aggregated temporal representation is requested), and which meet the temporal, query and geoquery restrictions.If an aggregated temporal representation is requested and any of the requested Attributes is not eligible for at least one of the aggregation methods specified in the request parameters, then an error of type InvalidRequest shall be raised.
- Pagination logic shall be in place as mandated by clause 5.5.9.
- If in the process of obtaining the query result it is necessary to issue a Context Source discovery operation, the same Context Source filter input parameter (if present) shall be propagated.
5.7.4.5 Output Data
A JSON-LD array representing the matching entities as defined by clause 5.2.21 and selected according to the behaviour described by clause 5.7.4.4.
If a restrictive list of Entity member names is present, every Entity within the payload body is reduced down to only contain the defined Entity members.
If an exclusionary list of Entity member names is present, the defined Entity members listed are removed from each Entity within the payload.
5.7.5 Retrieve Available Entity Types
5.7.5.1 Description
This operation allows retrieving a list of NGSI-LD entity types for which entity instances exist within the NGSI-LD system.
5.7.5.2 Use case diagram
A Context Consumer can retrieve a list of NGSI-LD entity types from the system as shown in Figure 5.7.5.2‑1.
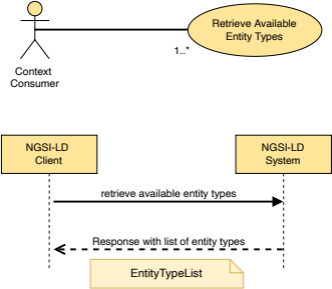
5.7.5.3 Input data
- An optional JSON-LD context.
5.7.5.4 Behaviour
- Return a JSON-LD object representing the list of entity types, as mandated by clause 5.2.24, for which entity instances exist within the NGSI-LD system. See clause 5.7.11 for architecture-related implementation aspects.
5.7.5.5 Output data
A JSON-LD object representing the list of available entity types, as mandated by clause 5.2.24.
5.7.6 Retrieve Details of Available Entity Types
5.7.6.1 Description
This operation allows retrieving a list with a detailed representation of NGSI-LD entity types for which entity instances exist within the NGSI-LD system. The detailed representation includes the type name (as short name if available in the provided @context) and the attribute names that existing instances of this entity type have.
5.7.6.2 Use case diagram
A Context Consumer can retrieve a list with a detailed representation of NGSI-LD entity types from the system as shown in Figure 5.7.6.2‑1.
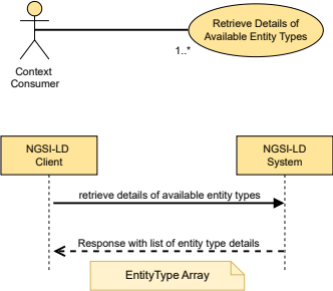
5.7.6.3 Input data
- An optional JSON-LD context.
5.7.6.4 Behaviour
- Return a list of JSON-LD objects representing the details of available entity types as mandated by clause 5.2.25 for which entity instances exist within the NGSI-LD system. See clause 5.7.11 for architecture-related implementation aspects.
5.7.6.5 Output data
A list of JSON-LD objects representing the details of available entity types as mandated by clause 5.2.25.
5.7.7 Retrieve Available Entity Type Information
5.7.7.1 Description
This operation allows retrieving detailed entity type information about a specified NGSI-LD entity type for which entity instances exist within the NGSI-LD system. The detailed representation includes the type name (as short name if available in the provided @context), the count of available entity instances and details about attributes that existing instances of this entity type have, including their name (as short name if available in the provided @context) and a list of types the attribute can have (e.g. Property, Relationship or GeoProperty).
5.7.7.2 Use case diagram
A Context Consumer can retrieve a detailed representation of a specified NGSI-LD entity type from the system as shown in Figure 5.7.7.2‑1.
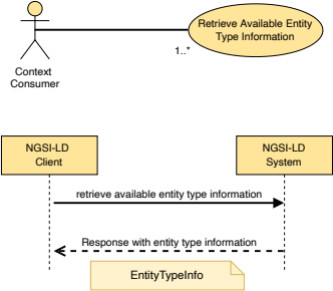
5.7.7.3 Input data
- Entity type name for which detailed information is to be retrieved.
- An optional JSON-LD context.
5.7.7.4 Behaviour
- Return a JSON-LD object representing the details of the specified entity type as mandated by clause 5.2.26, for which instances exist within the NGSI-LD system. See clause 5.7.11 for architecture-related implementation aspects.
5.7.7.5 Output data
A JSON-LD object representing the details of the specified entity type as mandated by clause 5.2.26.
5.7.8 Retrieve Available Attributes
5.7.8.1 Description
This operation allows retrieving a list of NGSI-LD attributes that belong to entity instances existing within the NGSI-LD system.
5.7.8.2 Use case diagram
A Context Consumer can retrieve a list of NGSI-LD attributes from the system as shown in Figure 5.7.8.2‑1.
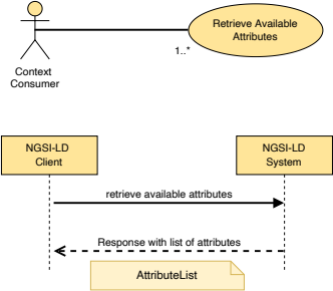
5.7.8.3 Input data
- An optional JSON-LD context.
5.7.8.4 Behaviour
- Return a JSON-LD object representing the list of attributes as mandated by clause 5.2.27 that belong to entity instances existing within the NGSI-LD system. See clause 5.7.11 for architecture-related implementation aspects.
5.7.8.5 Output data
A JSON-LD object representing the list of available attributes as mandated by clause 5.2.27.
5.7.9 Retrieve Details of Available Attributes
5.7.9.1 Description
This operation allows retrieving a list with a detailed representation of NGSI-LD attributes that belong to entity instances existing within the NGSI-LD system. The detailed representation includes the attribute name (as short name if available in the provided @context) and the type names for which entity instances exist that have the respective attribute.
5.7.9.2 Use case diagram
A context consumer can retrieve a list with a detailed representation of NGSI-LD attributes from the system as shown in Figure 5.7.9.2‑1.
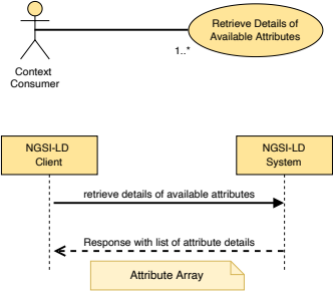
5.7.9.3 Input data
An optional JSON-LD context.
5.7.9.4 Behaviour
Return a list of JSON-LD objects representing the details of available attributes as mandated by clause 5.2.28 (restricted to the elements id, type, attributeName and typeNames) that belong to entity instances existing within the NGSI-LD system. See clause 5.7.11 for architecture-related implementation aspects.
5.7.9.5 Output data
A list of JSON-LD objects representing the details of available attributes as mandated by clause 5.2.28 (restricted to the elements id, type, attributeName and typeNames).
5.7.10 Retrieve Available Attribute Information
5.7.10.1 Description
This operation allows retrieving detailed attribute information about a specified NGSI-LD attribute that belongs to entity instances existing within the NGSI-LD system. The detailed representation includes the attribute name (as short name if available in the provided @context) and the type names for which entity instances exist that have the respective attribute, a count of available attribute instances and a list of types the attribute can have (e.g. Property, Relationship or GeoProperty).
5.7.10.2 Use case diagram
A context consumer can retrieve a list with a detailed representation of NGSI-LD attributes from the system as shown in Figure 5.7.10.2‑1.
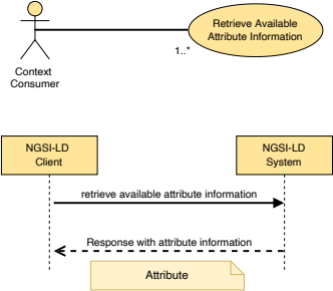
5.7.10.3 Input data
- Name of the attribute for which detailed information is to be retrieved.
- An optional JSON-LD context.
5.7.10.4 Behaviour
Return a JSON-LD object representing the details of available attributes as mandated by clause 5.2.28 that belong to entity instances existing within the NGSI-LD system. See clause 5.7.11 for architecture-related implementation aspects.
5.7.10.5 Output data
A JSON-LD object representing the details of available attributes as mandated by clause 5.2.28.
5.7.11 Architecture-related aspects of retrieval of Entity Types and Attributes
Retrieving information about available types or attributes can be an expensive operation depending on the scale and architectural design decisions of the NGSI-LD system. This is in particular the case for retrieving the information about all available entity types and attributes related to all entity information available in an NGSI-LD system. Especially in the case of distributed architecture (clause 4.3.3) and federated architecture (clause 4.3.4) checking all entities can be so expensive that it can become practically infeasible.
Therefore, implementations may only take into account only information that is available or can be derived from a local datastore and the Context Registry, when implementing the retrieval of available entity types and attributes, as described in clauses 5.7.5, 5.7.6, 5.7.7, 5.7.8, 5.7.9 and 5.7.10. Context registrations do not always reflect which entity instances are actually available from a Context Source at a particular point in time, but only which entity instances are possibly available from a Context Source, thus in this case the information about available entity types and attributes is to be interpreted as "possibly available". Also, context registrations can have different granularities, i.e. they possibly only contain entity type or attribute information, and thus the provided information about available entity types and attributes is possibly incomplete as a result. In particular the attributeNames in the EntityType data structure (clause 5.2.25), the attributeDetails in the EntityTypeInfo data structure (clause 5.2.26), and the attributeTypes and typeNames in the Attribute data structure (clause 5.2.27) may be provided as empty arrays if the information is not included in the respective context registration. Implementations may also provide estimates for the entity count or attribute count instead of the accurate count.
As an alternative to relying on local information only, the request can be forwarded to all Context Sources which support the respective operation according to the Context Source Registration describing them. In this case the returned lists are merged with the local list of entity types before returning them. This approach is more expensive but leads to a more accurate result.
5.8 Context Information Subscription
5.8.1 Create Subscription
5.8.1.1 Description
This operation allows creating a new subscription.
5.8.1.2 Use case diagram
A Context Subscriber can create a subscription to receive context updates within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.8.1.2‑1.
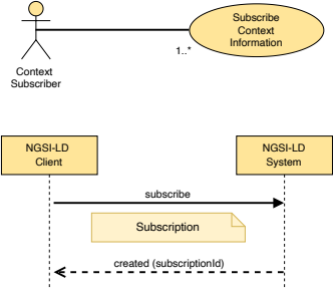
5.8.1.3 Input data
- A data structure (represented in JSON-LD) conforming to the Subscription data type as mandated by clause 5.2.12.
5.8.1.4 Behaviour
- If the data types, cardinalities and restrictions expressed by clause 5.2.12 are not met, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint already knows about this Subscription, as there is an existing Subscription whose id (URI) is equivalent, an error of type AlreadyExists shall be raised.
- If the subscription document does not include a Subscription identifier, a new identifier (URI) shall be automatically generated by the implementation.
- Then, implementations shall add a new Subscription. The parameters of the created Subscription shall be configured as follows:
- The Subscription expiration date shall be equal to the value of the expiresAt member. If the expiration timestamp provided represents a moment before the current date and time, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised. If there is no expiresAt member the Subscription shall be considered as perpetual.
- If the value of the isActive field is not included or is true then the initial status of the Subscription shall be set to "active".
- If the value of the isActive field is false, then the initial status of the Subscription shall be set to "paused".
- If present, the subscribed entities shall be those matching the conditions expressed under the EntitySelector, as defined in clause 5.2.33.
- Watched Attributes shall be those Attributes (subject to clause 5.5.7 Term to URI expansion) pertaining to the subscribed entities (if present) and conveyed through the watchedAttributes member. Watched Attributes are those that trigger a new notification when they are changed. A non-present watchedAttributes member means that all Attributes shall be watched. If no subscribed entities have been specified, all entities with attributes matching at least one member of watchedAttributes are subscribed to.
- The @context to be used for sending Notifications related to this Subscription shall be the one specified in the jsonldContext field. If not present, the jsonldContext field shall be initialized with the @context applicable for the Subscription (if @context is also not present in the Subscription, see clause 5.5.5). When the remote JSON-LD @context referenced by the jsonldContext field is not available implementations shall raise an error of type LdContextNotAvailable. If the remote JSON-LD @context referenced by the jsonldContext field is invalid, implementations shall raise an error of type BadRequestData.
- Based on the content of the Subscription, a Context Source Registration Subscription shall be created (clause 5.11.2). The mapping of the id of the Subscription to the returned subscriptionId of the Context Source Registration Subscription shall be stored to enable updating or deleting the Context Source Registration Subscription in case of changes to the Subscription.
- If the subscription defines a timeInterval member, a Notification shall be sent periodically, when the time interval (in seconds) specified in such value field is reached, regardless of Attribute changes.
- If timeInterval is not defined, whenever there is a change in the watched Attribute nodes (Properties or Relationships) of the concerned Entities, implementations shall post a new Notification as per the rules defined by clause 5.8.6.
- Each time a Context Source Notification with the subscriptionId of the previously created Context Source Registration Subscription is received, implementations shall do the following:
- For any exclusive, redirect and inclusive Context Source Registration received as part of the notification, implementation shall do the following depending on the triggerReason:
- If the triggerReason is "newlyMatching" and the Context Source Registration indicates support for the Create Subscription operation, a copy of the original Subscription shall be reduced to what is matched by the registration information. If the splitEntities member is explicitly set to true or, if not explicitly set, the default setting of the deployment allows split entities, the members q, geoQ and scopeQ shall be removed from the created copy of the original Subscription. Also from the notification member, the attributes, pick and omit members are to be removed. The copied Subscription is then forwarded to the Context Source as a new Subscription where the notification endpoint is set to that of the local Broker. The mapping of the received subscriptionId with the own Subscription identifier is stored to enable forwarding received notifications to the original subscriber. In addition, a mapping of the id of the Context Source Registration to the received subscriptionId is stored, to enable updating or deleting the subscription in case of changes.
- If the triggerReason is "updated" and the Context Source Registration indicates support for the Update Subscription operation, an update of the original Subscription, reduced to what is matched by the registration information, shall be created. If the splitEntities member is explicitly set to true or, if not explicitly set, the default setting of the deployment allows split entities, the members q, geoQ and scopeQ shall be removed from the updated Subscription. Also from the notification member the attributes, pick and omit members are to be removed. The updated Subscription is then forwarded to the Context Source with the subscriptionId related to the Context Source Registration. As an optimization, an implementation may keep the originally forwarded Context Source Registration and compare with the new one to only forward the update, if there was a relevant change.
- If the triggerReason is "noLongerMatching" and the Context Source Registration indicates support for the delete Subscription operation, a delete Subscription shall be forwarded to the Context Source with the subscriptionId related to the Context Source Registration.
- Implementations shall ensure that, when the Subscription expiration date is due, the status of the Subscription changes automatically to "expired", so that notifications will no longer be sent.
5.8.1.5 Output data
One subscription identifier (id) of type string, representing a URI. Implementations shall ensure that subscription identifiers are unique within an NGSI-LD system.
5.8.2 Update Subscription
5.8.2.1 Description
This operation allows updating an existing subscription.
5.8.2.2 Use case diagram
A Context Subscriber can update an existing subscription within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.8.2.2‑1.
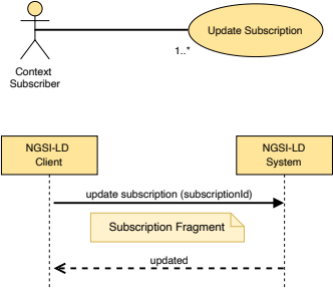
5.8.2.3 Input data
- Subscription identifier (URI), the target subscription.
- A JSON-LD document representing a Subscription Fragment.
5.8.2.4 Behaviour
- If the Subscription id is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD System does not know about the target Subscription, because there is no existing Subscription whose id (URI) is equivalent, an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- Execute the behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation.
- If the data types and restrictions expressed by clause 5.2.12 are not met by the Subscription Fragment, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- Term to URI expansion of Attribute names shall be observed as mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- If the jsonldContext field is present and the referenced JSON-LD @context is not available, implementations shall raise an error of type LdContextNotAvailable. If the referenced JSON-LD @context is invalid, implementations shall raise an error of type BadRequestData.
- Then, implementations shall modify the target Subscription as mandated by clause 5.5.8.
- Finally, the following extra behaviour shall be observed when updating Subscriptions:
- If isActive is equal to true and expiresAt is not present, then status shall be updated to "active", if and only if, the previous value of status was different than "expired".
- If isActive is equal to true and expiresAt corresponds to a DateTime in the future, then status shall be updated to "active".
- If isActive is equal to false and expiresAt is not present, then status shall be updated to "paused", if and only if, the previous value of status was different than "expired".
- If only expiresAt is included and refers to a DateTime in the future, then status shall be updated to "active", if and only if the previous value of status was "expired".
- If expiresAt is included but referring to a DateTime in the past, then a BadRequestData error shall be raised, regardless the value of isActive.
- Based on the mapping of the Subscription to its respective Context Source Registration Subscription (see clause 5.8.1.4), that Context Source Registration Subscription shall be updated (clause 5.11.3).
5.8.2.5 Output data
None.
5.8.3 Retrieve Subscription
5.8.3.1 Description
This operation allows retrieving an existing subscription.
5.8.3.2 Use case diagram
A Context Subscriber can retrieve a specific subscription from an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.8.3.2‑1.
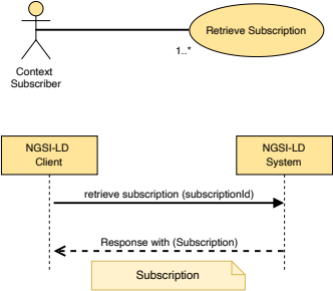
5.8.3.3 Input data
Id (URI) of the subscription to be retrieved (target subscription).
5.8.3.4 Behaviour
- If the subscription Id is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the identifier provided does not correspond to any existing subscription in the system then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- Otherwise implementations shall query the subscriptions and obtain the subscription data to be returned to the caller.
5.8.3.5 Output data
A JSON-LD object representing the subscription details as mandated by clause 5.2.12.
5.8.4 Query Subscriptions
5.8.4.1 Description
This operation allows querying existing Subscriptions.
5.8.4.2 Use case diagram
A Context Consumer can query the existent Subscriptions from an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.8.4.2‑1.
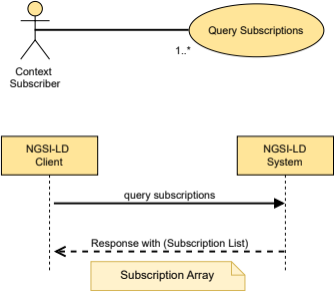
5.8.4.3 Input data
A limit to the number of subscriptions to be retrieved. See clause 5.5.9.
5.8.4.4 Behaviour
- The NGSI-LD system shall list all the existing subscriptions up to the limit specified as input data. If no limit is specified the number of subscriptions retrieved may depend on the implementation.
- Pagination logic shall be in place as mandated by clause 5.5.9.
5.8.4.5 Output data
A list (represented as a JSON array) of JSON-LD objects each one representing subscription details as mandated by clause 5.2.12.
5.8.5 Delete Subscription
5.8.5.1 Description
This operation allows deleting an existing subscription.
5.8.5.2 Use case diagram
A Context Subscriber can delete a subscription within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.8.5.2‑1.
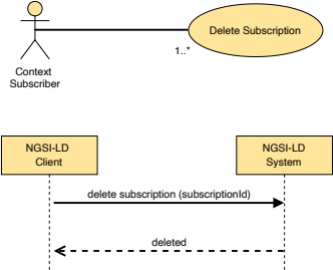
5.8.5.3 Input data
A subscription identifier (URI).
5.8.5.4 Behaviour
- If the subscription Id is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the subscription id provided does not correspond to any existing subscription in the system then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- Otherwise implementations shall delete the Subscription and no longer perform notifications concerning such Subscription.
- Using the mapping of the own Subscription identifier to each of the subscriptionId of a subscription to a Context Source, a delete Subscription shall be forwarded to each such Context Source, if the delete Subscription operation is supported as indicated in the corresponding Context Source Registration:
- Based on the mapping of the Subscription to its respective Context Source Registration Subscription (see clause 5.8.1.4), that Context Source Registration Subscription shall be deleted (clause 5.11.6).
5.8.5.5 Output data
None.
5.8.6 Notification behaviour
A notification is a message that allows a subscriber to be aware of the changes in subscribed Entities. Implementations shall exhibit the following behaviour:
- Notifications shall only be sent if and only if the status of the corresponding subscription (subscription.status) is "active", i.e. not "paused" nor "expired".
- If a Subscription defines a timeInterval member, a Notification shall be sent periodically, when the time interval (in seconds) specified in such value field is reached, regardless of Attribute changes. The notification message shall include all the subscribed Entities that match the query, geoquery and Scope query conditions. If none of query, geoquery and Scope query are defined, then all subscribed Entities shall be included. For each entity in the notification, only the Attribute instances are to be included that match the datasetId member in Subscription. If there are no matching Entities, no Notification is sent.
- If a Subscription does not define a timeInterval term, the notification shall be sent whenever there is a change in the watched Attributes. An Attribute is considered to change when any of the members (including children) in its corresponding JSON-LD node is updated with a value different than the existing one. The notification message shall include all the subscribed Entities that changed and that match (as mandated by clauses 4.9, 4.10 and 4.19) the query, geoquery and Scope query conditions. If query, geoquery and scopeQuery are all not defined then all subscribed Entities that changed shall be included. If, for an Entity, there are multiple instances of the GeoProperty on which the geoquery is based, it is sufficient if any of these instances meets the geospatial restrictions. For each entity in the notification, only the Attribute instances are to be included that match the datasetId member in Subscription. Finally, if a Context Source filter is defined, then only the subscribed Entities whose origin Context Source matches the referred filter shall be included.
- If a Notification with a subscriptionId is received that has a mapping to a local Subscription identifier, the Notification shall be copied.
If the splitEntities member of the local Subscription is explicitly set to true or, if not explicitly set, the default setting of the deployment allows split entities,
- the Entities contained in the data member of the Notification shall be retrieved locally and from all Context Sources that have information about these Entities, except for the one from which the Notification has been received.
- The retrieved Entities then shall be merged with the Entities in the data member.
- All Entities that do not match the query, geoquery and Scope query conditions of the local Subscription shall be removed from the data member.
- If there are Entities in the data member of the Notification copy, the Notification copy shall be forwarded to the Notification endpoint specified in the local Subscription, using this local Subscription identifier instead of the subscriptionId received.
- A Notification shall be sent as follows:
- The structure of the notification message shall be as mandated by clause 5.3.1.
- The @context to be used is the one specified in the jsonldContext field of the corresponding Subscription.
- The Attributes included (Properties or Relationships) shall be those specified by the notification.attributes member in the Subscription data type (clause 5.2.12). Term to URI expansion shall be observed (clause 5.5.7). The absence of the notification.attributes member of a Subscription means that all Attributes shall be included. If the notification was triggered by the deletion of an Entity and the notification.showChanges member is not set to true, only the deletedAt system property shall be provided. In case notification.sysAttrs is set to true, also createdAt and modifiedAt shall be provided.
- If an Attribute has been deleted, only the name of the attribute as key and the URI "urn:ngsi-ld:null" as value shall be provided, unless more information is required. The latter is the case, if:
- a datasetId needs to be provided;
- the notification.sysAttrs is set to true and thus the system generated sub-attributes (see clause 4.8) have to be provided;
- notification.showChanges is set to true and thus a previous value or object has to be provided.
- If the notification.formatmember value is set, the representation of the entities changes:
- If the notification.format is set to "concise" then a concise representation of the entities shall be provided as defined by clause 4.5.1.
- If the notification.format is set to "simplified" (or "keyValues" as a synonym), then a simplified representation of the entities (as mandated by clause 4.5.4) shall be provided.
- Otherwise the normalized format as defined by clause 4.5.1 shall be used.
- If the notification.pickmember value is set, every Entity within the payload body is reduced down to only contain the defined entity members listed.
- If the notification.omitmember value is set, the defined entity members listed are removed from each Entity within the payload.
- If the notification.joinmember value is set then Linked Entityretrieval(as mandated by clause 4.5.23) shall be provided.
- If the ngsildConformance field of the corresponding Subscription is set, the notification shall undergo a backwards compatibility operation as defined by clause 4.3.6.8 and be amended to conform to the supplied version of the NGSI-LD specification.
- A Notification shall be sent (as mandated by each concrete binding and including any optional endpoint.receiverInfodefined by clause 5.2.22) to the endpoint specified by the endpoint.urimember of the notification structure defined by clause 5.2.14. The Notification content shall be JSONby default. However, this can be changed to JSON-LD or GeoJSONby means of the endpoint.acceptmember.
- The notification.timesSent member shall be incremented by one.
- The notification.lastNotification member shall be updated with a timestamp representing the current date and time.
- If the response to the notification request is 200 OK then implementations shall:
- Update notification.lastSuccess with a timestamp representing the current date and time.
- Update notification.status to "ok".
- If the response to the notification request is different than 200 OKthen implementations shall:
- Update notification.lastFailure with a timestamp representing the current date and time.
- Update notification. Status to "failed".
5.9 Context Source Registration
5.9.1 Introduction
As described in clause 5.2.9, Context Source Registrations have a similar structure as Entities and are generally handled in the same way. However, there are some aspects that are specific to Registrations, in particular with respect to the handling of required properties. Thus, the operation descriptions for Registrations reference the respective operations for Entities and in addition specify any deviations and additions that are necessary for handling Context Source Registrations.
Context Source Registrations either contain information about Context Sources providing the latest information or about Context Sources providing temporal information, but not both. Context Sources that can provide both thus have to use two separate Context Source Registrations. If no temporal query is present, only Context Source Registrations for Context Sources providing latest information are returned, i.e. those which do not specify time intervals used for temporal queries. If a temporal query is present in a request for Context Source Registrations, only those Context Source Registrations that have a matching time interval are returned.
5.9.2 Register Context Source
5.9.2.1 Description
This operation allows registering a context source within an NGSI-LD system.
5.9.2.2 Use case diagram
A Context Provider can register one or more context sources within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.9.2.2‑1.
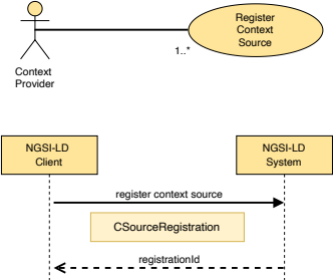
5.9.2.3 Input data
A data structure conforming to the CSourceRegistration data type as mandated by clause 5.2.9.
5.9.2.4 Behaviour
Implementations shall generally exhibit the behaviour described in clause 5.6.1.4, but instead of any type of entities only Context Source Registrations can be provided. Deviating from clause 5.6.1.4, implementations shall exhibit the following behaviour:
- If the data types and restrictions expressed by clause 5.2.9 are not met by the Context Source Registration, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If a contextSourceInfo array is defined and the restrictions expressed by clause 4.3.6.6 are not met by the Context Source Registration, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the Context Source to be registered has its mode property defined as exclusive, the following additional restrictions apply:
- If an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration already matches against the Entity ID (URI) and any of the Attributes defined in the registration, an error of type Conflict shall be raised.
- If an Entity already exists for the supplied Entity ID (URI) and the existing Entity contains any of the Attributes defined in the registration, an error of type Conflict shall be raised.
- If the Context Source to be registered has its mode property defined as redirect, the following additional restriction applies:
- If an existing Entity already matches the Context Source Registration, an error of type Conflict shall be raised.
- If the Context Source to be registered has its mode property defined as auxiliary, the following additional restriction applies:
- If the operations property is not defined as one of: "retrieveOps", "retrieveEntity" or "queryEntity", or a combination thereof, an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the property expiresAt is not defined then the Context Source Registration shall last forever (or until it is deleted from the system).
- If expiresAt is a date and time in the past, an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If expiresAt is a date and time in the future, implementations shall delete the Registration when this point in time is reached.
- If the registration identifier, id, is contained in the Context Source Registration, implementations have to check whether this is a valid identifier that conforms to its policies and is unique within its scope. Otherwise, it can replace the 'id' with a valid registration identifier.
- Implementations shall add the concerned Context Source Registration and return an 'ok' response together with a registration identifier (id).
- This id shall be used if NGSI-LD clients need to manage the registration later.
5.9.2.5 Output data
One registration identifier (id) of type string, representing a URI. Implementations shall ensure that registration identifiers are unique within an NGSI-LD system.
5.9.3 Update Context Source Registration
5.9.3.1 Description
This operation allows updating a Context Source Registration in an NGSI-LD system.
5.9.3.2 Use case diagram
A Context Provider can update a Context Source Registration in an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.9.3.2‑1.
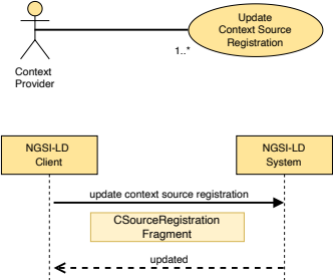
5.9.3.3 Input data
- Context Source Registration identifier (URI), the target Context Source Registration.
- A JSON-LD document representing a Context Source Registration Fragment (clause 5.4).
5.9.3.4 Behaviour
- If the target Context Source Registration id (id) is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If a "contextSourceInfo" array is defined and the restrictions expressed by clause 4.3.6.6 are not met by the Context Source Registration, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD System does not know about the target Context Source Registration, because there is no existing Context Source Registration whose id (URI) is equivalent, an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- Execute the behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation.
- If the data types and restrictions expressed by clause 5.2.9 are not met by the Context Source Registration Fragment, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- Term to URI expansion of Attribute names shall be observed as mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- If the Context Source Registration to be updated has its mode property defined as exclusive, the following additional restrictions apply:
- If an exclusive or redirect Context Source Registration already matches against the Entity ID (URI) and any of the Attributes defined in the registration, an error of type Conflict shall be raised.
- If an Entity already exists for the supplied Entity ID (URI) and the existing Entity contains any of the Attributes defined in the registration, an error of type Conflict shall be raised.
- If the Context Source Registration to be updated has its mode property defined as redirect, the following additional restriction applies:
- If an existing Entity already matches the Context Source Registration, an error of type Conflict shall be raised.
- If the Context Source to be updated has its mode property defined as auxiliary, the following additional restriction applies:
- If the operations property is not defined as one of: "retrieveOps", "retrieveEntity" or "queryEntity", an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- Then, implementations shall modify the target Context Source Registration as mandated by clause 5.5.8.
5.9.3.5 Output data
None.
5.9.4 Delete Context Source Registration
5.9.4.1 Description
This operation allows deleting a Context Source Registration from an NGSI-LD system.
5.9.4.2 Use case diagram
A context provider can delete a context source registration from an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.9.4.2‑1.
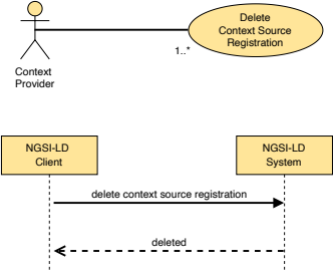
5.9.4.3 Input data
Registration identifier (URI) of the context source registration to be deleted (target registration).
5.9.4.4 Behaviour
- If the target context source registration id is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target context source registration, because there is no existing context source registration whose id (URI) is equivalent, then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- Otherwise the context source registration shall be removed.
5.9.4.5 Output data
None.
5.10 Context Source Discovery
5.10.1 Retrieve Context Source Registration
5.10.1.1 Description
This operation allows retrieving a specific context source registration from an NGSI-LD system.
5.10.1.2 Use case diagram
A context consumer or a context provider can retrieve a specific context source registration from an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.10.1.2‑1.
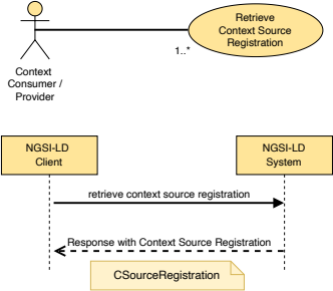
5.10.1.3 Input data
Context source registration identifier (id) of the context source registration to be retrieved (target registration).
5.10.1.4 Behaviour
- If the context source registration id (id) is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about the target context source registration, because there is no existing context source registration whose id (URI) is equivalent, then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- Term to URI expansion of Attribute names shall be observed as mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- Otherwise return a JSON-LD object representing the Context Source Registration as mandated by clause 5.2.9.
5.10.1.5 Output data
A JSON-LD object representing the target context source registration as mandated by clause 5.2.9.
5.10.2 Query Context Source Registrations
5.10.2.1 Description
This operation allows discovering context source registrations from an NGSI-LD system. The behaviour of the discovery of context source registrations differs significantly from the querying of entities as described in clause 5.7.2. The approach is that the client submits a query for entities as described in clause 5.7.2, but instead of receiving the Entity information, it receives a list of Context Source Registrations describing Context Sources that possibly have some of the requested Entity information. This means that the requested Entities and Attributes are matched against the 'information' property as described in .
If no temporal query is present, only Context Source Registrations for Context Sources providing latest information, i.e. without specified time intervals, are considered. If a temporal query is present only Context Source Registrations with matching time intervals, i.e. observationInterval or managementInterval, are considered.
5.10.2.2 Use case diagram
A Context Consumer can discover context source registrations that may be able to provide (part of) the context information specified in the query from an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.10.2.2‑1.
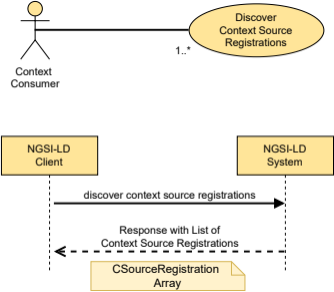
5.10.2.3 Input data
- A reference to a JSON-LD @context (optional).
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17. Both type name (short hand string) and fully qualified type name (URI) are allowed (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Entity identifiers (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Attribute names (called query projection attributes) (optional).
- An id pattern as a regular expression (optional).
- An NGSI-LD query (to filter out Entities by Attribute values, used here to identify relevant attributes) as per clause 4.9 (optional).
- An NGSI-LD geoquery (to filter out Entities by spatial relationships, used here to identify relevant GeoProperties and for geographical scoping) as per clause 4.10 (optional).
- In the case of GeoJSON representation:
- The name of the GeoProperty attribute to use as the geometry for the GeoJSON representation as mandated by clause 4.5.16 (optional).
- A datasetId specifying which instance of the value is to be selected if the GeoProperty value has multiple instances as defined by clause 4.5.5 (optional).
- An NGSI-LD temporal query as per clause 4.11 (optional).
- An NGSI-LD context source query as per clause 4.9 (optional).
- A NGSI-LD Scope query as mandated by clause 4.19 (optional).
- A limit to the number of Context Source Registrations to be retrieved. See clause 5.5.9.
- A specified language filter as per clause 4.15 (optional).
It is not possible to retrieve a set of context source registrations related to entities by only specifying desired Entity identifiers, without further specifying restrictions on the entities' types or attributes, either explicitly, via lists of Entity types or of Attribute names, or implicitly, within an NGSI-LD query or geoquery.
5.10.2.4 Behaviour
- Execute the behaviour defined in clause 5.5.4 on JSON-LD validation.
- At least one of the following input data shall be provided:
- Term to URI expansion of type and Attribute names shall be performed, as mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- Otherwise, implementations shall run a query that shall return context source registrations that meet all the applicable conditions:
- If present, the entity specification in the query consisting of a combination of entity type selector and entity id/entity id pattern (optional) matches an EntityInfo specified in a RegistrationInfo of the information property in a context source registration. If there is no EntityInfo specified in the RegistrationInfo, the entity specification is considered matching. This matching is further described in .
- If present, at least one Attribute name specified in the query matches one Property or Relationship in the RegistrationInfo element of the information property in a context source registration. If no Properties or Relationships are specified in the RegistrationInfo, the Attribute names are considered matching. This matching is further described in .
- If present, the geoquery is matched against the GeoProperty identified in the geoquery. If no GeoProperty is specified in the geoquery, the default property is location. The geoquery matches the GeoProperty specified in the Context Source Registration, if the location directly matches or if the location possibly contains locations that would match the geoquery.
- If no temporal query is present, only Context Source Registrations for Context Sources providing latest information, i.e. without specified time intervals, are considered.
- If a temporal query is present, only Context Source Registrations with specified time intervals, i.e. observationInterval or managementInterval are considered. If the timeproperty is observedAt or no timeproperty is specified in the temporal query (default: observedAt), the temporal query is matched against the observationInterval (if present). If the timeproperty is createdAt, modifiedAt or deletedAt, the temporal query is matched against the managementInterval (if present). If the relevant interval is not present, there is no match:
- The semantics of the match is that the timeAt in the case of the "before" and "after" relation is contained in or is an endpoint of a time period included in the specified time interval. In the case of the "between" relation there is a match if there is an overlap between the interval specified by the timeAt and endTimeAt and the specified time interval.
- If present, the conditions specified by the context source query filter match the respective Context Source Properties (as mandated by clause 4.9).
- If present, the Scope query (as mandated by clause 4.19) is matched against the scope property.
- Pagination logic shall be in place as mandated by clause 5.5.9.
5.10.2.5 Output data
A JSON-LD array of matching Context Source Registrations as defined by clause 5.2.9. Instead of the original Context Source Registration which may contain a lot of irrelevant information, implementations should return filtered Context Source Registrations, which only contain context source registration information relevant for the query, in particular only matching RegistrationInfo elements.
5.11 Context Source Registration Subscription
5.11.1 Introduction
Context Source Registration Subscriptions in general work like context information subscriptions; however, instead of resulting in notifications with context information, the notifications contain Context Source Registrations describing Context Sources that can potentially provide the requested context information. If no temporal query is present, only Context Source Registrations for Context Sources providing latest information, i.e. without such time intervals, are considered. If a temporal query is present only Context Source Registrations with matching time intervals, i.e. observationInterval or managementInterval, are considered.
5.11.2 Create Context Source Registration Subscription
5.11.2.1 Description
This operation allows creating a new Context Source Registration Subscription.
5.11.2.2 Use case diagram
A Context Source Subscriber can subscribe to a new Context Source Registration as shown in Figure 5.11.2.2‑1.
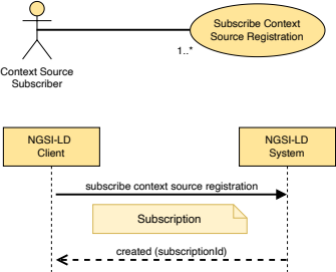
5.11.2.3 Input data
- A data structure (represented in JSON-LD) conforming to the Subscription data type as mandated by clause 5.2.12.
5.11.2.4 Behaviour
- The behaviour shall be as described in clause 5.8.1.4, restricted to the local case, with the following exceptions:
- If an exclusive Context Source Registration is being created:
- If an Entity matching the Registration already exists for this id (URI) and attributes, an error of type Conflict shall be raised.
- If an exclusive Context Source Registration already exists for this id (URI) and attributes, an error of type AlreadyExists shall be raised.
- If a redirect Context Source Registration is being created and an Entity matching the Registration already exists for this id (URI) and attributes, an error of type Conflict shall be raised.
- If all checks described in clause 5.8.1.4 pass, implementations shall add a new Context Source Registration Subscription. The parameters of the created subscription shall be configured as described in clause 5.8.1.4.
- Instead of directly matching the entities and watched Attributes from the Subscription with the Context Source registrations, the entities specified in the subscription, the watched Attributes and the Attributes specified in the notification parameter are matched against the respective information property of the Context Source registrations. If either the watched Attributes or the Attributes in the notification are not present or of length 0, all possible Attributes (if present in the Context Source Registrations) for matching entities match. This matching is further described in .
- If present, the geoquery in the geoQ element is matched against the GeoProperty of the subscription identified in the geoQ element. If no GeoProperty is specified in the geoquery, the default property is 'location'. The geoquery matches the GeoProperty specified in the Context Source Registration, if the location directly matches or if the location possibly contains locations that would match the geoquery.
- If no temporal query is present in the temporalQ element, only Context Source Registrations for Context Sources providing latest information, i.e. without specified time intervals for observationInterval or managementInterval, are considered.
- If a temporal query in the temporalQ element is present, only Context Source Registrations with specified time intervals are considered. If the timeproperty is "observedAt" or no timeproperty is specified in the temporal query (default: observedAt), the temporal query is matched against the observationInterval (if present). If the timeproperty is "createdAt", "modifiedAt" or "deletedAt", the temporal query is matched against the managementInterval (if present). If the relevant interval is not present, there is no match:
- The semantics of the match is that the timeAt in the case of the "before" and "after" relation is contained in or is an endpoint of a time period included in the specified time interval. In the case of the "between" relation there is a match if there is an overlap between the interval specified by the timeAt and endTimeAt and the specified time interval.
- If present, the conditions specified by the context source filter match the respective Context Source Properties (as mandated by clause 4.9).
- If the subscription defines a timeInterval term, a CsourceNotification (clause 5.3.2) with all matching Context Source Registrations shall be sent periodically, initially on subscription and when the time interval (in seconds) specified in such value field is reached, independent of any changes to the set of Context Source registrations.
- If timeInterval is not defined, initially on subscription and whenever there is a change of a matching Context Source Registration (creation, update, deletion), implementations shall post a new CsourceNotification to the endpoint specified in the notification parameters informing about this change by providing the Context Source Registration(s) together with the appropriate trigger reason in the triggerReason member.
- If present, the conditions specified by the context source query match the respective Context Source Properties (as mandated by clause 4.9).
- If present, the Scope query (as mandated by clause 4.19) is matched against the scope property.
5.11.2.5 Output data
One subscription identifier (id) of type string, representing a URI. Implementations shall ensure that subscription identifiers are unique within an NGSI-LD system.
5.11.3 Update Context Source Registration Subscription
5.11.3.1 Description
This operation allows updating an existing Context Source Registration Subscription.
5.11.3.2 Use case diagram
A context source subscriber can update a Context Source Registration Subscription as shown in Figure 5.11.3.2‑1.
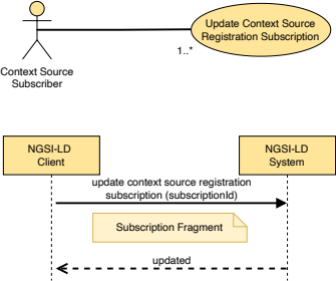
5.11.3.3 Input data
- Subscription identifier (URI), the target Context Source Registration Subscription.
- A JSON-LD document representing a Subscription Fragment.
5.11.3.4 Behaviour
- If the Subscription Id is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the data types and restrictions expressed by clause 5.2.12 are not met by the Subscription Fragment, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- Then, implementations shall modify the target subscription as mandated by clause 5.5.8.
- Finally, send a notification with all currently matching Context Source Registrations.
5.11.3.5 Output data
None.
5.11.4 Retrieve Context Source Registration Subscription
5.11.4.1 Description
This operation allows retrieving an existing Context Source Registration Subscription.
5.11.4.2 Use case diagram
A Context Source subscriber can retrieve a specific Context Source Registration Subscription as shown in Figure 5.11.4.2‑1.
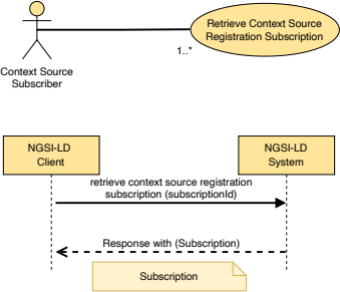
5.11.4.3 Input data
Id (URI) of the subscription to be retrieved (target subscription).
5.11.4.4 Behaviour
- If the subscription Id is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the identifier provided does not correspond to any existing subscription in the system then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- Otherwise implementations shall query the Context Source Registration Subscriptions and obtain the subscription data to be returned to the caller.
5.11.4.5 Output data
A JSON-LD object representing the subscription details as mandated by clause 5.2.12.
5.11.5 Query Context Source Registration Subscriptions
5.11.5.1 Description
This operation allows querying existing Context Source Registration Subscriptions.
5.11.5.2 Use case diagram
A context source subscriber can query all existing Context Source Registration Subscriptions as shown in Figure 5.11.5.2‑1.
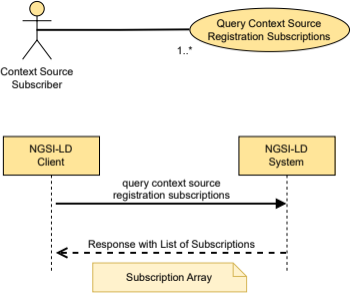
5.11.5.3 Input data
A limit to the number of Context Source Registration Subscriptions to be retrieved. See clause 5.5.9.
5.11.5.4 Behaviour
- The NGSI-LD System shall list all the existing Context Source Registration Subscriptions.
- Pagination logic shall be in place as mandated by clause 5.5.9.
5.11.5.5 Output data
A list (represented as a JSON array) of JSON-LD objects each one representing subscription details as mandated by clause 5.2.12.
5.11.6 Delete Context Source Registration Subscription
5.11.6.1 Description
This operation allows deleting an existing Context Source Registration Subscription.
5.11.6.2 Use case diagram
A context source subscriber can delete a Context Source Registration Subscription as shown in Figure 5.11.6.2‑1.
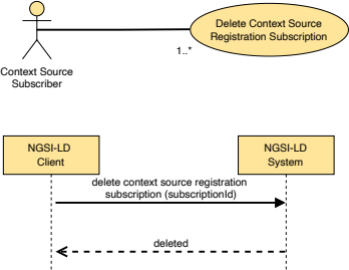
5.11.6.3 Input data
- A subscription identifier (URI).
5.11.6.4 Behaviour
- If the subscription Id is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the subscription id provided does not correspond to any existing subscription in the system then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- Otherwise implementations shall delete the Context Source Registration Subscription and no longer perform notifications concerning that Subscription.
5.11.6.5 Output data
None.
5.11.7 Notification behaviour
A Context Source Notification is a message that allows a subscriber to be aware of the changes in the set of Context Source Registrations describing Context Sources that can potentially provide the requested context information. Implementations shall exhibit the behaviour described in clause 5.8.6 with the following exceptions:
- If a subscription defines a timeInterval member, a CsourceNotification (clause 5.3.2) shall be sent on initial subscription and periodically, when the time specified time interval (in seconds) has elapsed, regardless of any changes to the set of context source registrations. The CsourceNotification message shall include all the Context Source Registrations whose information property matches the entities and watched Attributes or Attributes specified in the notification parameter and, if present, have a matching geoquery. If either the watched Attributes or the Attributes in the notification are not present or of length 0, all possible Attributes (if present in the Context Source Registrations) for fitting entities match.
- If a subscription does not define a timeInterval term, the csource notification shall be sent on initial subscription and whenever there is a change in a matching csource registration. Such a change may be triggered by the creation of a new matching csource registration, the update of a csource registration (whether matching before the update, after the update or in both cases) or the deletion of a matching csource registration. The notification message shall include the matching csource registration(s) together with the appropriate trigger reason in the triggerReason member.
- Instead of providing the original Context Source Registration which may contain a lot of irrelevant information, implementations should return filtered Context Source Registrations, which only contain context source registration information relevant for the subscription, in particular only matching RegistrationInfo elements.
- A csource notification shall be sent as follows:
- The structure of the csource notification message shall be as mandated by clause 5.3.2.
- A csource notification shall be sent to the endpoint.
- The notification.timesSent member shall be incremented by one.
- The notification.lastNotification member shall be updated with the current timestamp.
- If the notification is sent successfully:
- Update notification.lastSuccess with the current timestamp.
- If the notification is not sent successfully:
- Update notification.lastFailure with the current timestamp.
- Update the subscription status to "failed".
5.12 Matching Context Source Registrations
When querying Context Source Registrations as described in clause 5.10.2 and subscribing to Context Source Registrations as described in clause 5.11.2, the Entities and/or Attributes specified in the request have to be matched against the set of Context Source Registrations, extracting the matching ones. This clause describes this matching.
The relevant specification information in the query for Context Source Registrations are the selector of Entity Types (if present), the list of Entity identifiers (if present), the id pattern (if present) and the list of Attribute names (if present). In the case of subscriptions to Context Source Registrations, it is the Entities as specified in the array of type EntitySelector in the Subscription, the watchedAttributes element of the Subscription and the attributes specified as part of the NotificationParams element of the Subscription. If the attributes in the NotificationParams element are empty or not present, the matching is done as if no attribute identifiers have been specified, otherwise the combination of the watchedAttributes and the attributes in the NotificationParams element are used as the specified attribute identifiers for the matching.
Even though the way relevant Entities are specified differs in queries and subscriptions, they consist of the same information, so for the purpose of this clause, the specification of Entity Types or Attributes refers to the relevant elements for matching, i.e. Entity Types, Entity identifiers, id pattern and Attribute names. A specification of Entity Types or Attributes shall contain at least one of:
- selector of Entity Types; or
- list of Attribute names.
A specification of Entity Types or Attributes matches a Context Source Registration if at least one of the RegistrationInfo elements in the information element matches. An Entity specification matches a RegistrationInfo if the following conditions hold:
- If present, the selector of Entity Types, Entity identifiers and id pattern match at least one of the EntityInfo elements of the RegistrationInfo (see below).
- If present, the Attribute identifiers match the combination of Properties and Relationships specified in the RegistrationInfo (see below).
An Entity specification consisting of selector of Entity Types, Entity identifiers and id pattern matches an EntityInfo element of the RegistrationInfo if the type selector matches the entity types in the EntityInfo element and one of the following conditions holds:
- The EntityInfo contains neither an id nor an idPattern.
- One of the specified Entity identifiers matches the id in the EntityInfo.
- At least one of the specified Entity identifiers matches the idPattern in the EntityInfo.
- The specified id pattern matches the id in the EntityInfo.
- Both a specified id pattern and an idPattern in the Entity Info are present (since in the general case it is not easily feasible to determine if there can be identifiers matching both patterns).
Attribute names match the combination of Properties and Relationships if one of the following conditions hold:
- No Attribute names have been specified (as this means all Attributes are requested).
- The combination of Properties and Relationships is empty (as this means only Entities have been registered and the Context Sources may have matching Property or Relationship instances).
- If at least one of the specified attribute names matches a Property or Relationship specified in the RegistrationInfo.
If the request that triggered the matching includes a datasetId parameter and the CSourceRegistration to be matched contains a datasetId element, the CSourceRegistration should only be considered matching, if both have at least one value in common. If only one of them specifies a datasetId, it is considered a match.
In the case of distributed operations (see clause 4.3.6.4), where a listing of all previously encountered Context Sources is supplied with the request, no registration shall match if the CSourceRegistration contextSourceAlias can be found within the listing of previously encountered Context Sources.
Note that distributed queries (see clause 4.3.6.7), can be supplied with an EntityMap (see clause 4.5.25) which lists all Entity ids successfully matched during a previous request. If the location of an EntityMap is passed into a subsequent request, the retrieved EntityMap shall be used in preference to the matching algorithm described above, provided that the EntityMap is valid and has not expired.
5.13 Storing, Managing and Serving @contexts
5.13.1 Introduction
Context Brokers optionally (see clause 4.3.5) offer the capability to store and serve @contexts to clients. The stored @contexts may be managed by clients directly, via the APIs specified in clause 5.13. Clients can store custom user @contexts at the Context Broker, effectively using the Context Broker as a @context server.
Moreover, in order to optimize performance, brokers may automatically store and use the stored copies of common @contexts as a local cache, downloading them just once, thus avoiding fetching them over and over again at each NGSI-LD request. In order for the broker to understand if a needed @context is already in the local storage or not, the broker uses the URL, where the @context is originally hosted, as an identifier for it in the local storage. Consequently, the broker has no ability to cache @contexts that arrive to it as embedded parts within the NGSI-LD documents, since they are not uniquely (and implicitly) identified by any URL; Context Brokers only cache @contexts that are referred to by means of explicit URLs (either in the HTTP Link header or as URLs in the payload body). Thus, the recommended best-practice, in order to exploit caching, is that clients do not embed their user @contexts into their NGSI-LD documents; instead clients should explicitly host their user @contexts at their premises, or use the broker's capability to host user @contexts on their behalf.
When an external @context is stored, either explicitly upon a client's request or implicitly downloaded for caching purposes, the Context Broker generates a unique local @context identifier. The original @context's URL, if any, is stored alongside the generated local id. The local id is then used for subsequent managing operations on the specific @context, that are specified in clauses 5.13.2 to 5.13.5. Moreover, the broker tags the entry with the current timestamp, (createdAt) so that, subsequently, clients can check the timestamp before deciding whether to force a refresh of the stored copy of the @context. This is primarily intended as a means for clients to well-behave, thus avoiding triggering continuous refresh of a stored @context on the broker, for fear that it is not at the latest version.
Stored @contexts are flagged as one of three kinds: "Cached", "Hosted", "ImplicitlyCreated":
- Cached:
@contexts implicitly and automatically fetched by the broker from external URLs during normal NGSI-LD operations are flagged as "Cached". A locally unique identifier is generated for each @context not already in the internal storage. The downloaded content, its URL and the current time in UTC are stored alongside the locally unique identifier. Implementations shall periodically invalidate the "Cached" @contexts. Depending on the binding of the NGSI-LD API to a specific protocol, that specific protocol may provide explicit indications about expiration times of cached content. In such cases, implementations shall comply with the indications provided by the protocol. Implementations should assign a heuristic expiration time when an explicit time is not specified. Entries flagged as "Cached" shall not be served by brokers on-demand, but only be used as a local cache to improve performance. - Hosted:
@contexts that are explicitly added by users are flagged as "Hosted". These entries shall be served by brokers on-demand. - ImplicitlyCreated:
@contexts that are implicitly, but ex-novo, created by the broker as a result of a user request are flagged as "ImplicitlyCreated". For instance, when a client creates a subscription using an @context that is an array, and the broker has to notify with Content-Type "application/json", then the broker needs this @context array to be hosted at a URL. Hence the broker has to create a new @context that is an array, and it is going to be served from an own URL. These entries shall be served by brokers on-demand.
5.13.2 Add @context
5.13.2.1 Description
With this operation, a client can ask the broker to store the full content of a specific @context, by giving it to the broker.
5.13.2.2 Use case diagram
A client can add an @context to be stored within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.13.2.2‑1.
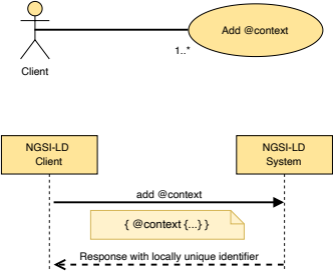
5.13.2.3 Input data
A JSON object that has a top-level field named @context, i.e. a JSON object representing a JSON-LD "local context". As specified in the JSON-LD specification [2], all extra information located outside of the @context subtree in the referenced object shall be discarded.
5.13.2.4 Behaviour
A new entry is created in the local storage and a locally unique identifier is generated for it. The JSON object representing the client-supplied @context and the current UTC time are stored alongside the locally unique identifier. That identifier shall be given back as a result in the output data. The entry is flagged as being of kind "Hosted".
The behaviour described in clause 5.5.4 about JSON and JSON-LD validation shall be applied in case of invalid @context.
5.13.2.5 Output data
The locally unique identifier that identifies the @context in the broker's internal storage.
5.13.3 List @contexts
5.13.3.1 Description
With this operation a client can obtain a list of URLs that represent all of the @contexts stored in the local context store of the broker. Each URL can be used to download the corresponding @context, and, in case the @context's kind is "Cached", it shall be the original URL the broker downloaded the @context from.
In case a details flag is set to true, the client obtains a list of JSON objects, each representing information (metadata) about an @context currently stored by the broker. Each JSON object contains information about the @context's original URL (if any), its local identifier in the broker's storage, its kind ("Cached", "Hosted" and "ImplicitlyCreated"), its creation timestamp, its expiry date, and additional optional information.
5.13.3.2 Use case diagram
A client can list all @contexts stored within an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.13.3.2‑1.
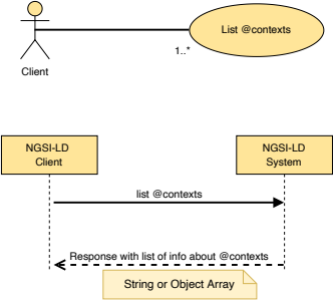
5.13.3.3 Input data
- A kind filter indicating the kind of stored @contexts that are to be included in the output list. Currently, possible kinds are "Cached", "Hosted" and "ImplicitlyCreated" (optional).
- A boolean details flag indicating that detailed JSON objects representing metadata about the stored @contexts instead of simple URLs are requested (optional).
5.13.3.4 Behaviour
The broker shall provide a URL or JSON object for each @context currently stored in the internal broker's storage, that match the filter. If no filter is specified, all kinds are included.
5.13.3.5 Output data
A list of URLs, or a list of resulting JSON objects containing the following fields:
- URL;
- localId;
- kind;
- createdAt;
- expiresAt [OPTIONAL];
- lastUsage [OPTIONAL];
- numberOfHits [OPTIONAL, number of times the @context was found in the storage];
- extraInfo [OPTIONAL, used by implementations to report any kind of custom information].
5.13.4 Serve @context
5.13.4.1 Description
With this operation a client can obtain the full content of a specific @context (only for @contexts of kind "Hosted" or "ImplicitlyCreated"), which is currently stored in the broker's internal storage, or its metadata (for all kinds of stored @contexts).
5.13.4.2 Use case diagram
A client can request the broker to serve a specific @context stored within the NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.13.4.2‑1.
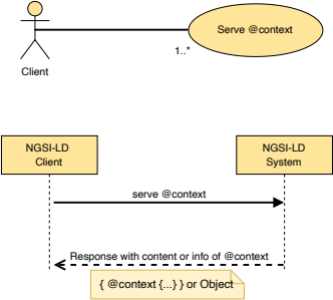
5.13.4.3 Input data
- The locally unique identifier that identifies the desired @context in the broker's internal storage. Such unique identifiers are obtained by the client as a result of either a "Add @context" (clause 5.13.2) API operation or of a "List @contexts" (clause 5.13.3) API operation. For @contexts of kind "Cached" this can also be the original URL the broker downloaded the @context from.
- A boolean details flag indicating that a JSON object representing metadata about the @context, instead of the full content, is requested (optional).
5.13.4.4 Behaviour
- If details is set to false, or details is not present, the broker shall give back the full content of the @context that corresponds to the indicated local identifier, serving it from its internal storage, if the @context that corresponds to the indicated local identifier is of kind "Hosted" or "ImplicitlyGenerated". It shall give back OperationNotSupported error if it is of kind "Cached". It shall give back ResourceNotFound if the identifier is not found.
- Otherwise, if details is set to true, the broker shall give back metadata about the @context that corresponds to the indicated local identifier. It shall give back ResourceNotFound error if the identifier is not found.
5.13.4.5 Output data
The full content of the indicated @context (or its metadata as specified in clause 5.13.3.5), or ResourceNotFound/OperationNotSupported errors.
5.13.5 Delete and Reload @context
5.13.5.1 Description
With this operation, a client supplies a local identifier to the broker, indicating a stored @context, that the broker shall remove from its storage. For @contexts of kind "Cached" this can also be the original URL the broker downloaded the @context from. If the entry in the local storage that corresponds to the identifier is itself an array of @contexts, this operation will not delete the children, i.e. the @contexts in the array, but just the entry.
5.13.5.2 Use case diagram
A client can request the broker to delete (and optionally reload) a specific @context stored within the NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.13.5.2‑1.
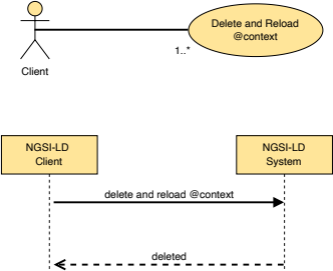
5.13.5.3 Input data
- The locally unique identifier that identifies the desired @context in the broker's internal storage. For @contexts of kind "Cached" this can also be the original URL the broker downloaded the @context from.
- A reload boolean flag indicating that reloading of the @context shall be attempted (optional).
5.13.5.4 Behaviour
- If the @context identifier is not supplied, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the @context identifier does not correspond to any existing entry in the @context storage, then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- If reload is true and the kind of the @context is "Cached", implementations shall try to re-download the identified @context from its original URL, before removing it from the internal storage. If downloading fails, or the downloaded @context is invalid according to JSON and JSON-LD validation of clause 5.5.4, then an error of type LdContextNotAvailable shall be raised. More detailed information about the errors shall be specified in the ProblemDetails (see IETF RFC 7807 [10]) field of the response. In case of any error, the operation ends without removing the existing @context. Otherwise, the existing @context is replaced with the newly downloaded one.
- If reload is true and the kind of the @context is not "Cached", implementations shall return a BadRequestData error.
- If reload is false (or reload is not supplied), implementations shall remove from the internal storage the @context that corresponds to the given identifier. The local identifier is used for finding the @contexts in the internal broker's storage. If the local identifier is not in the storage, a ResourceNotFound error shall be raised.
5.13.5.5 Output data
None.
5.14 Context Source Entity Mapping
5.14.1 Retrieve EntityMap
5.14.1.1 Description
With this operation a client can obtain a cached EntityMap which is currently stored in the broker's internal storage, or memory.
5.14.1.2 Use case diagram
A client can request the broker to retrieve a specific EntityMap within the NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.14.1.2‑1.
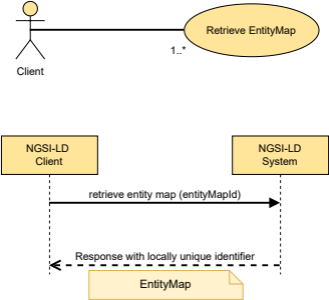
5.14.1.3 Input data
EntityMap ID (URI) of the EntityMap to be retrieved (target EntityMap).
5.14.1.4 Behaviour
- If the Entity ID is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about a matching EntityMap for the EntityMap ID, then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- Otherwise, return a JSON-LD object representing the EntityMap as mandated by clause 5.2.39.
5.14.1.5 Output data
A JSON-LD object representing the target EntityMap as mandated by clause 5.2.39.
5.14.2 Update EntityMap
5.14.2.1 Description
This operation allows performing a partial update on an NGSI-LD EntityMap. A partial update only changes the elements provided in the EntityMap Fragment, leaving the rest as they are.
5.14.2.2 Use case diagram
A client can request the broker to update an EntityMap which is currently stored in the broker's internal storage as shown in Figure 5.14.2.2‑1.

5.14.2.3 Input data
- EntityMap ID (URI) of the EntityMap to be retrieved (target EntityMap).
- A JSON-LD document representing an EntityMap.
5.14.2.4 Behaviour
- If the EntityMap ID is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about a matching EntityMap for the EntityMap ID, then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- Perform an update operation on the target EntityMap using the fields specified within then JSON-LD document. Any provided output-only fields shall be ignored.
5.14.2.5 Output data
None.
5.14.3 Delete EntityMap
5.14.3.1 Description
This operation allows deleting an NGSI-LD EntityMap.
5.14.3.2 Use case diagram
A client can request the broker to completely delete an EntityMap held within the NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.14.3.2‑1.
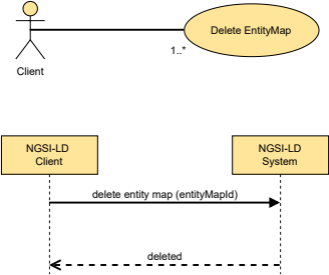
5.14.3.3 Input data
EntityMap ID (URI) of the EntityMap to be retrieved (target EntityMap).
5.14.3.4 Behaviour
- If the EntityMap ID is not present or it is not a valid URI, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the NGSI-LD endpoint does not know about a matching EntityMap for the EntityMap ID, then an error of type ResourceNotFound shall be raised.
- The EntityMap shall be removed from the broker's internal storage, or memory.
5.14.3.5 Output data
None.
5.14.4 Create EntityMap for Query Entities
5.14.4.1 Description
This operation is very similar to the Query Entities operation in clause 5.7.2, except that it does not directly return Entities, but creates and returns an Entity map including the identifiers of the Entities that are candidates to be part of the query results. The Entity map can then be used for paginating through the included Entities.
5.14.4.2 Use case diagram
A Context Consumer can retrieve an Entity map with the Entities that match a specific query from an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.14.4.2‑1.

5.14.4.3 Input data
- A reference to a JSON-LD @context (optional).
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17 (optional).
Both type names (short hand string) and fully qualified type names (URI) are allowed in the selector. - A list (one or more) of Entity identifiers (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Attribute names of which at least one shall exist in order for an Entity to be selected, and also used as query projection attributes (optional).
- A restrictive list of Entity member names ("id", "type", "scope" or an Attribute name) to be retrieved (projection attributes as defined by clause 4.21) (optional).
- An exclusionary list member names ("id", "type", "scope" or an Attribute name) to be removed (projection attributes as defined by clause 4.21) (optional).
- An id pattern as a regular expression (optional).
- An NGSI-LD query (to filter out Entities by Attribute values) as per clause 4.9 (optional).
- An NGSI-LD geoquery (to filter out Entities by spatial relationships) as mandated by clause 4.10 (optional).
- In the case of GeoJSON representation:
- The name of the GeoProperty attribute to use as the geometry for the GeoJSON representation as mandated by clause 4.5.16 (ignored).
- A datasetId specifying which instance of the value is to be selected if the GeoProperty value has multiple instances as defined by clause 4.5.5 (ignored).
- A NGSI-LD Scope query (to filter out Entities based on their Scope) as mandated by clause 4.19 (optional).
- An NGSI-LD query (called context source filter, to filter out Context Sources by the values of properties that describe them) as per clause 4.9 (optional).
- A limit to the number of Entities to be retrieved. See clause 5.5.9 (ignored).
- A specified language filter as per clause 4.15 (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Attribute names whose values shall be expanded to URIs prior to executing a query (optional).
- An optional flag indicating whether to include additional Linked Entities corresponding to the Relationships retrieved and how to format those Linked Entities. See clause 4.5.23 (optional).
- A limit to the depth of Linked Entities to search whilst traversing an Entity Graph. See clause 4.5.23 (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Linked Entity identifiers previously encountered whilst traversing an Entity Graph. See clause 4.5.23 (optional).
- A flag indicating whether to return the location of the EntityMap used within the operation (ignored, EntityMap is always returned).
A suggested expiry time for the EntityMap (optional).
- The location of a resource holding an EntityMap of matching Entity registrations (ignored).
- A datasetId parameter that specifies which Attribute instances are to be selected as defined by clause 4.5.5 (optional).
- A flag indicating whether split Entities are to be expected, i.e. Entities whose information is distributed across different Context Sources (optional).
In the general case, it is not possible to retrieve a set of entities by only specifying desired Entity identifiers, without further specifying restrictions on the Entities' types or attributes, either explicitly, via selector of Entity types or of Attribute names, or implicitly, within an NGSI-LD Query or GeoQuery. If the execution of the operation is limited to the local scope (see clause 5.5.13), no further restrictions have to be provided.
5.14.4.4 Behaviour
- At least one of the following input data shall be provided:
- If projection attributes are present and indicate the use of Linked Entity retrieval, and the use of Linked Entity retrieval is not specified, or the projected attribute depth exceeds the Linked Entity retrieval depth, then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- If the filter conditions specified by the query includes Linked Entity attributes, and the use of Linked Entity retrieval is not specified, or the Linked Entity attribute query depth exceeds the Linked Entity retrieval depth, an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised (too deep query).
- If geometryProperty parameter is present and the Accept Header is not set to "application/geo+json", then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- Otherwise,
- Term to URI expansion of type and Attribute names shall be performed, as mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- If a list of Attribute names whose values shall be expanded to URIs has been supplied, JSON-LD type coercion shall be performed as mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- If split entities flag is explicitly set to true or, if not explicitly set, the default setting of the deployment allows split entities, and local scope is not specified, implementations shall run a query that shall return an EntityMap containing the identifiers of all the Entities found locally that meet all of the following conditions:
- id is equal to any of the id(s) passed as a parameter;
- the Entity Type names match the selector of Entity Types (expanded) that is passed as a parameter;
- id matches the id pattern passed as a parameter.
- Otherwise, implementations shall run a query that shall return an EntityMap containing the identifiers pf all Entities found locally that meet all of the following conditions (given the respective parameter is provided):
- id is equal to any of the id(s) passed as a parameter;
- the Entity Type names match the selector of Entity Types (expanded) that is passed as a parameter;
- Attribute matches any of the expanded attribute(s) in the list that is passed as a parameter;
- id matches the id pattern passed as a parameter;
- the filter conditions specified by the query are met (as mandated by clause 4.9);
- the geospatial restrictions imposed by the geoquery are met (as mandated by clause 4.10); if there are multiple instances of the GeoProperty on which the geoquery is based, it is sufficient if any of these instances meets the geospatial restrictions;
- if the Scope query is present, it shall match a present Entity Scope (as mandated by clause 4.19, for an example see annex C, clause C.5.15);
- if the Attribute list is present, in order for an Entity to match, it shall contain at least one of the Attributes in the projection Attribute list.
- Unless local scope is specified (see clause 5.5.13), for Context Source Registrations that match the query and support the "createEntityMapQueryEntity" operation (see operations and operation groups in clause 4.20), implementations shall do the following:
- If split entities flag is explicitly set to true or, if not explicitly set, the default setting of the deployment allows split entities, the filters (filter conditions specified by the query, geospatial restrictions imposed by the geoquery, Scope query, Attributes) shall be removed before forwarding the request.
- For each matching Context Source Registration, the request is forwarded for remote querying by matching endpoints. The result of each remote query is an EntityMap. The mapping between the Context Source Registration and the EntityMap Id is added to the linkedMaps element of the local EntityMap and for the Entity ids included in the returned EntityMaps a mapping to the Context Source Registration is added to the entityMap element of the local EntityMap.
- The local EntityMap is stored and made accessible based on its identifier.
5.14.4.5 Output data
The location of the local EntityMap shall be returned in a specific field in the response, as well as the EntityMap itself.
5.14.5 Create EntityMap for Query Temporal Evolution of Entities
5.14.5.1 Description
This operation is very similar to the Query Temporal Evolution of Entities operation in clause 5.7.4, except that it does not directly return the Temporal Evolution of Entities but creates and returns an Entity map including the identifiers of the Entities that are candidates to be part of the query results. The Entity map can then be used for paginating through Temporal Evolution of the included Entities.
5.14.5.2 Use case diagram
A Context Consumer can retrieve an Entity map with the Temporal Evolution of a set of Entities which matches a specific query from an NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.14.5.2‑1.

5.14.5.3 Input data
To simplify the operation, the same parameters as for the Query Temporal Evolution of Entities operation (clause 5.7.4) are allowed, but some of these are irrelevant for creating an Entity map and thus will be ignored.
- An NGSI-LD temporal query as mandated by clause 4.11.
- A reference to a JSON-LD @context (optional).
- A selector of Entity types as specified by clause 4.17 (optional).
Both type name (short hand string) and fully qualified type name (URI) are allowed. - A restrictive list of Entity member names ("id", "type", "scope" or an Attribute name) to be retrieved (projection attributes as defined by clause 4.21) (optional).
- An exclusionary list of Entity member names ("id", "type", "scope" or an Attribute name) to be removed (projection attributes as defined by clause 4.21) (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Entity identifiers (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Attribute names of which at least one shall exist in order for an Entity to be selected, and also used as query projection attributes (optional).
- An id pattern as a regular expression (optional).
- An NGSI-LD query (to filter out Entities by Attribute values) as per clause 4.9 (optional).
- An NGSI-LD geoquery (to filter out Entities by spatial relationships) as mandated by clause 4.10 (optional).
- A NGSI-LD Scope query (to filter out Entities based on their Scope) as mandated by clause 4.19 (optional).
- An NGSI-LD query (called context source filter, to filter out Context Sources by the values of properties that describe them) as per clause 4.9 (optional).
- A limit to the number of Entities to be retrieved. See clause 5.5.9 (ignored).
- A parameter (lastN) conveying that only the last N instances (per Attribute) within the concerned temporal interval shall be retrieved (optional).
- A specified language filter as per clause 4.15 (optional).
- A list (one or more) of Attribute names whose values shall be expanded to URIs prior to executing a query (optional).
- A flag indicating whether to return the location of the EntityMap used within the operation (ignored, EntityMap is always returned).
A suggested expiry time for the EntityMap (optional).
- The location of a resource holding an EntityMap of matching Entity registrations (ignored).
- A datasetId parameter that specifies which Attribute instances are to be selected as defined by clause 4.5.5 (optional).
A flag indicating whether split Entities are to be expected, i.e. Entities whose information is distributed across different Context Sources (optional).
- In the general case, it is not possible to retrieve a set of entities by only specifying desired Entity identifiers, without further specifying restrictions on the entities' types or attributes, either explicitly, via selector of Entity types or of Attribute names, or implicitly, within an NGSI-LD query or geoquery. If the execution of the operation is limited to the local scope (see clause 5.5.13), no further restrictions have to be provided.
5.14.5.4 Behaviour
- If a temporal query is not provided then an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- At least one of the following input data shall be provided:
- If projection attributes or filter conditions indicate the use of Linked Entity retrieval, an error of type BadRequestData shall be raised.
- Term to URI expansion of type and Attribute names shall be observed mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- If a list of Attribute names whose values shall be expanded to URIs has been supplied, JSON-LD type coercion shall be performed as mandated by clause 5.5.7.
- The lastN parameter refers to a number, n, of Attribute instances which shall correspond to the last n timestamps (in descending ordering) of the temporal property (by default observedAt) within the concerned temporal interval.
- Otherwise,
- Let S be the set of selected Entities i.e. the query result set.
- If the split entities flag is explicitly set to true or, if not explicitly set, the default setting of the deployment allows split entities, and local scope is not specified, implementations shall run a query so that the result set contains all the Entities found locally, that meet all of the following conditions (given the respective parameter is provided):
- If id(s) is provided, keep in S only those Entities whose id is equivalent to any of the id(s) passed as a parameter.
- If an id pattern is provided, keep in S only those Entities whose id matches the id pattern.
- If a selector of Entity Types is provided, keep in S only those Entities whose Entity Type names match the selector of Entity Types.
- From S, select only those Entities any of whose Attribute instances (corresponding to the Attributes specified by the query or all if none are specified) match the temporal restrictions imposed by the temporal query (as mandated by clause 4.11); i.e. if the time series, for all the concerned Attributes of an Entity, does not include data corresponding to the temporal query interval, then such Entity shall be removed from S, thus it shall not appear in the final result set. Let S4 be this new subset.
- Otherwise implementations shall run a query that shall return the set of matching Entities (all Entities stored locally, in case only a local scope is specified); the logical steps to select the final result set of Entities, and the Attribute instances included as part of their temporal representation, are enumerated as follows:
- If id(s) is provided, keep in S only those Entities whose id is equivalent to any of the id(s) passed as a parameter.
- If an id pattern is provided, keep in S only those Entities whose id matches the id pattern.
- If a selector of Entity Types is provided, keep in S only those Entities whose Entity Type names match the selector of Entity Types.
- From S, select only those Entities any of whose Attribute instances (corresponding to the Attributes specified by the query or all if none are specified) match the temporal restrictions imposed by the temporal query (as mandated by clause 4.11); i.e. if the time series, for all the concerned Attributes of an Entity, does not include data corresponding to the temporal query interval, then such Entity shall be removed from S, thus it shall not appear in the final result set. Let S1 be this new subset.
- If a values filter query is provided, from S1, select those Entities whose Attribute instances (during the interval defined by the temporal query) meet the matching conditions specified by the query (as mandated by clause 4.9); i.e. the values filter query shall be checked against all the Attribute instances resulting from the initial filtering performed by the temporal query. Let S2 be this new subset.
- If no values filter query is provided, then S2 is equal to S1.
- If geoquery is present, from S2, select those Entities whose GeoProperty instances meet the geospatial restrictions imposed by the geoquery (as mandated by clause 4.10); those geospatial restrictions shall be checked against the GeoProperty instances that are within the interval defined by the temporal query. Let S3 be this new subset.
- If no geoquery is provided, then S3 is equal to S2.
- If the Scope query is present, from S3, select those Entities whose Entity Scope instances match the Scope query (as mandated by clause 4.19, for an example see annex C, clause C.5.16). Let S4 be the new subset.
- If no Scope query is provided, then S4 is equal to S3.
- The local EntityMap is created based on S4.
- Unless local scope is specified (see clause 5.5.13), for Context Source Registrations that match the query and support the "createEntityMapQueryTemporal" operation (see operations and operation groups in clause 4.20), implementations shall do the following:
- If split entities flag is explicitly set to true or, if not explicitly set, the default setting of the deployment allows split entities, the filters (filter conditions specified by the query, geospatial restrictions imposed by the geoquery, Scope query, Attributes) shall be removed before forwarding the request.
For each matching Context Source Registration, the request is forwarded for remote querying by matching endpoints. The result of each remote query is an EntityMap. The mapping between the Context Source Registration and the EntityMap Id is added to the linkedMaps element of the local EntityMap and for the Entity ids included in the returned Entity Maps a mapping to the Context Source Registration is added to the entityMap element of the local EntityMap.
- The local EntityMap is stored and made accessible based on its identifier.
5.7.4.5 Output Data
5.15 Context Source Identity Information
5.15.1 Retrieve Context Source Identity Information
5.15.1.1 Description
With this operation, a client can obtain Context Source identity information which uniquely defines the Context Source itself. In the multi-tenancy use case (see clause 4.14), a client can obtain identify information about a specific Tenant within a Context Source.
5.15.1.2 Use case diagram
A client can request the broker to retrieve identity information about a specific Context Source within the NGSI-LD system as shown in Figure 5.15.1.2‑1.
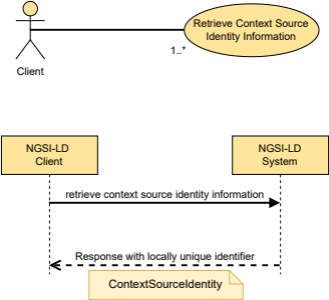
5.15.1.3 Input data
None.
5.15.1.4 Behaviour
- If the Context Source is unable to supply identity information about itself, then error of type NotImplemented shall be raised.
- Return a JSON-LD object representing the identity of the Context Source itself as mandated by clause 5.2.40. This can also include additional configurational data dependent on the specificContext Source implementation.
5.14.1.5 Output data
A JSON-LD object representing the identity of the Context Source as mandated by clause 5.2.40.